Forme Fruste Wegener’s Granulomatosis
An incomplete or frustrated form (forme fruste) of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA, Wegener’s Granulomatosis) which we believe to be the cause behind some cases of inflammatory subglottic or tracheal stenosis.
Forme Fruste GPA vs. GPA
Unlike full-fledged GPA, this forme fruste variant may or may not necessarily involve the sinus and nasal cavities, and in the author’s caseload of about 60 patients, it has not ever progressed to involve the lungs and kidneys.
Treatment Methods
Such patients can go for years with only the need for intermittent dilation of the subglottic or tracheal narrowing. This disorder may be the same as what some call “idiopathic subglottic stenosis,” for which some have recommended cricotracheal resection and reanastomosis as treatment.
Subglottic / Tracheal Stenosis
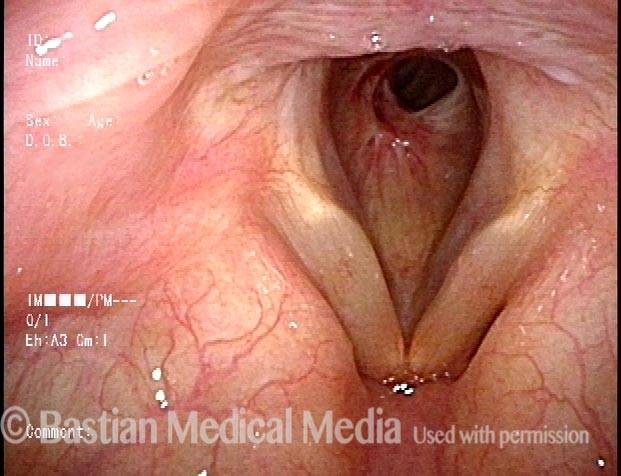
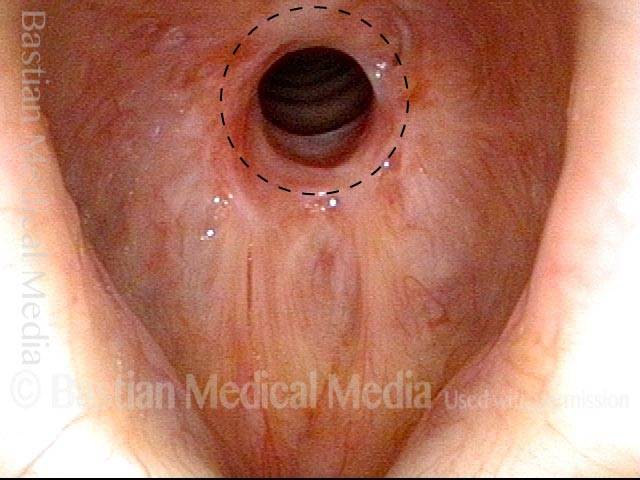
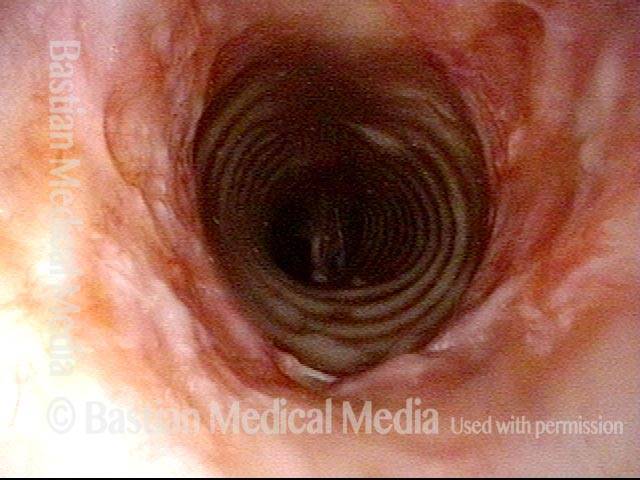
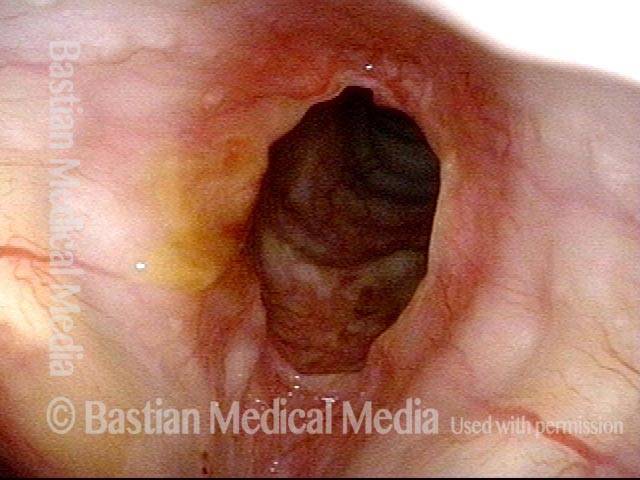
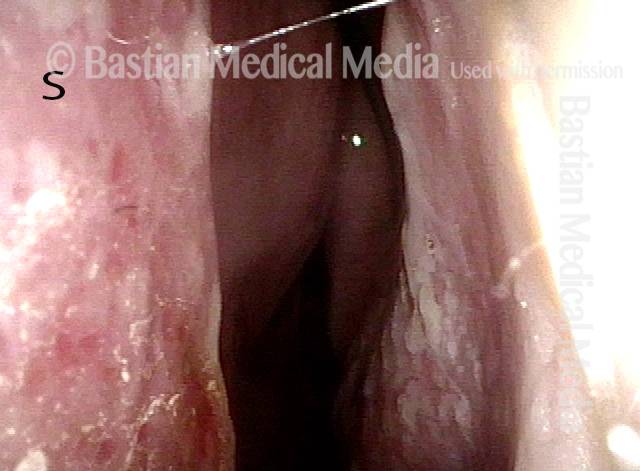
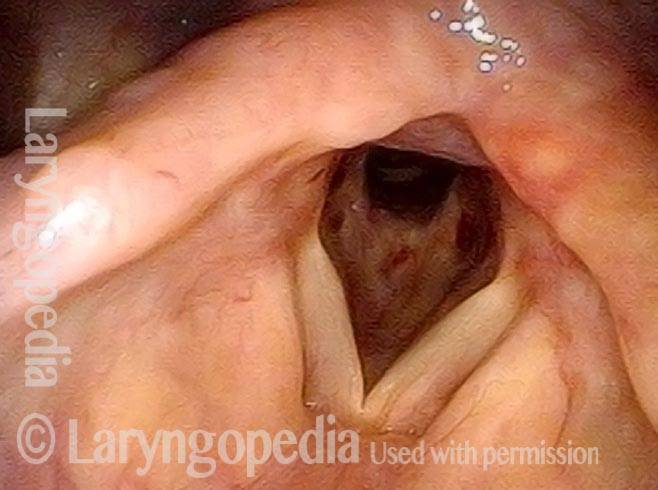
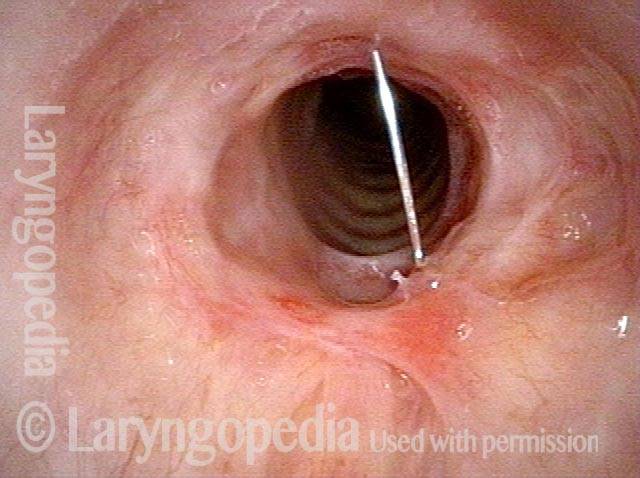
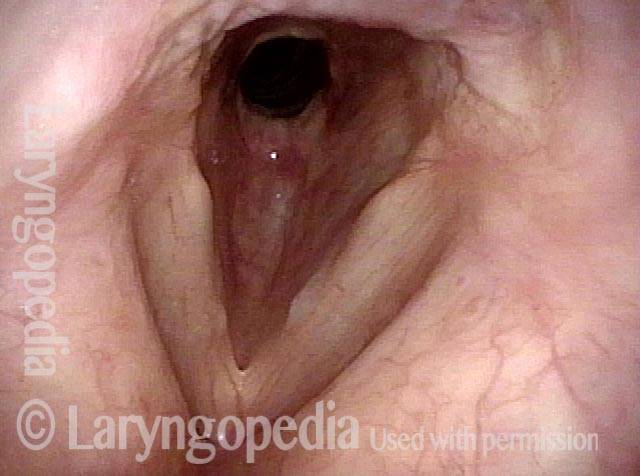
Wegener’s granulomatosis (1 of 4)
Wegener’s granulomatosis (1 of 4)
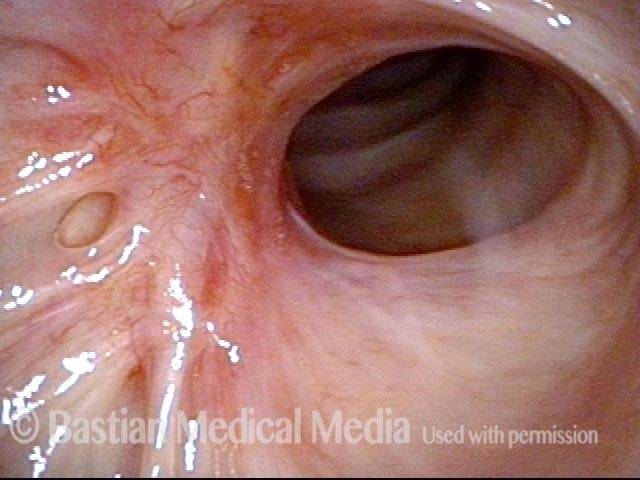
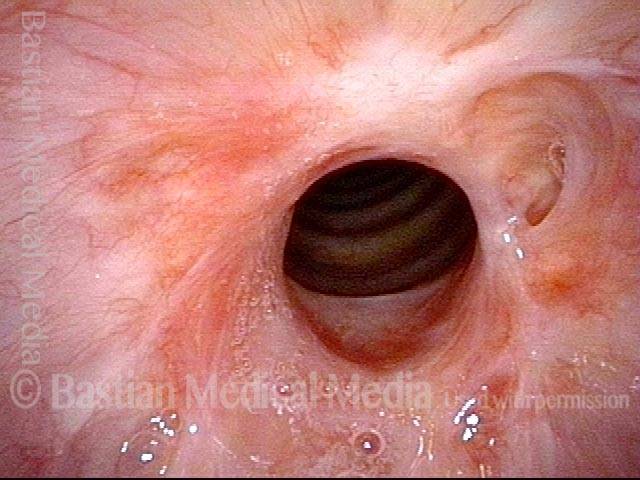
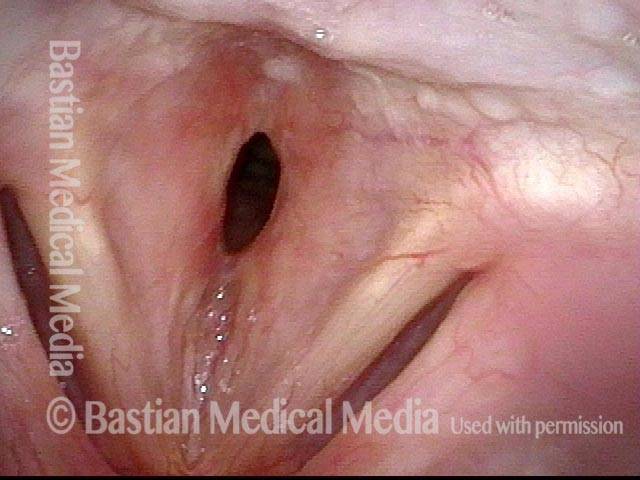
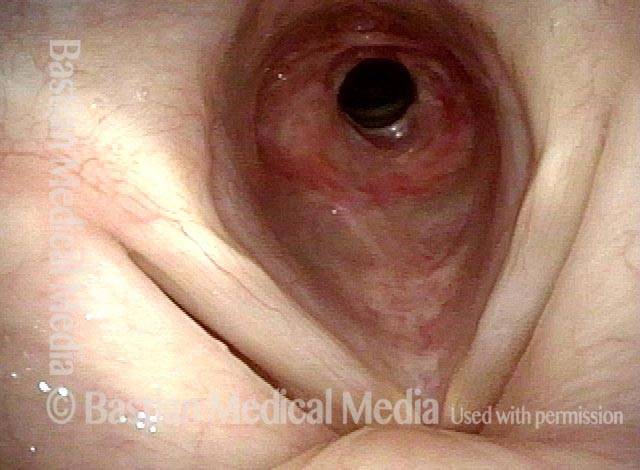
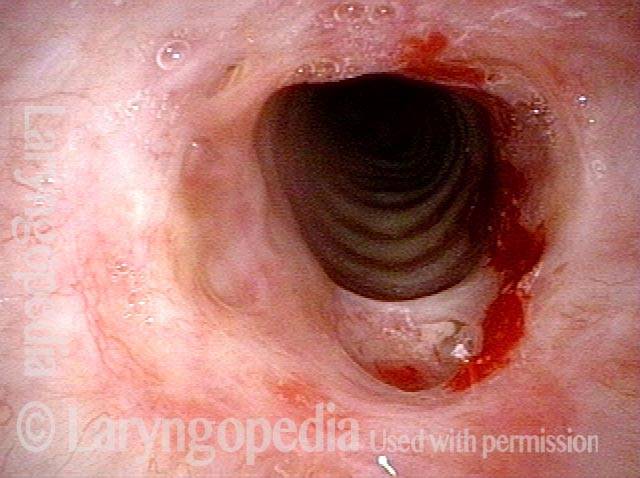
Subglottic / Tracheal stenosis (2 of 4)
Subglottic / Tracheal stenosis (2 of 4)
