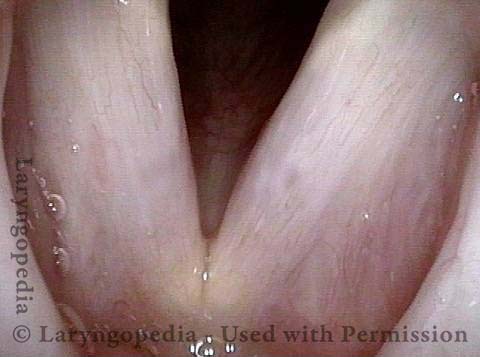
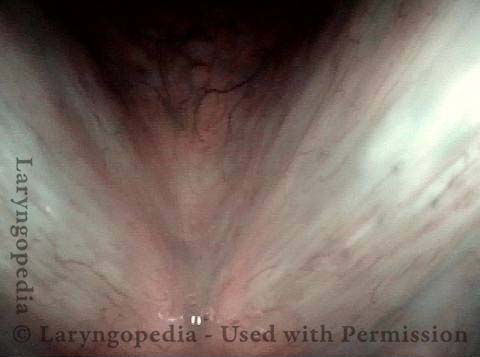
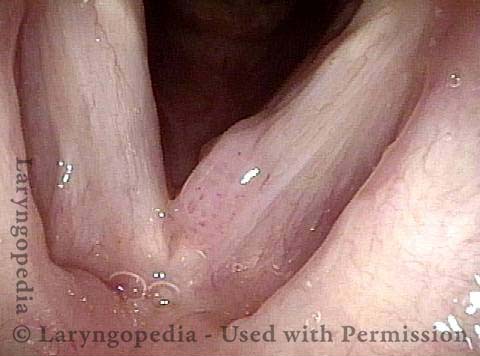
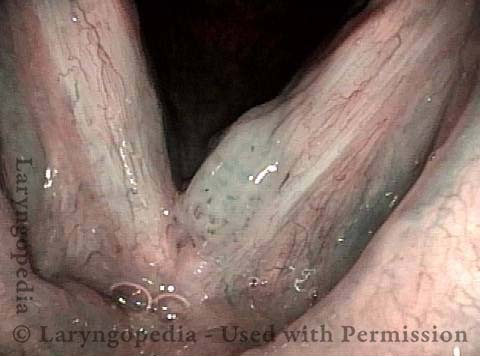
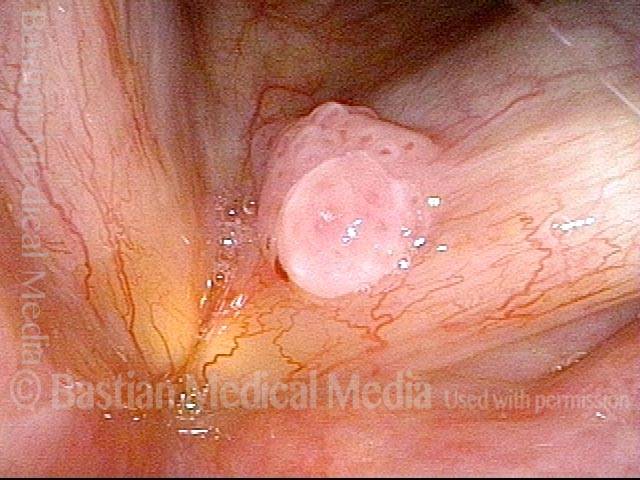
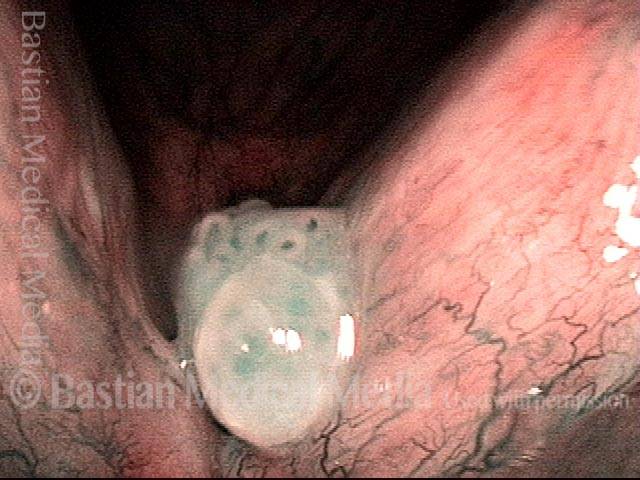
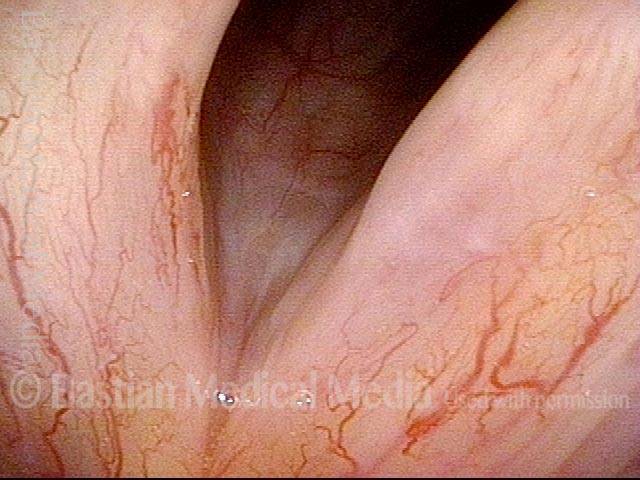
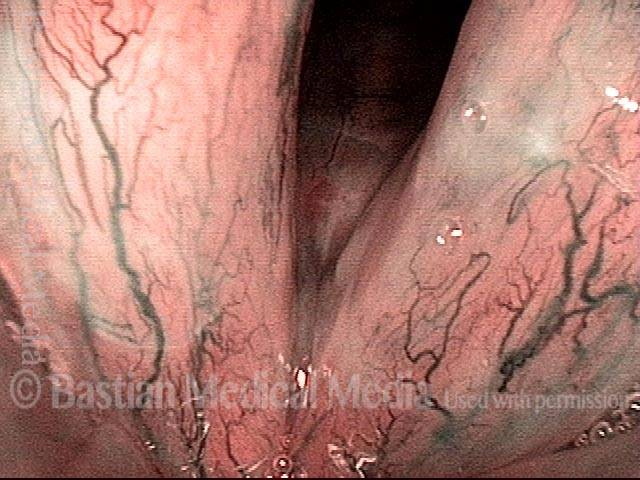
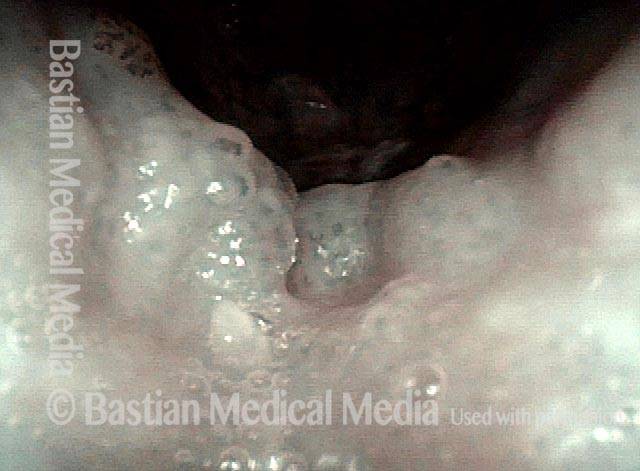
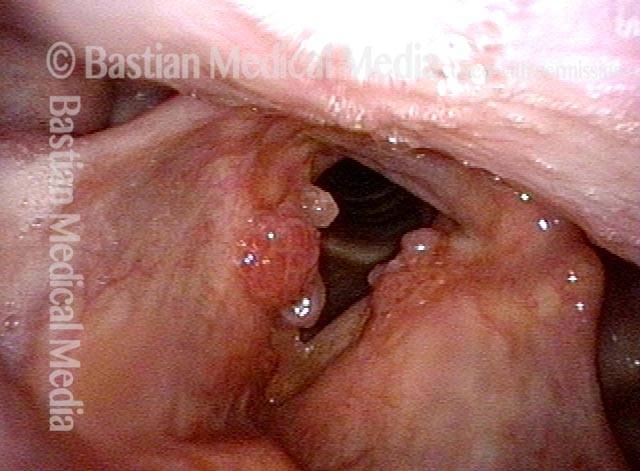
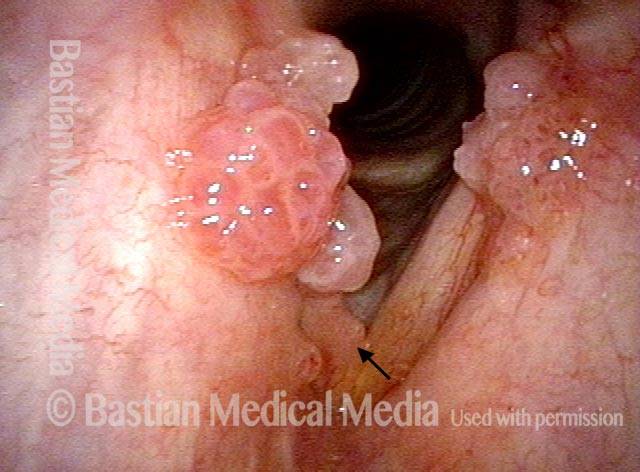
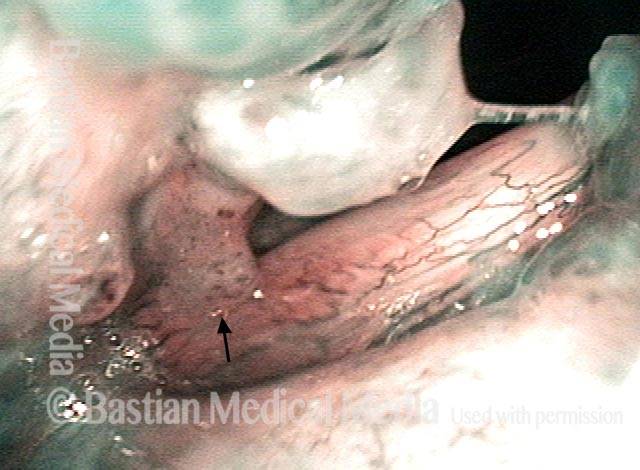
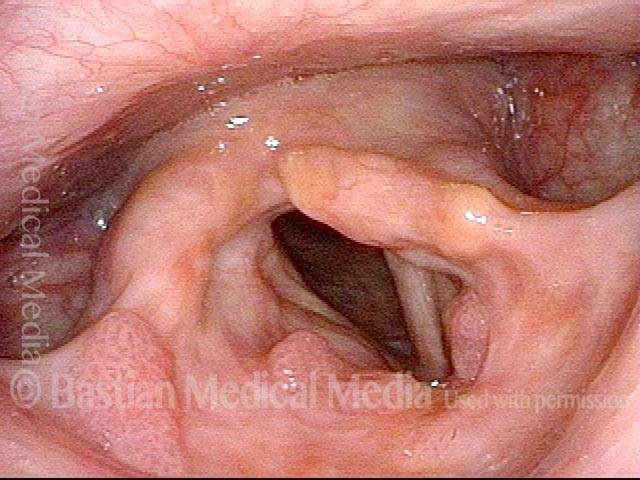
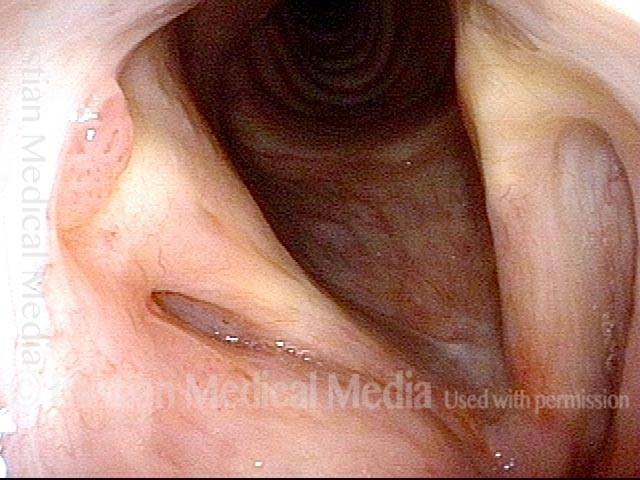
