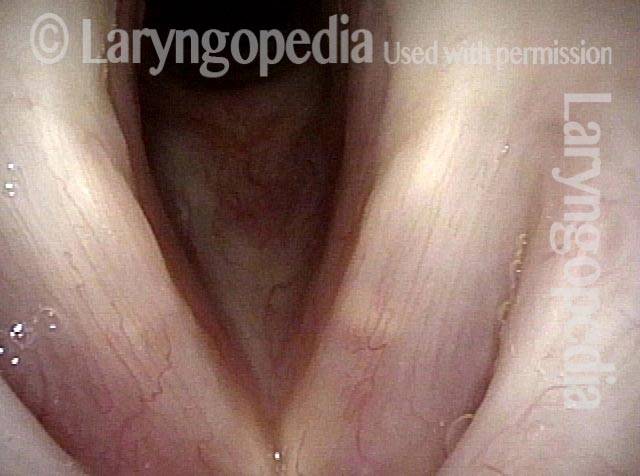
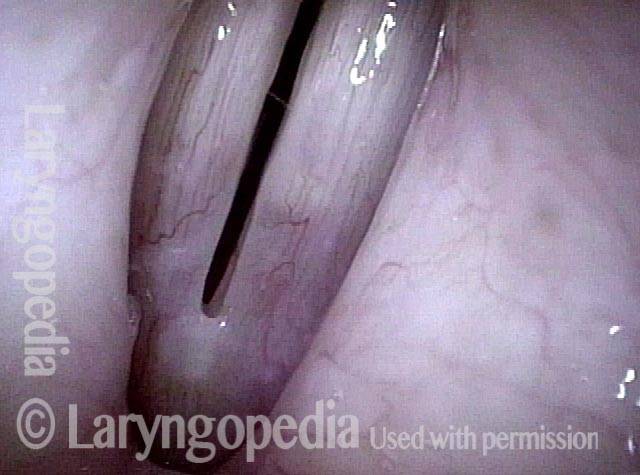
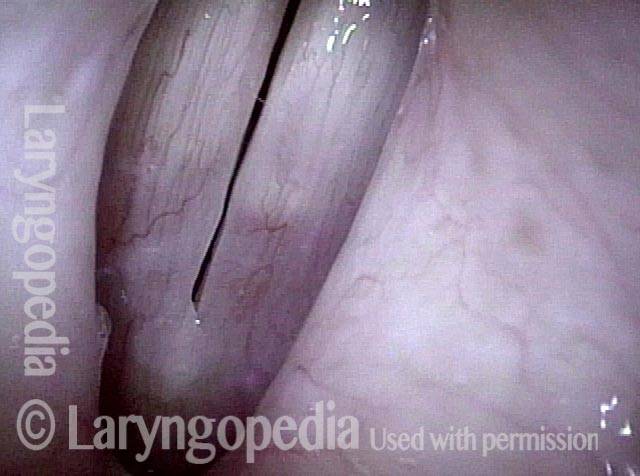
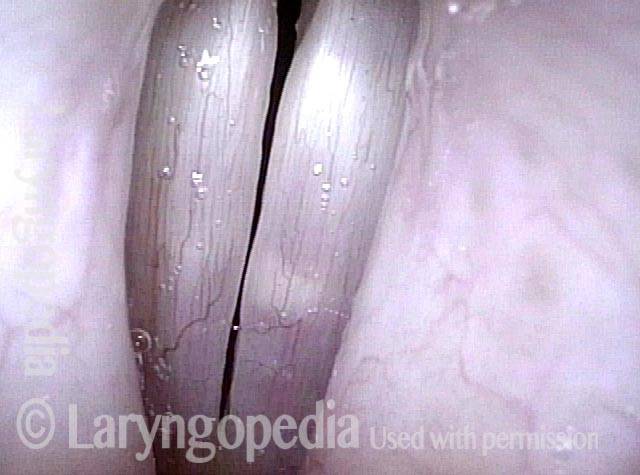
Dysphonia is the abnormal production of vocal sound; more commonly used as a synonym for hoarseness. Dysphonia may be the result of injury to the mucosa of the vocal cords; or it may be neurogenic, the result of a benign or malignant tumor; or it may be nonorganic.
Dysphonia vs. Dysphagia vs. Dysesthesia vs. Dysphasia
Dysphagia is the medical term for difficulty swallowing. This may involve discomfort, the sensation of food sticking, or actual impairment of the swallowing process such as when food or liquid “goes down the wrong tube” (aspiration) and induces coughing.
Dysesthesia refers to an abnormal sensation—often unpleasant—such as burning, tingling, or prickling. It may be an exaggerated response to a normal stimulus, or it can occur in the absence of any stimulus at all.
Dysphasia refers to difficulty with language processing (not voice or articulation). There are two broad types:
- Expressive dysphasia, in which the person knows what they want to say but struggles to produce the words.
- Receptive dysphasia, in which the person has trouble understanding spoken or written language. Sometimes both types occur together.
Word Roots
A word-root tip: As you continue learning, you’ll find that understanding word roots is very helpful—and even fun. You’re probably doing this already, but here’s a little encouragement to keep going:
- The prefix dys– means “abnormal.”
- Esthesia refers to sensation—so dysesthesia means abnormal sensation. An– means “without,” so anesthesia means the absence of sensation.
- Phagia refers to swallowing. Add dys– and you get “abnormal swallowing.” Begin with odyno– (pain) and you get odynophagia—”painful swallowing.”
- Phasia refers to language production or understanding. Add dys– and you get “abnormal language processing.”
- Phonia refers to voice, or sound. Add dys– and you get “abnormal voice, or hoarseness.” Add a– and you get “absence of voice”
The more you learn the roots, the easier it is to decode medical terms. So keep looking for those roots—they’ll serve you well!