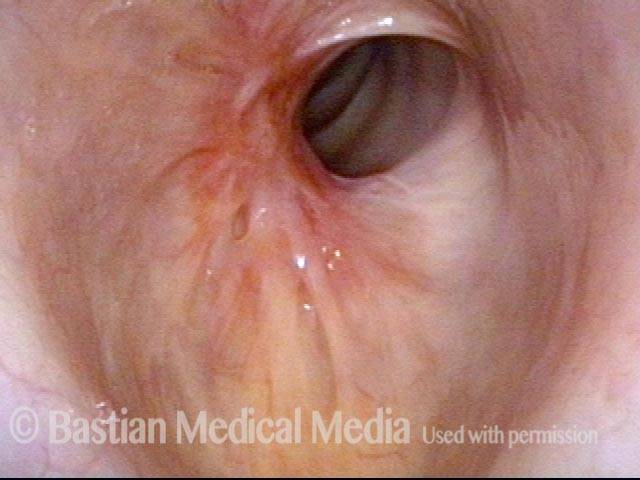
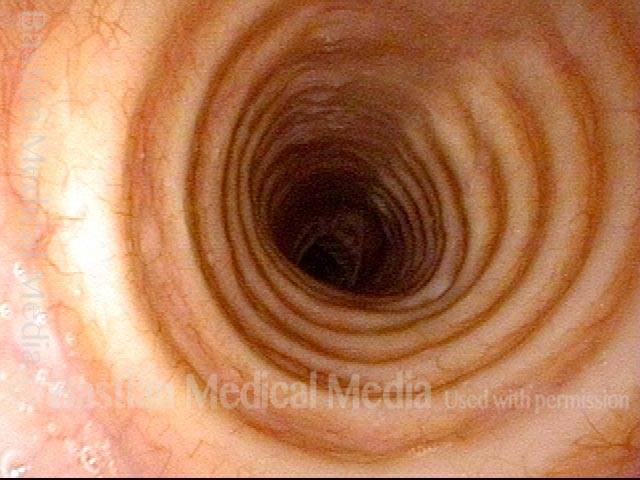
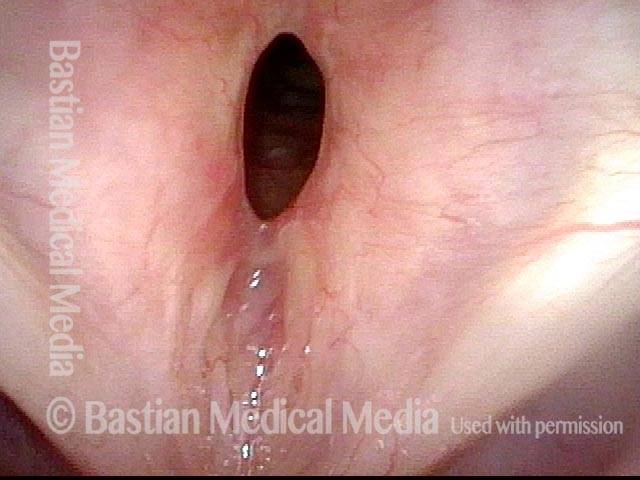
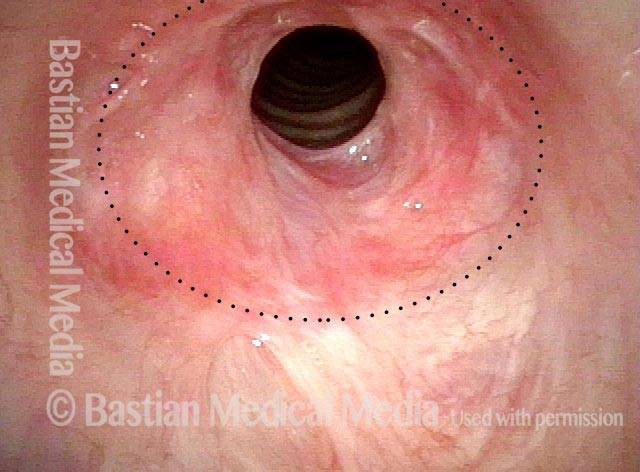
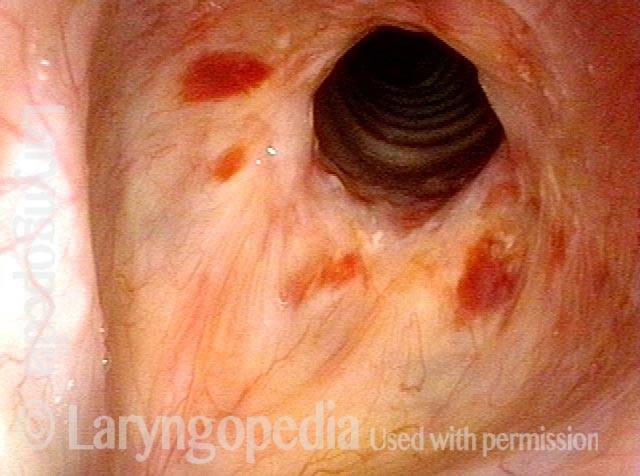
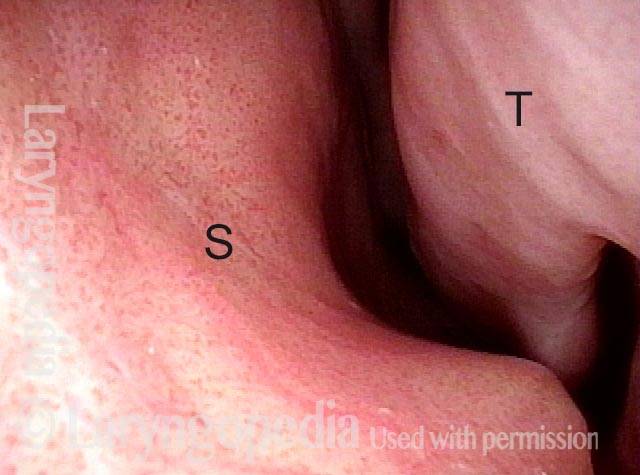
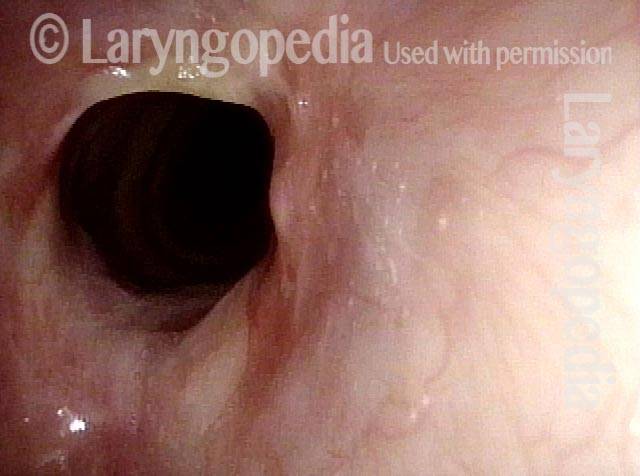
Subglottic / Tracheal stenosis (3 of 4)
Subglottic / Tracheal stenosis (3 of 4)
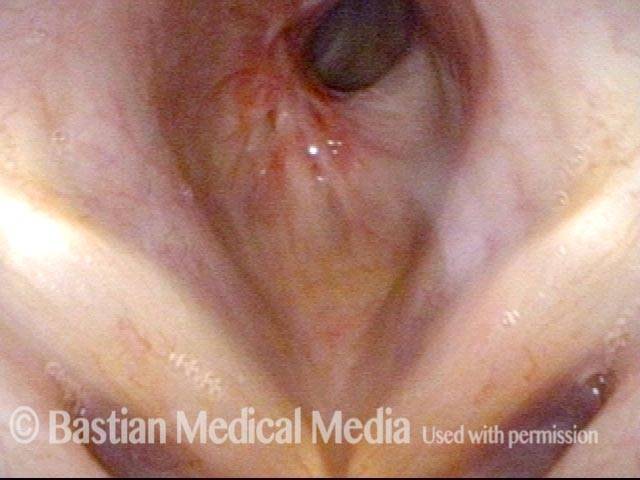
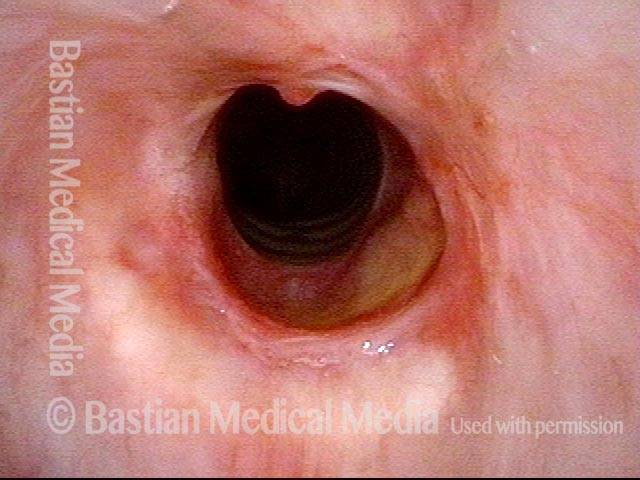
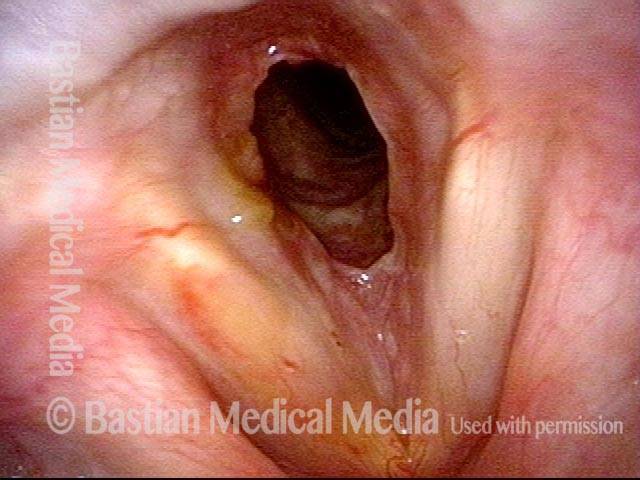
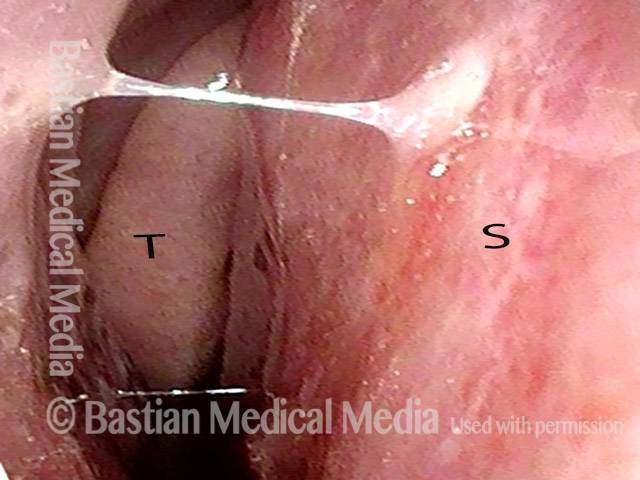
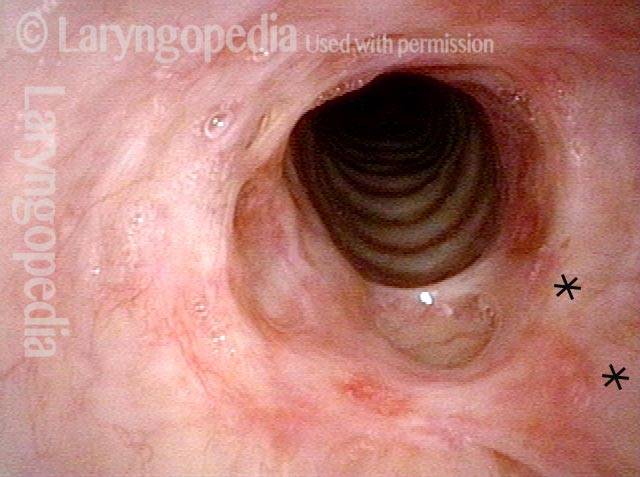
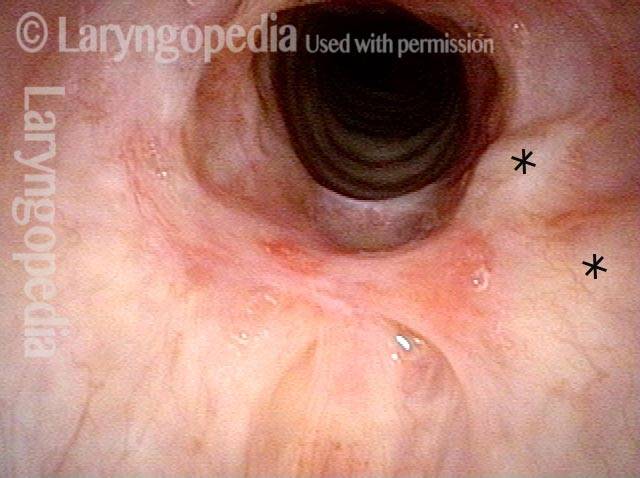
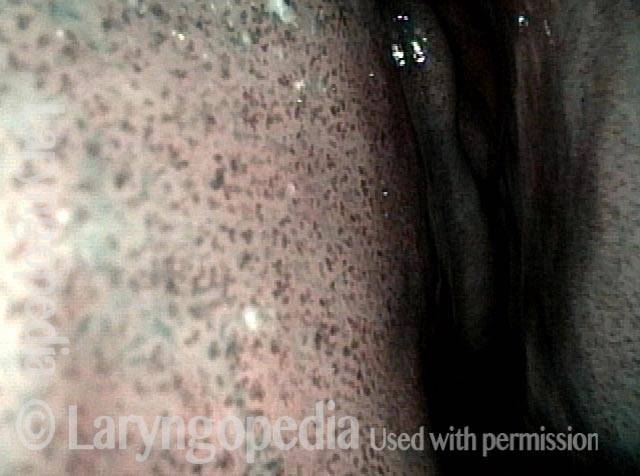
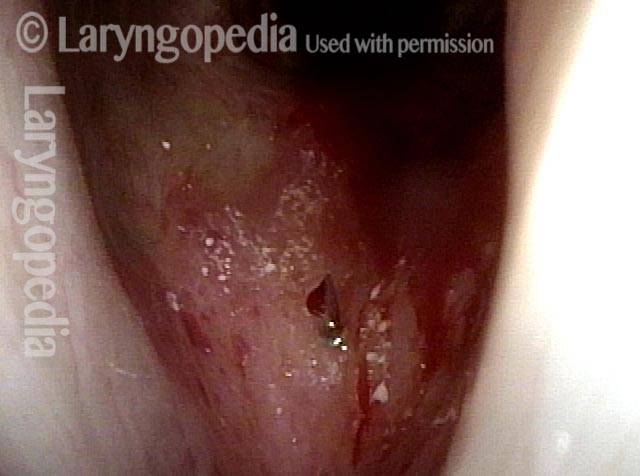
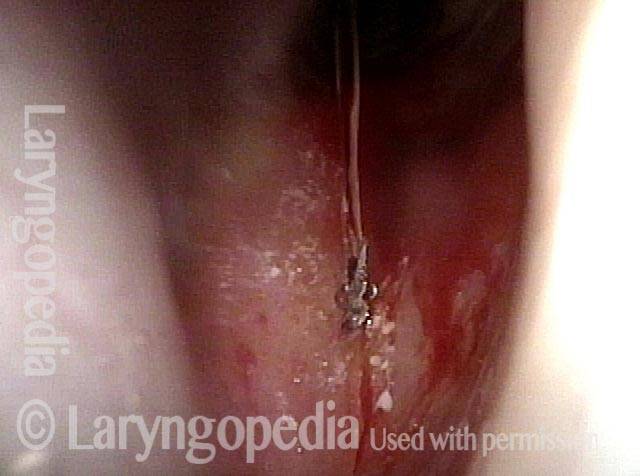