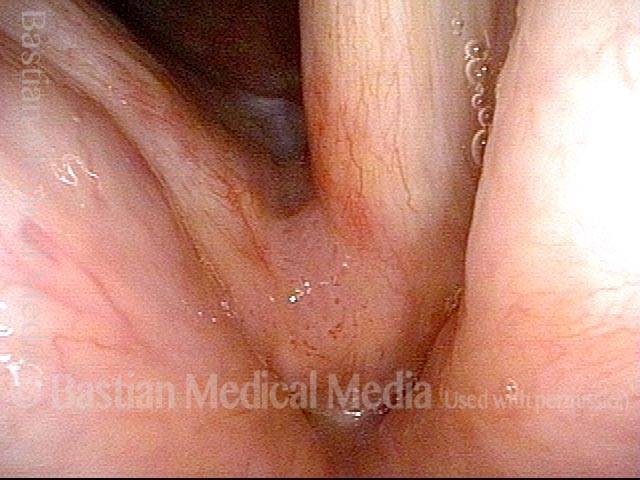
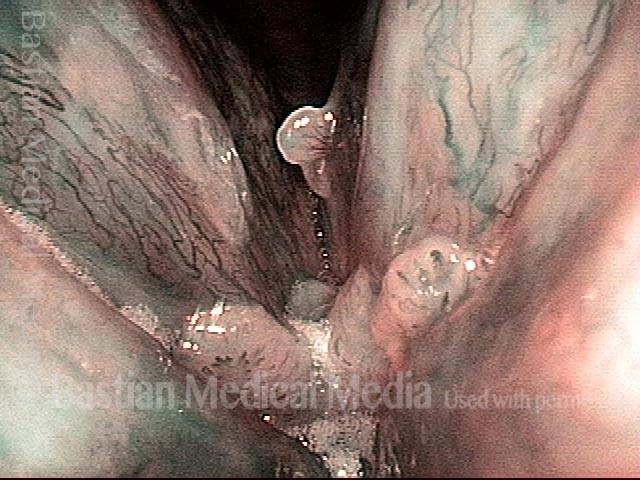
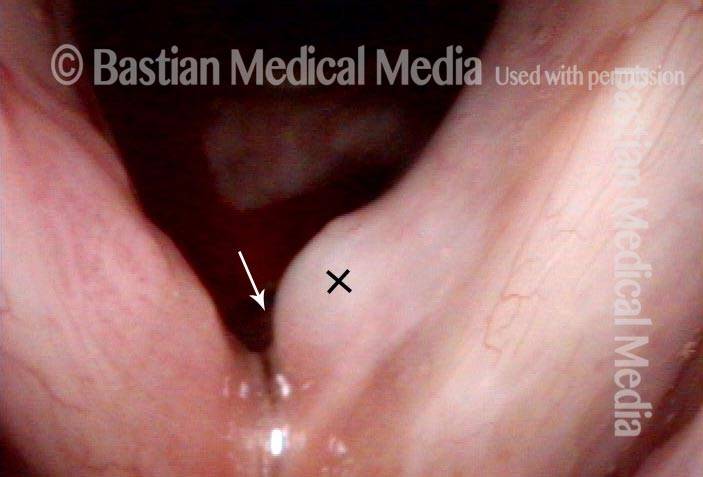
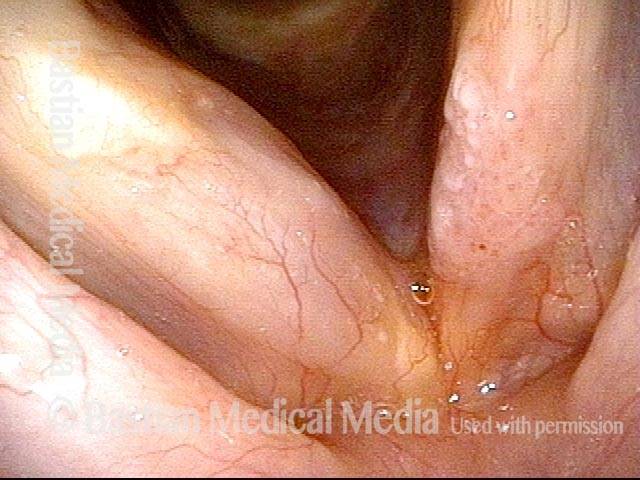
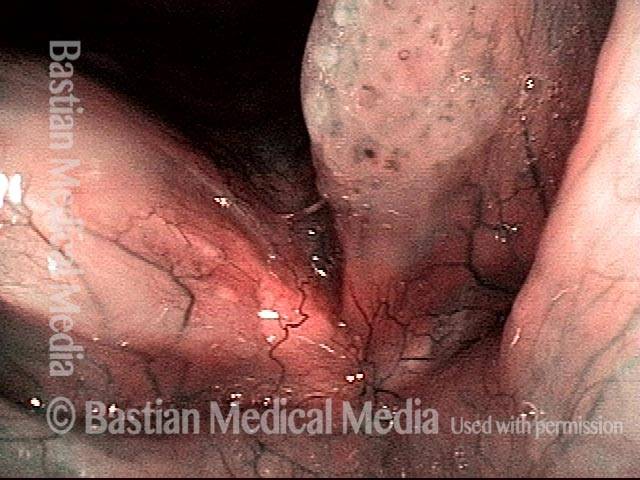
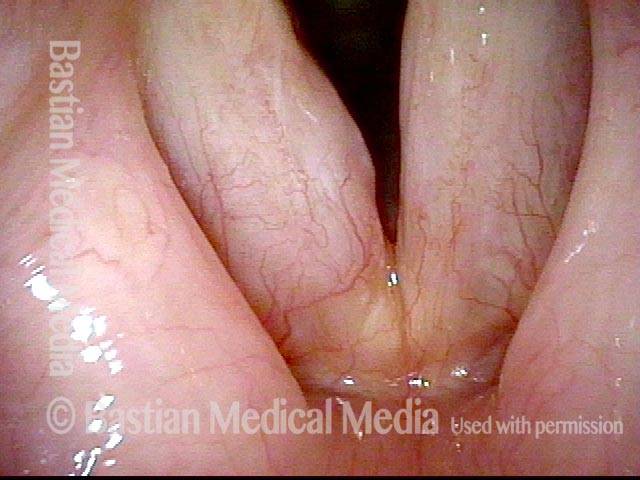
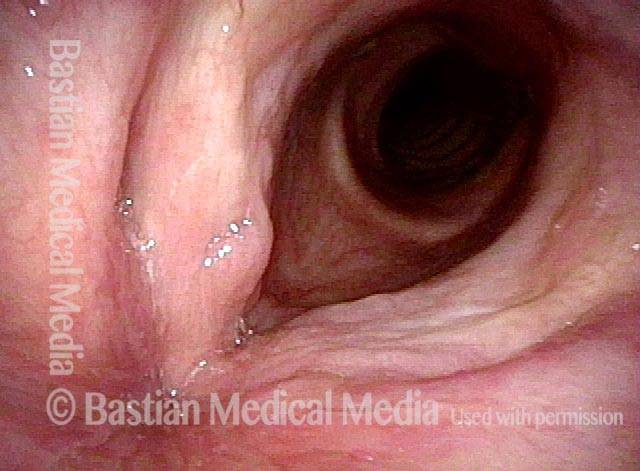
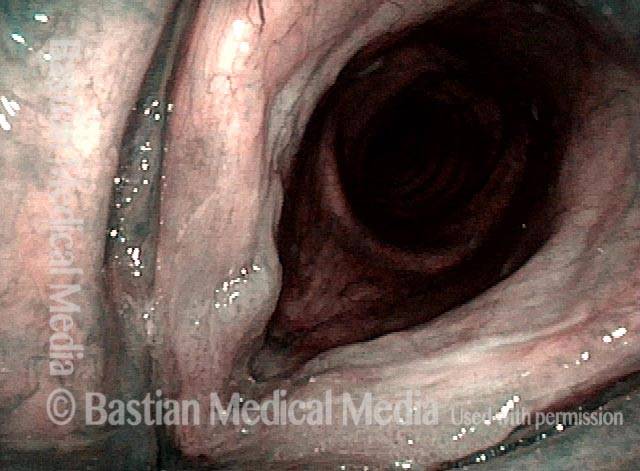
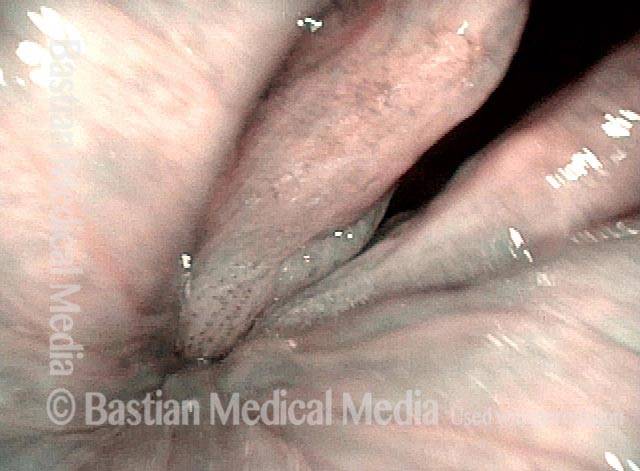
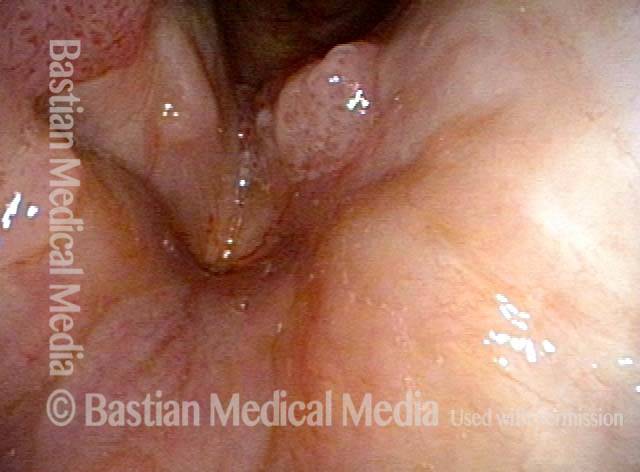
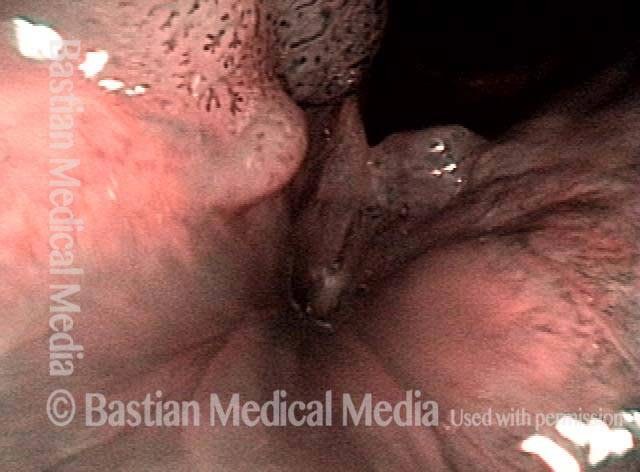
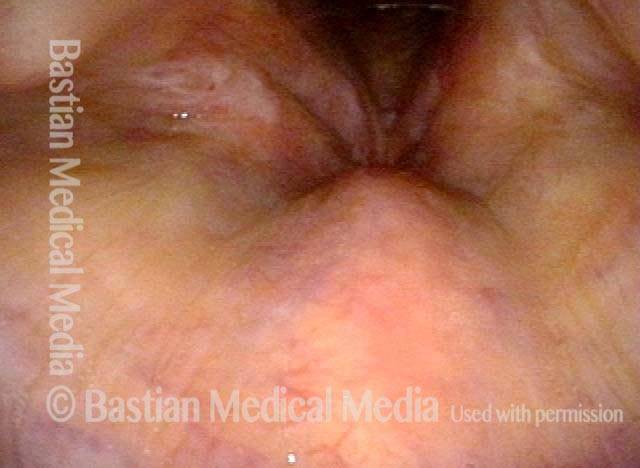
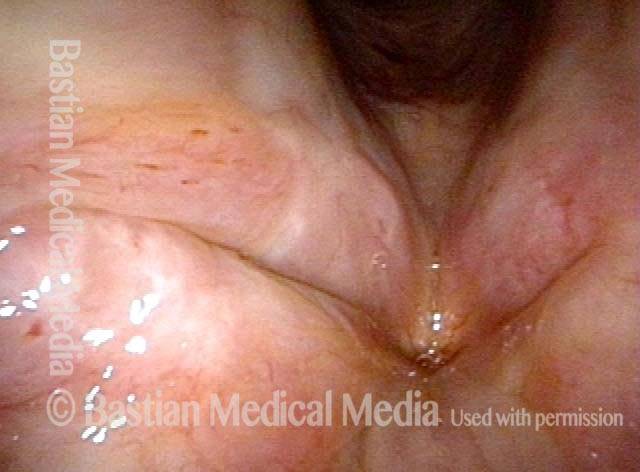
