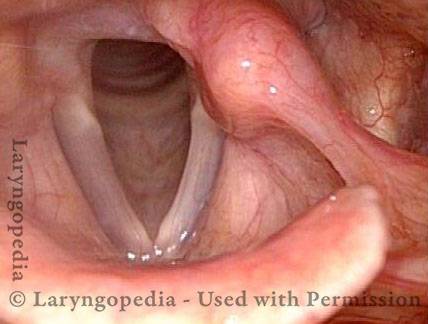
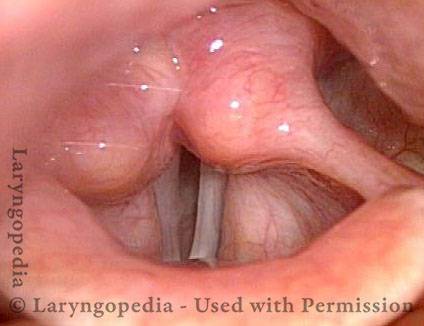
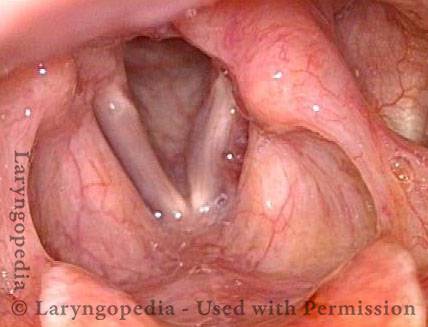
Air-wasting dysphonia is a kind of hoarseness that refers to the breathiness (see breathy dysphonia) that one is hearing. Typically, the length of time a person can sustain voice without taking a new breath (maximum phonation time) is decreased. The voice may be described as whispery or foggy or fuzzy. Among other things, possible causes include vocal fold paralysis or paresis, vocal fold bowing and atrophy, or functional (especially nonorganic) voice problems.