Inflammed Stenosis (4 of 4)
Inflammed Stenosis (4 of 4)
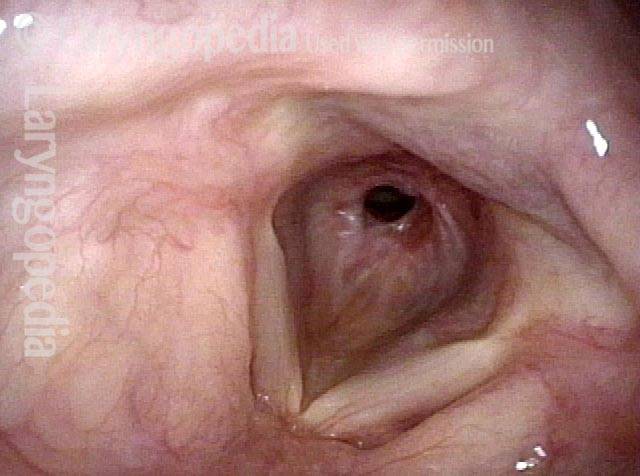
Tracheal Stenosis, Due to Forme Fruste Wegener’s Granulomatosis
Tracheal stenosis (1 of 3)
Tracheal stenosis (1 of 3)
Tracheal stenosis (2 of 3)
Tracheal stenosis (2 of 3)
Just below the tracheal stenosis (3 of 3)
Just below the tracheal stenosis (3 of 3)
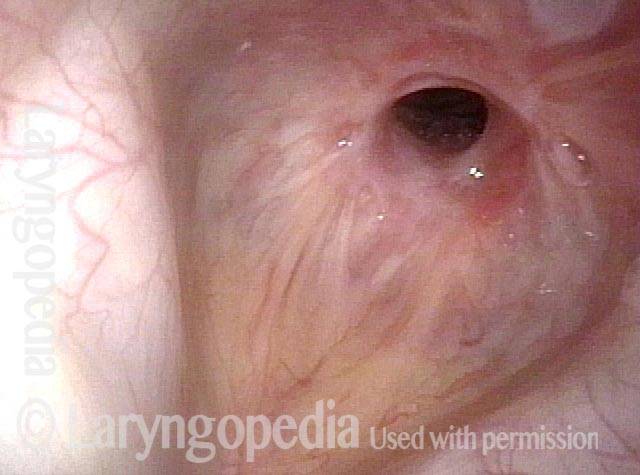
Subglottic Stenosis, Before and After Dilation
Subglottic stenosis, before dilation (1 of 2)
Subglottic stenosis, before dilation (1 of 2)
Subglottic stenosis, after dilation (2 of 2)
Subglottic stenosis, after dilation (2 of 2)
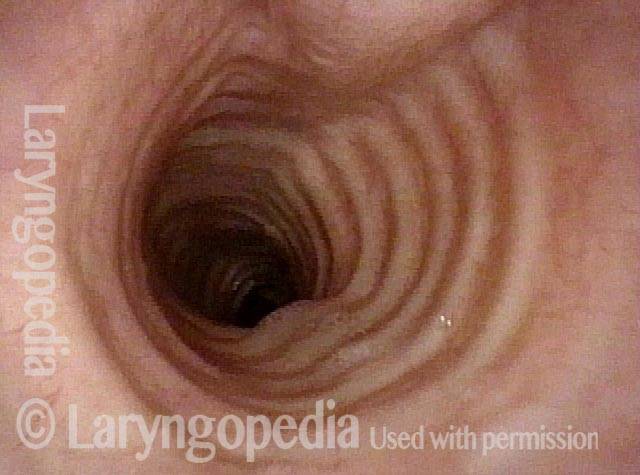
Example 2