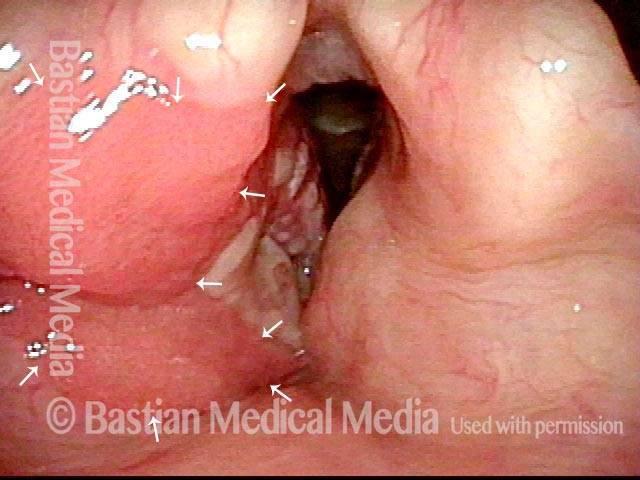
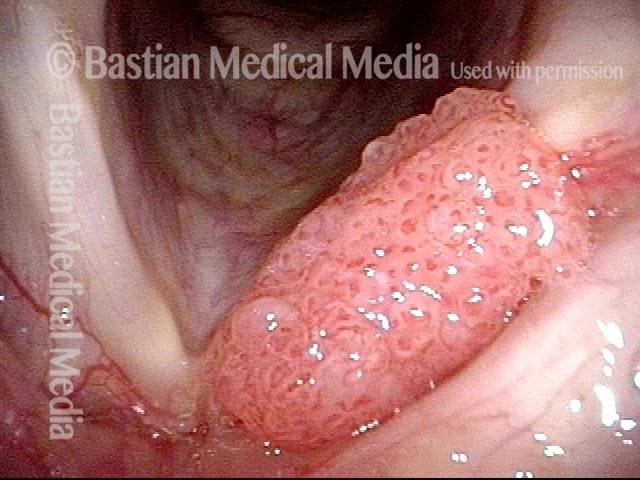
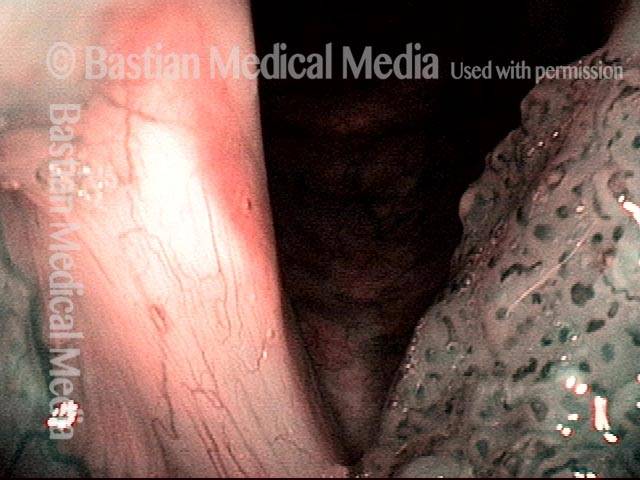
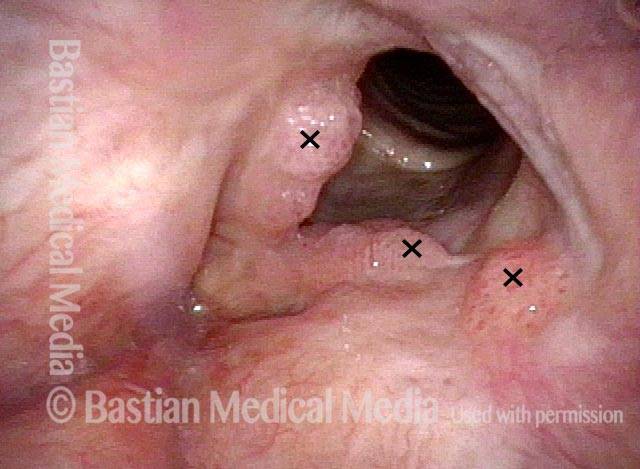
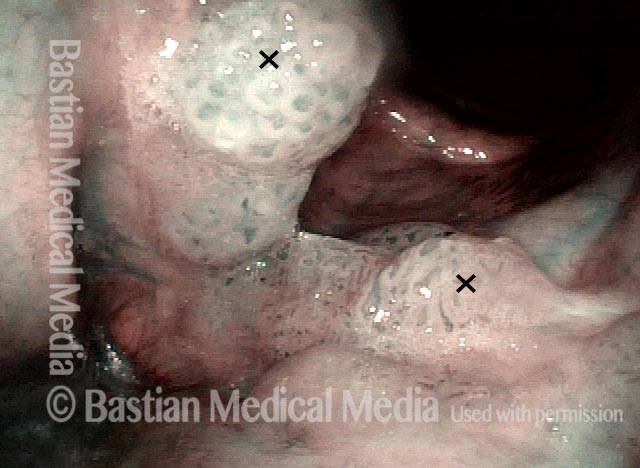
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a DNA virus that may cause cutaneous warts, genital warts, or the clinical condition recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) in susceptible individuals. Human papillomavirus (HPV) may occur in as many as 150 or more subtypes. The most common subtypes seen in patients with RRP are HPV 6 and 11.
