Respiratory Dystonia
Respiratory dystonia is a syndrome caused by laryngeal dystonia in which the larynx’s breathing function is affected. Laryngeal dystonia much more commonly affects the voice (spasmodic dysphonia) rather than breathing, but occasionally it affects only breathing, or both breathing and voice.
Individuals afflicted with respiratory dystonia may have difficulty inhaling air through a glottis closed by adductory spasms, or may be able to inhale without difficulty but then to find it hard to breathe out, as the victim of involuntary breath-holding.
Respiratory Dystonia and the Struggle to Breathe
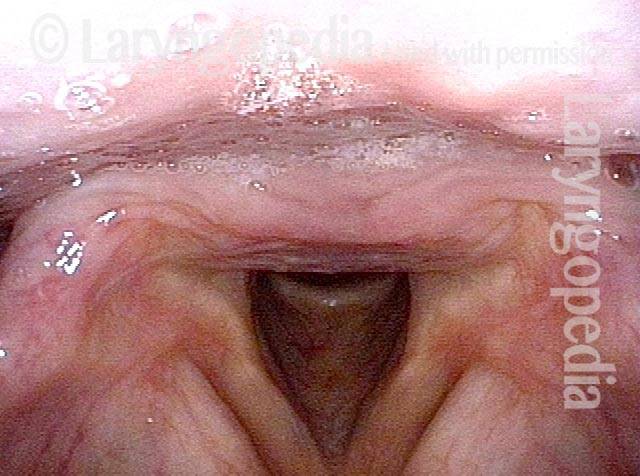
AD SD (1 of 2)
AD SD (1 of 2)
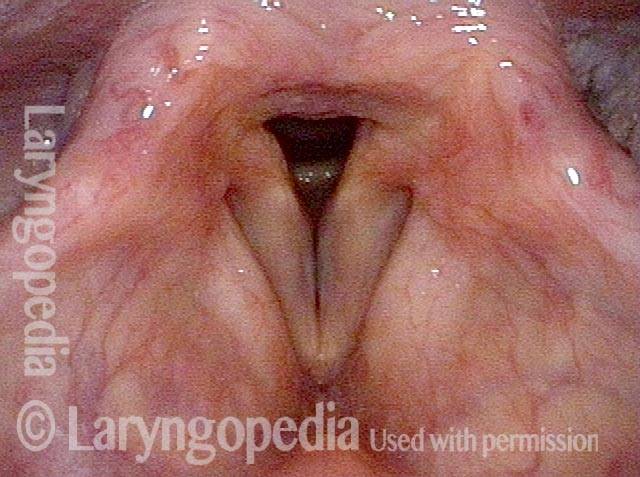
Involuntarily adduction (2 of 2)
Involuntarily adduction (2 of 2)

Respiratory Dystonia
When Spasms Affect the Voice
In a peculiar disorder of breathing, “respiratory dystonia,” tiny spasms in the vocal cords prevent the smooth in- and out-flow of air to the lungs. It is as though the air comes in or goes out in little pieces rather than in a unified inspiration or expiration.
Quiet involuntary noises are heard from the throat, most often while trying to breathe in, and sometimes tiny “grunts” when breathing out.