Subglottic stenosis (1 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis (1 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, worsened (2 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, worsened (2 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, worsened (3 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, worsened (3 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, after dilation (4 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, after dilation (4 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, after dilation (5 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis, after dilation (5 of 5)
A Soft Finding to Support a Diagnosis of Forme Fruste Wegener’s Granulomatosis
Inflammatory subglottic stenosis ( 1 of 4)
Inflammatory subglottic stenosis ( 1 of 4)
Closer view indicates a forme fruste of Wegener’s granulomatosis (2 of 4)
Closer view indicates a forme fruste of Wegener’s granulomatosis (2 of 4)
Inflammation on septum (3 of 4)
Inflammation on septum (3 of 4)
Closer view of septum (4 of 4)
Closer view of septum (4 of 4)
Stenosis Before and After Dilation for Forme Fruste Wegener’s
Subglottic stenosis (1 of 5)
Subglottic stenosis (1 of 5)
Inflammation (2 of 5)
Inflammation (2 of 5)
Flexible scope (3 of 5)
Flexible scope (3 of 5)
Post-dilation (4 of 5)
Post-dilation (4 of 5)
Post-operative bruising (5 of 5)
Post-operative bruising (5 of 5)
A Different Approach to Inflammatory Tracheal Stenosis
Planning on periodical injections (1 of 4)
Planning on periodical injections (1 of 4)
Long-acting steroid (2 of 4)
Long-acting steroid (2 of 4)