Other less common subtypes that can induce papillomas or other growths within the larynx include HPV 16, 18, 31, 44, 45, 55, 69, 84 & 11, 33 & 45 and some of these subtypes are associated with a higher risk of cancer formation. See the photo series below, displaying all of the subtypes mentioned above. For a paper describing HPV subtypes in the larynx, see also this Bastian Voice Institute article.
Common Questions About HPV
What is the relationship between the terms RRP, HPV, and Papilloma?
The underlying disorder is HPV (human papilloma virus) infection of the airway, especially the larynx. The virus “sets up house” chronically inside airway and stimulates a kind of proliferation called papillomas, or papillomatosis.
Because these lesions tend to recur after surgical removal, the clinical syndrome has become referred to as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP).
HPV apparently has different subtypes. What can you tell me about them?
Human papilloma virus infection can consist of as many as 150 different subtypes. Some are related to skin infection (causing warts). Some are more common in genital or respiratory sites. Genital lesions are typically called condylomata, or genital warts.
In the airway, the lesions are typically called papillomas. Commonest subtypes in the airway are types 6 and 11. These two subtypes comprise the vast majority of our patients at Bastian Voice Institute (BVI). We have patients who have also tested positive for types 16, 18, 45, 55, and a few others.
I have a low-risk subtype of HPV. Can you explain what that means?
The human papilloma virus (HPV) comes in 150 or more subtypes. Think of it like the many models of automobiles that all fall under the designation “Ford.” Subtypes found most often in the respiratory and genital tracts are 6 and 11.
HPV infection is associated with some degree of risk of stimulating, or converting to, a carcinoma. Hence the higher risk of cervical cancer in women with HPV infection.
Some subtypes are considered to have a low risk of viral carcinogenesis; others have a high risk. At BVI, the majority of our many adult patients have 6 or 11, both of which are low-risk subtypes. We also have one or two who have both 6 and 11. Then we have a handful of patients with intermediate or high risk for cancer.
