Parkinson’s Disease-Related Voice Change
Voice change that accompanies Parkinson’s disease (PD) typically has two components. One component is a change to the “inner engine” of the voice. It is as if the inner motivation or vitality of communication or voice is damped down; think of the “motor” being limited mostly to “idle” rather than “first, second, third, and fourth” gears. When coaxed or even goaded to produce more vigorous voice, a person with advanced PD may find it hard to impossible (depending upon severity) to increase loudness. If the average person can “choose” vocal loudness settings of 1 through 5, it is as though levels 2 through 5 become inaccessible to the person with PD.
A second component of PD-related voice change is that the larynx becomes weak and atrophied. This is not surprising, since any body part will tend to atrophy if it is never used in a vigorous way. The phenomenology of PD-related voice change is that the voice is overly quiet and soft-edged, and though speech does not tend to become slurred, it can lose its crispness of articulation, and the pace of speech may diminish.
Parkinson’s-related Voice Change
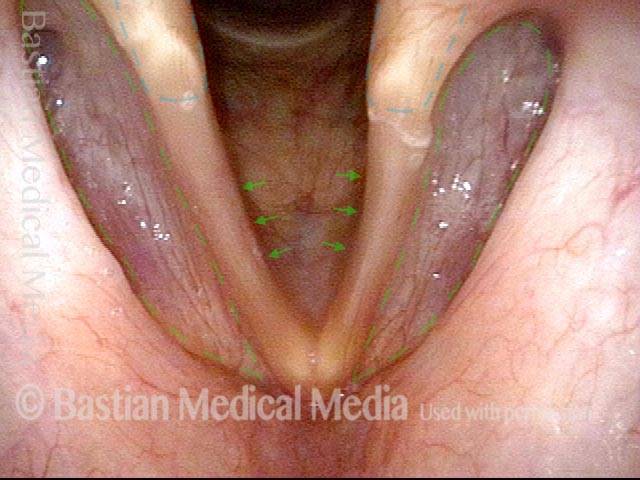
Parkinson’s-related voice change (1 of 3)
Parkinson’s-related voice change (1 of 3)
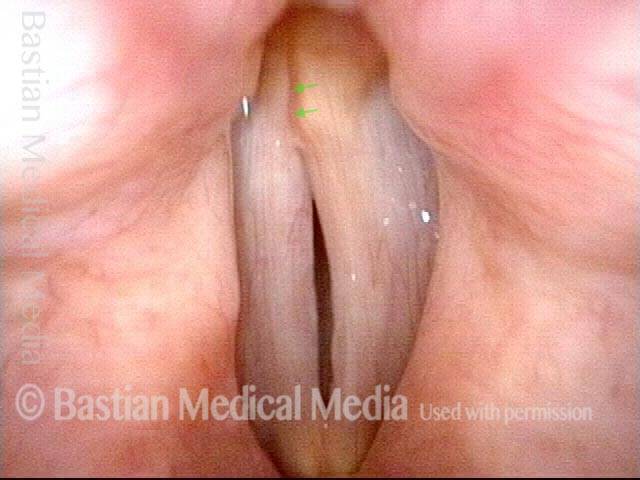
Parkinson’s-related voice change (2 of 3)
Parkinson’s-related voice change (2 of 3)
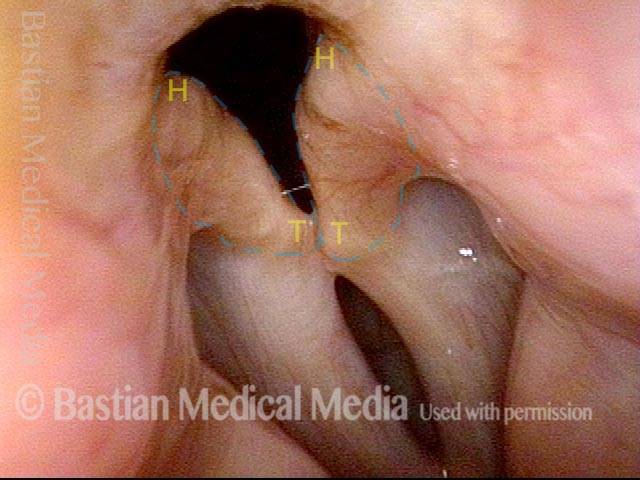
Parkinson’s-related voice change (3 of 3)
Parkinson’s-related voice change (3 of 3)