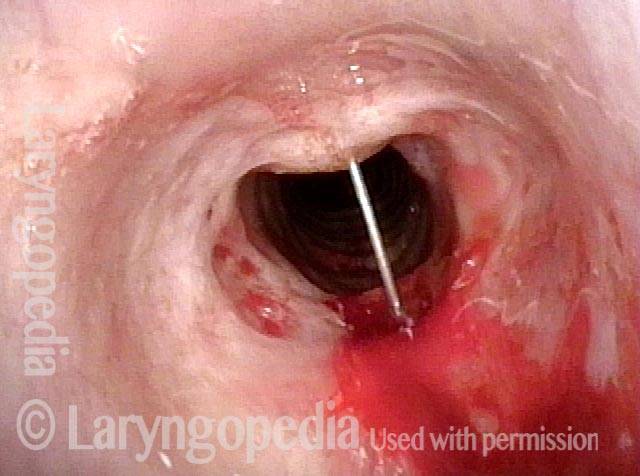
Needle going into the posterior of stenosis (3 of 4)
Needle going into the posterior of stenosis (3 of 4)
Posterior tracheal wall (4 of 4)
Posterior tracheal wall (4 of 4)
Vascular Manifestations of Wegener’s-related Septum Changes, and Subglottic Stenosis Indistinguishable from Forme Fruste Wegener’s
View inside left nostril (1 of 4)
View inside left nostril (1 of 4)
Narrow band light (2 of 4)
Narrow band light (2 of 4)
Distant view (3 of 4)
Distant view (3 of 4)
Closer view (4 of 4)
Closer view (4 of 4)
One Way to Deliver Topical Anesthesia Despite A Powerful Gag Reflex…
Powerful gag reflex (1 of 4)
Powerful gag reflex (1 of 4)
Patient inhaling (2 of 4)
Patient inhaling (2 of 4)
Patient coughs (3 of 4)
Patient coughs (3 of 4)
Topical anesthesia applied (4 of 4)
Topical anesthesia applied (4 of 4)

Wegener’s Granulomatosis: Forme Fruste (incomplete expression)
Wegener’s granulomatosis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which blood vessels become inflamed. The inflammation causes swelling and scarring. Three typical organs attacked are sinus/nasal cavities, lungs, and kidneys.
In the forme fruste variant, it is mostly an inflammatory stenosis (narrowing) of the area below the vocal cords, and also the trachea. A person becomes short of breath and begins to make harsh breathing sounds due to the narrowed passageway.
This is an example of one means of management: dilation of the narrowed area during a very brief general anesthetic in an outpatient operating room.