A few of these high-risk subtypes have in fact caused cancers in our population of ~150 adult patients with RRP. Thankfully, all have responded well to treatment and none to my memory have died from their cancer.
Subtype 6
More common subtype seen in the airway. HPV 6 is associated with a lesser risk of cancer formation, as is HPV 11.
Humility Before the HPV Virus—A Recurrence of Papillomas at Ten Years
HPV infection is considered chronic, and causes recurrent growth of papillomas in the larynx. Still, we sometimes see what appear to be cures, or at least long-term remissions. That appears to be the case here. After an 8 year interval of perfect voice, the patient had a sudden increase of hoarseness occurring in the few weeks prior to the last examination below.
This is an illustration of why we often say to a patient who appears to be cured, “You may be cured, but we usually say “long term remission.” This patient’s scenario is not rare. Was her longterm, 8-year remission due to meticulous surgery? Cidofovir? Her immune response? It is impossible to say if it was one or all of these factors.
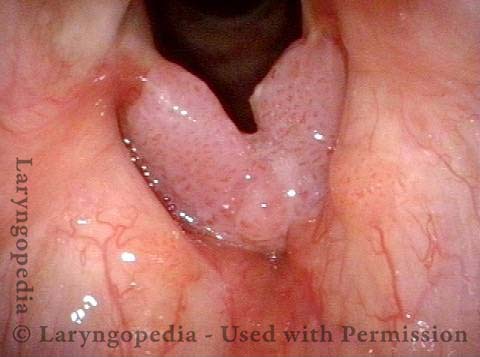
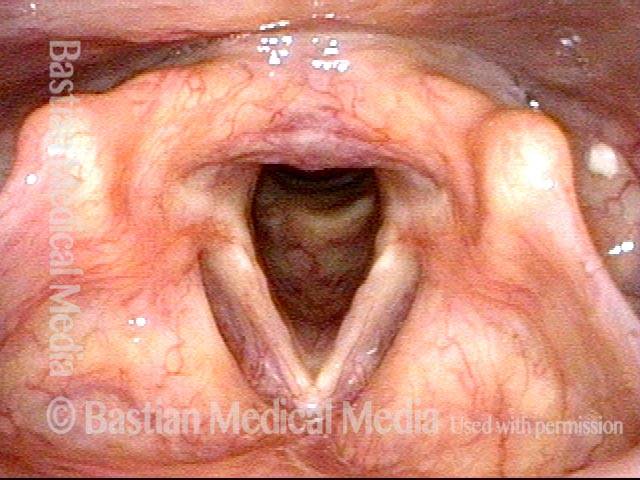
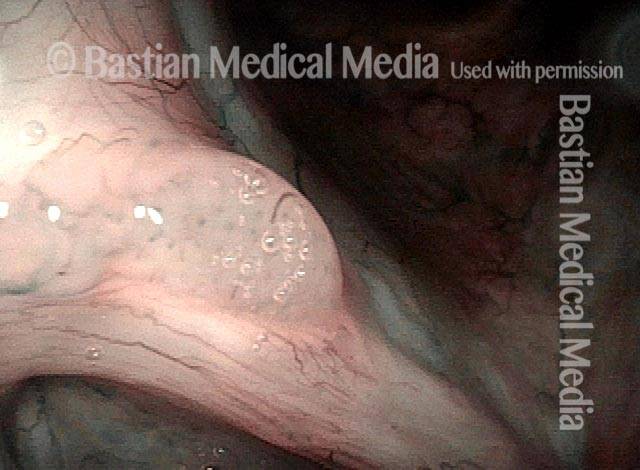
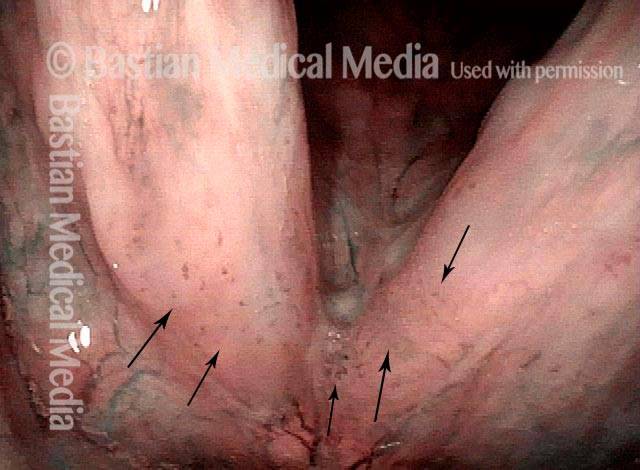
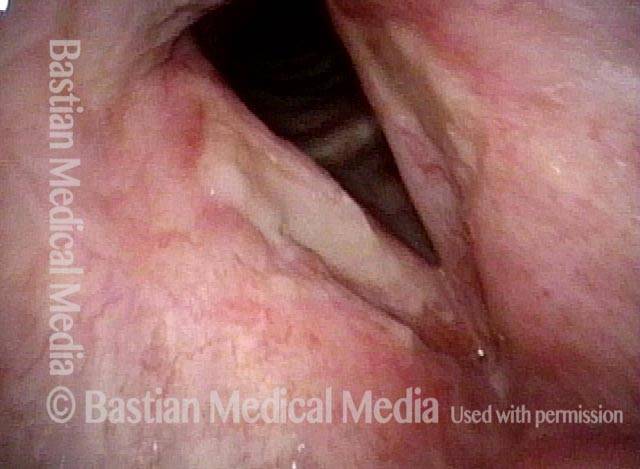
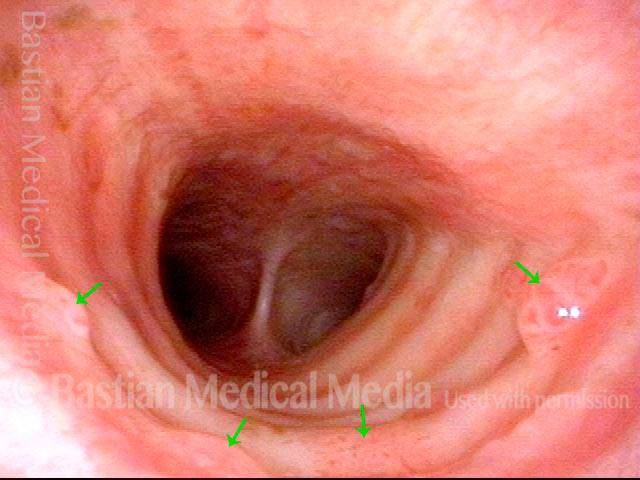
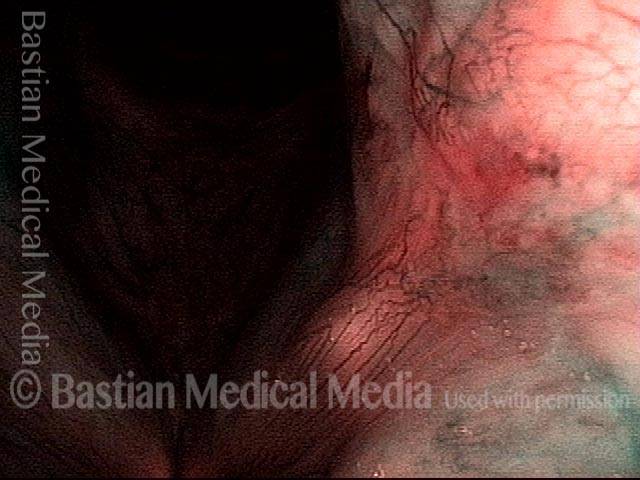
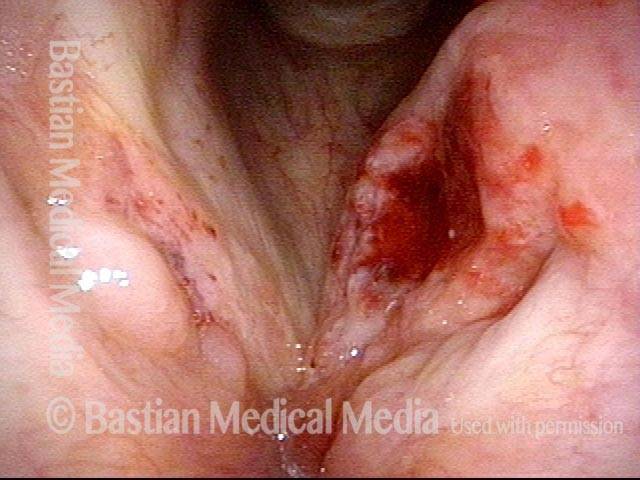
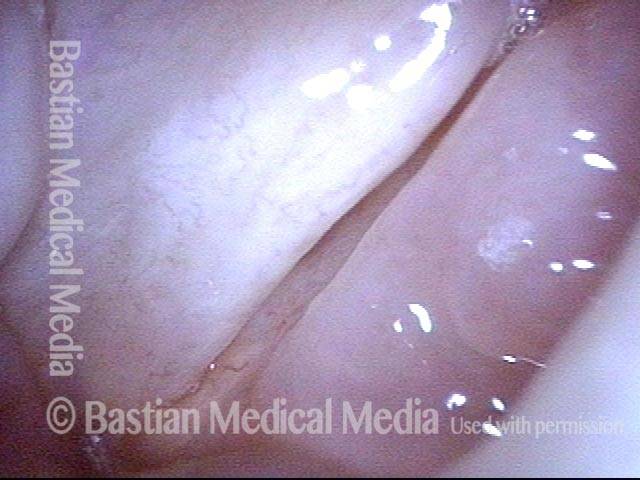
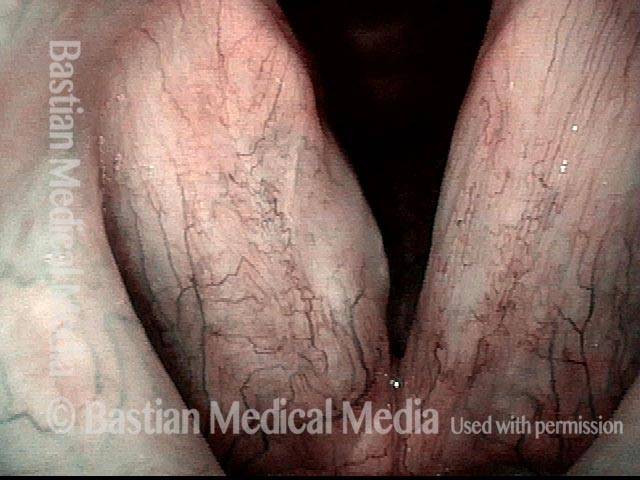
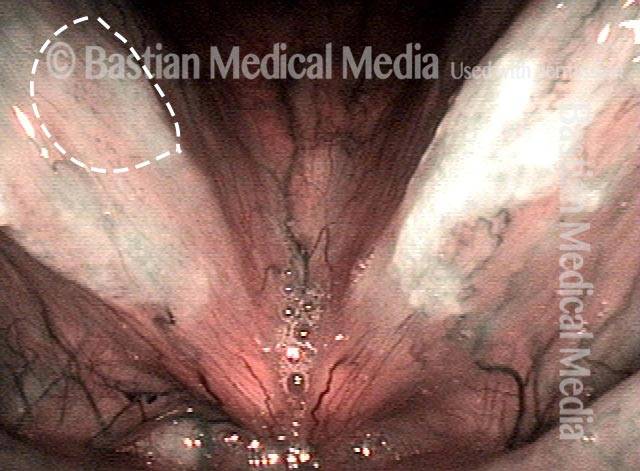
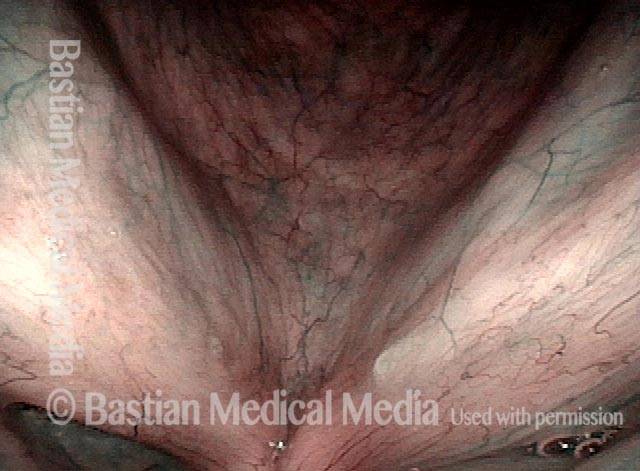
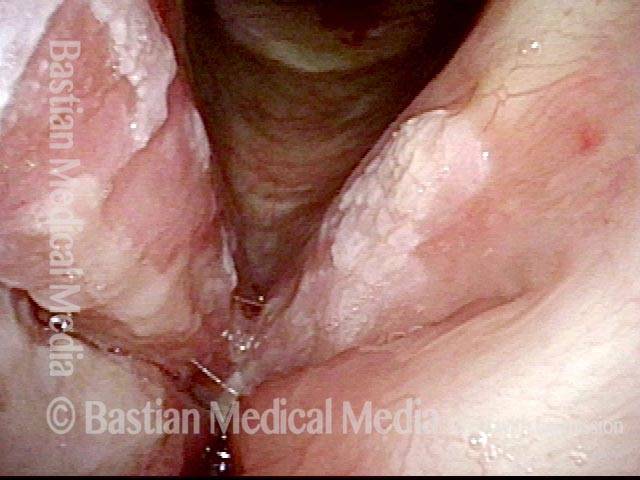
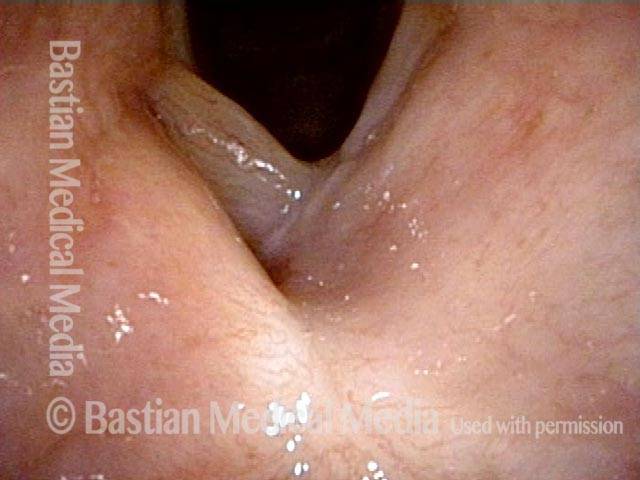
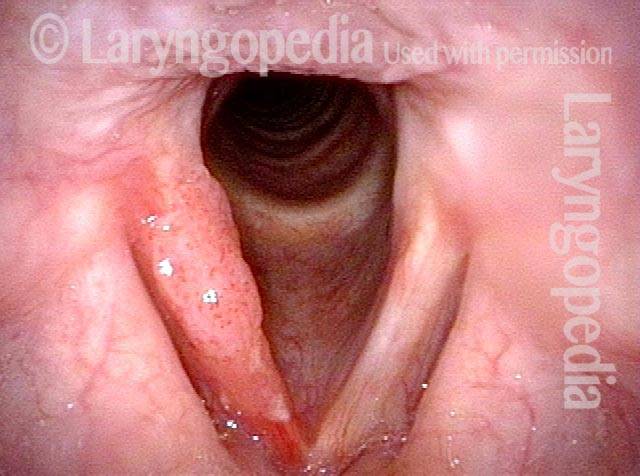
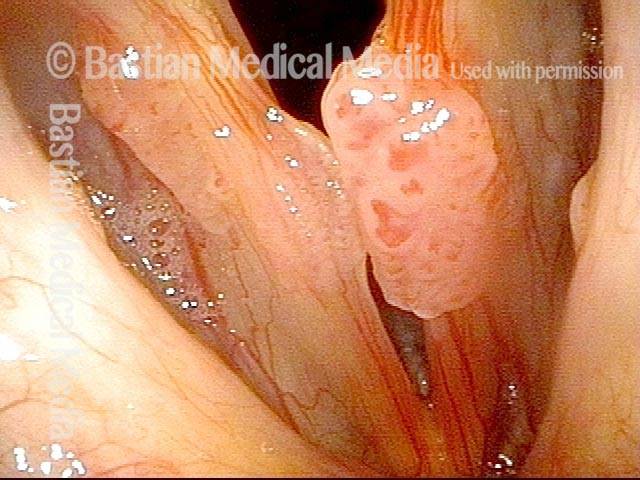
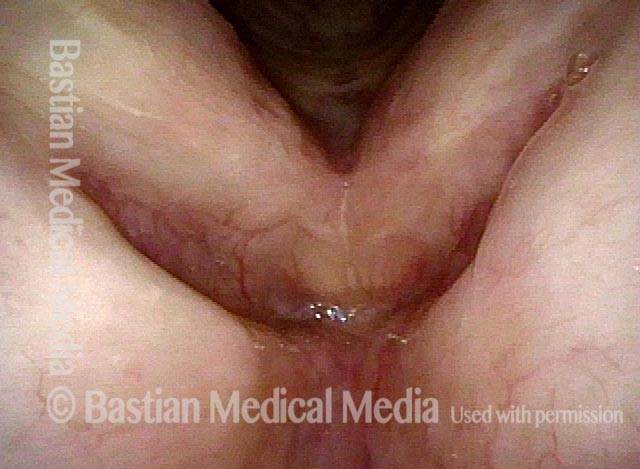
Stippled Vascularity (1 of 8)
Stippled Vascularity (1 of 8)
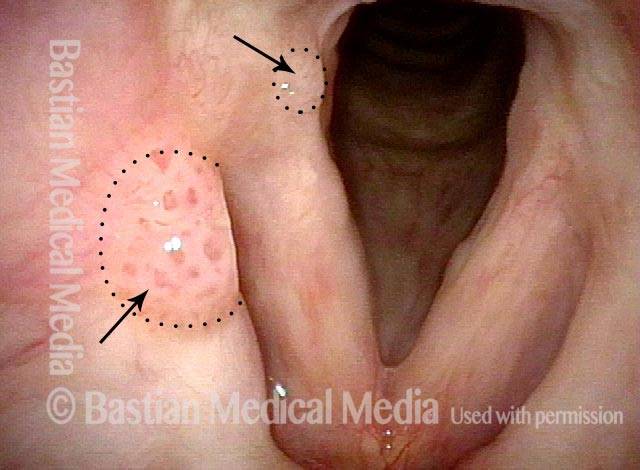
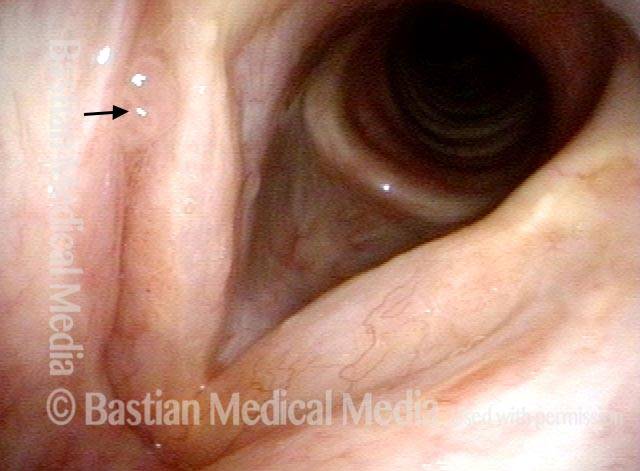
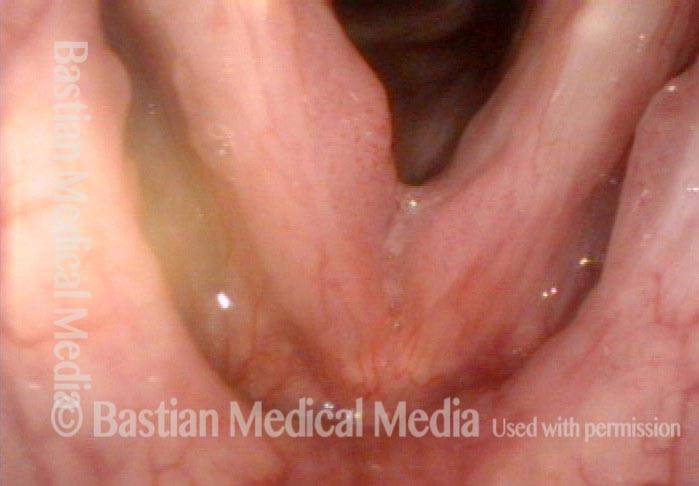
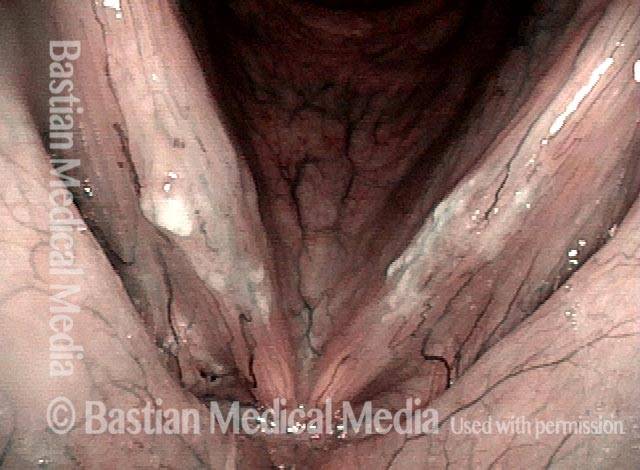
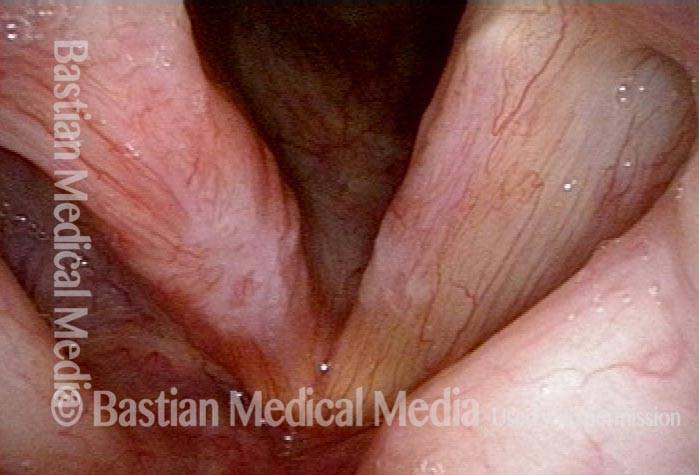
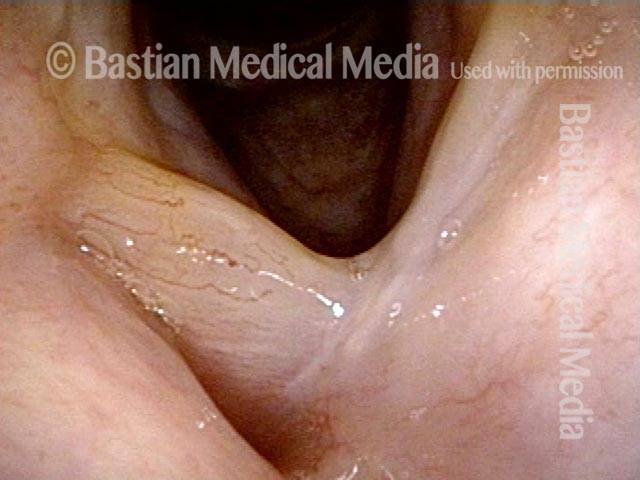
HPV infection (2 of 8)
HPV infection (2 of 8)
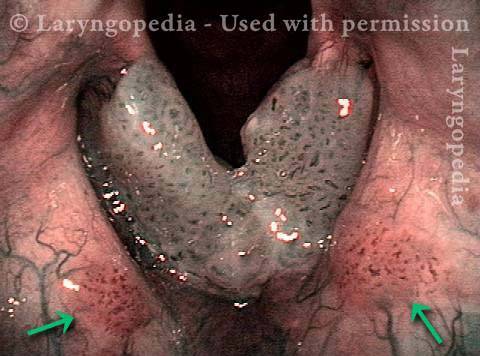
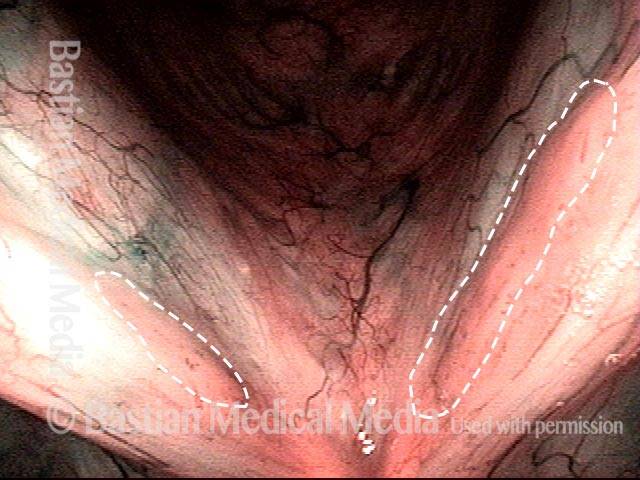
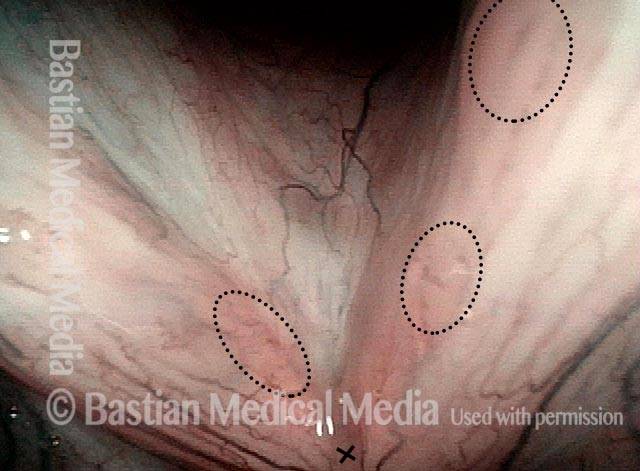
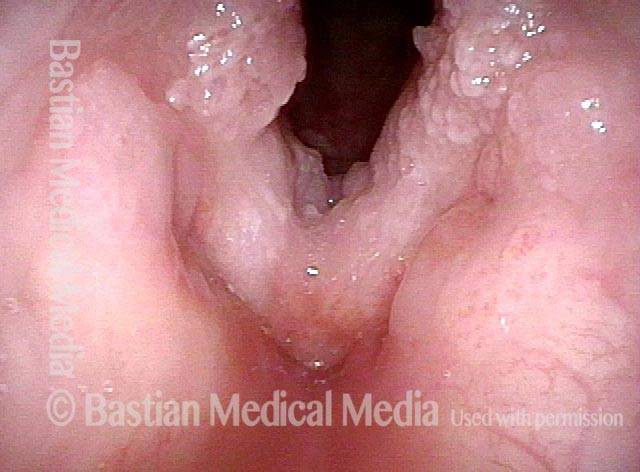
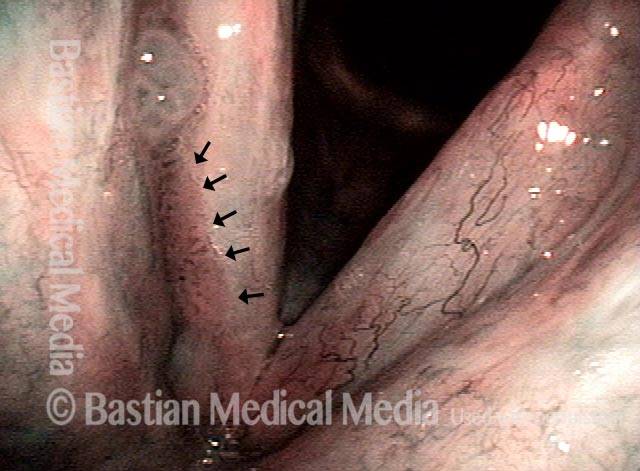
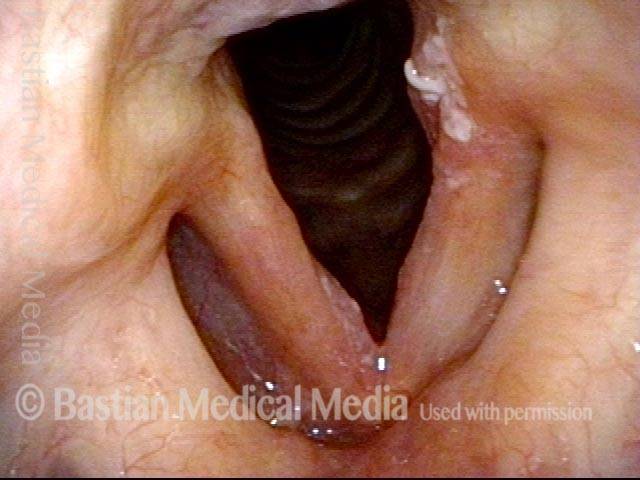
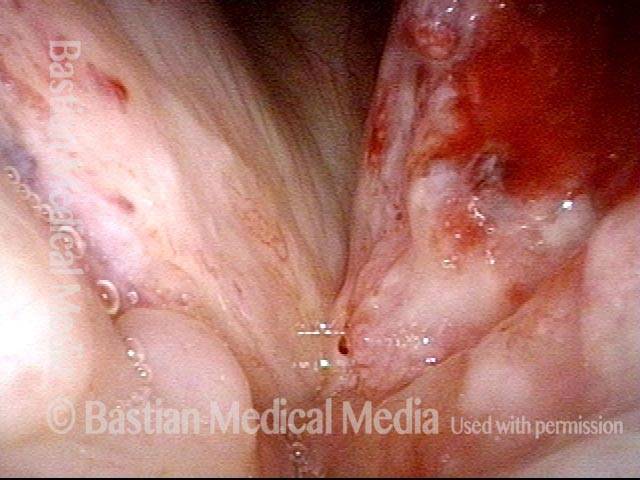
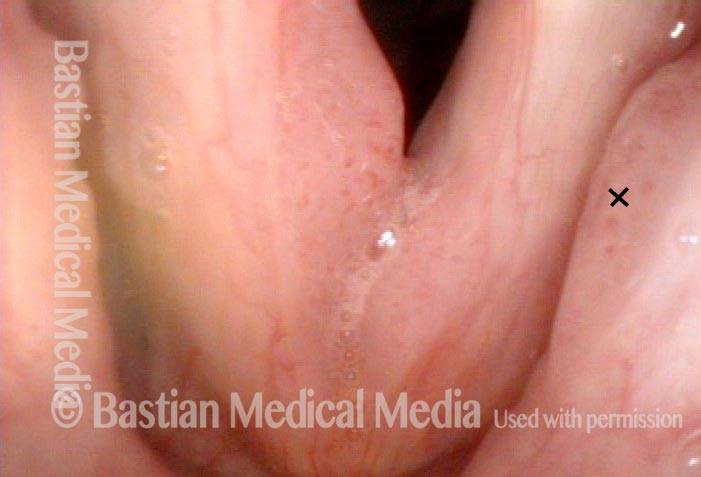
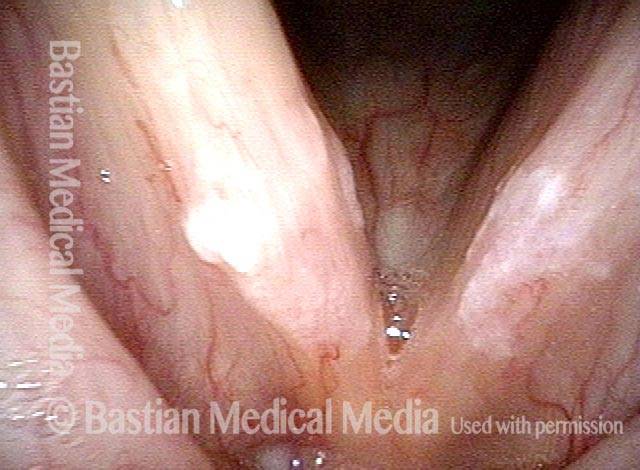
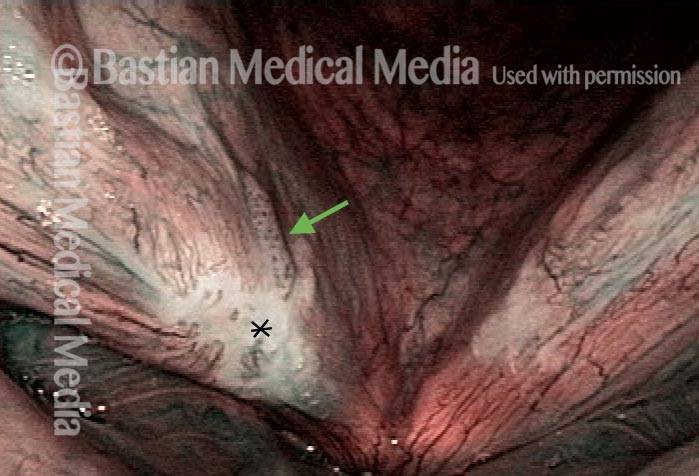
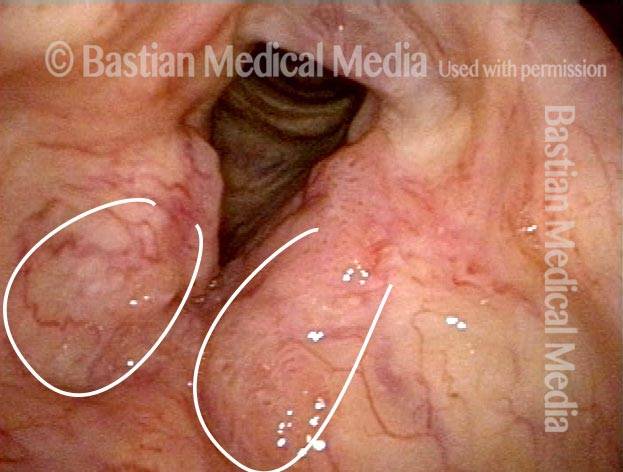
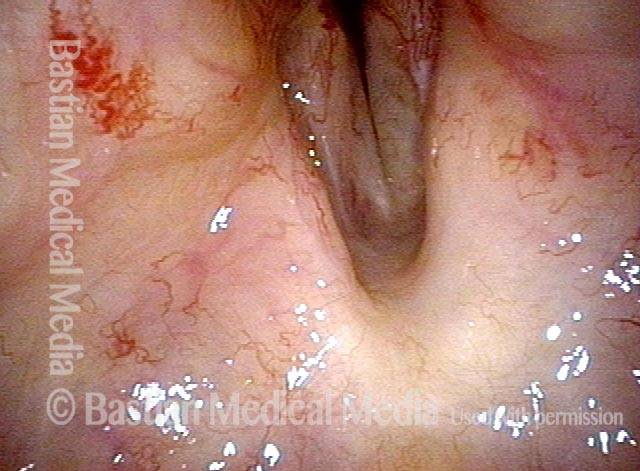
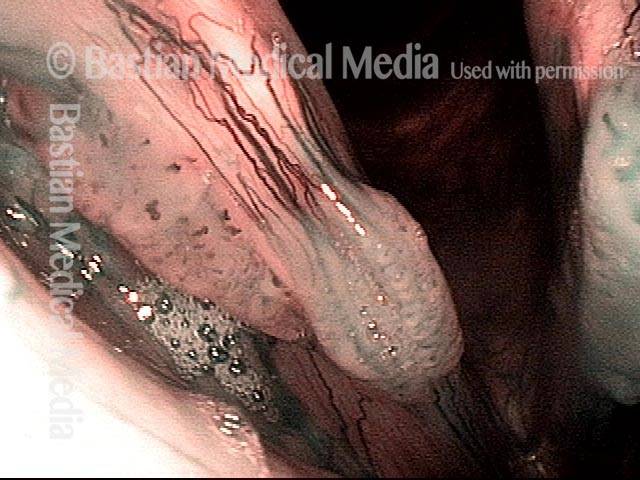
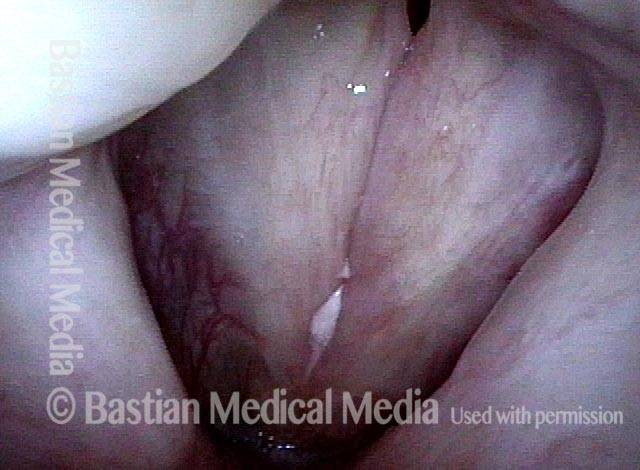
Stippled vascularity (3 of 8)
Stippled vascularity (3 of 8)
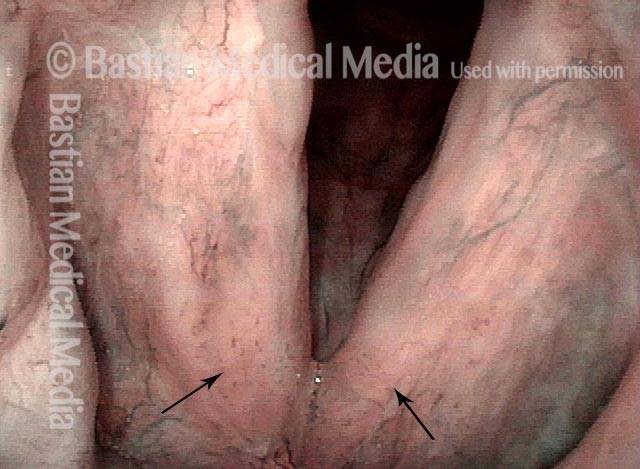
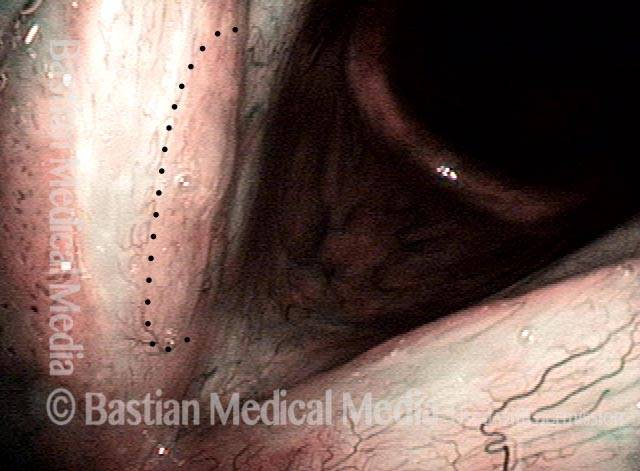
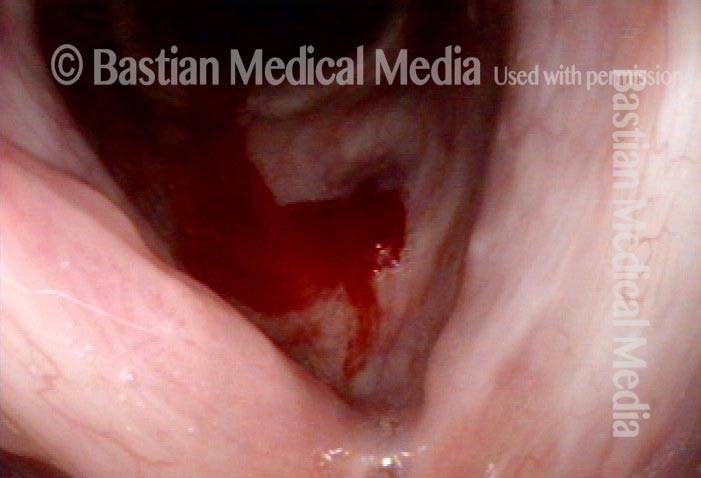
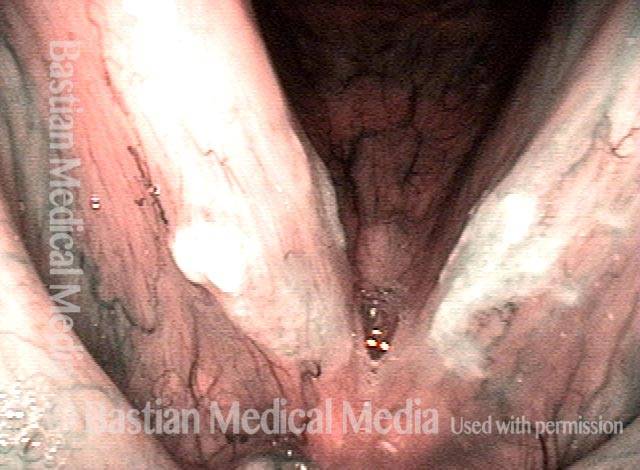
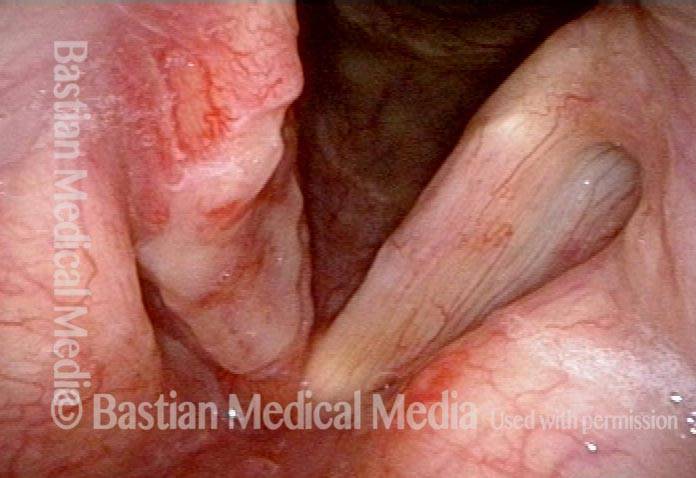
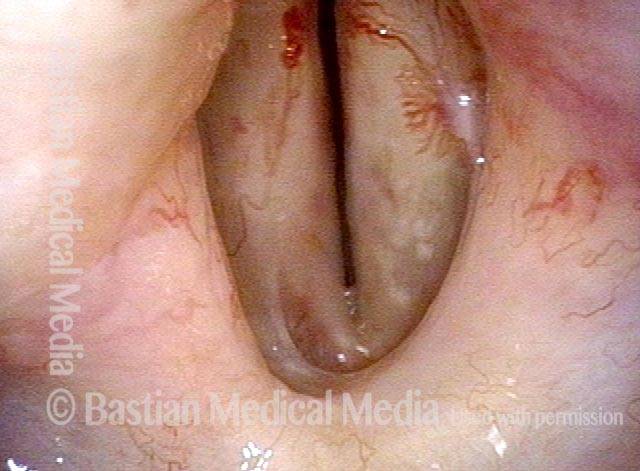
HPV vascular effect (4 of 8)
HPV vascular effect (4 of 8)
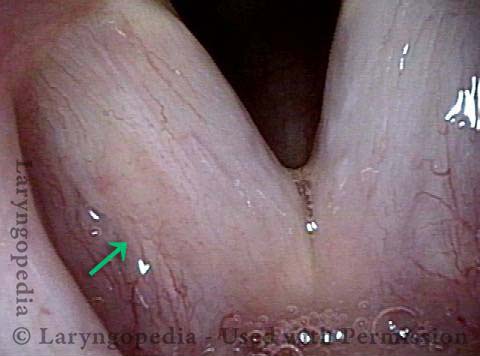
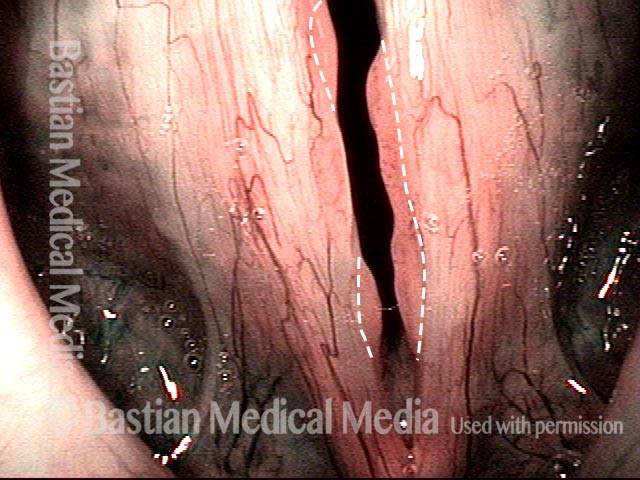
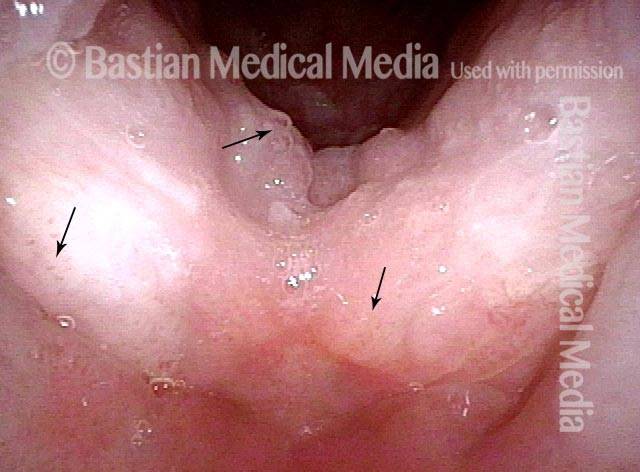
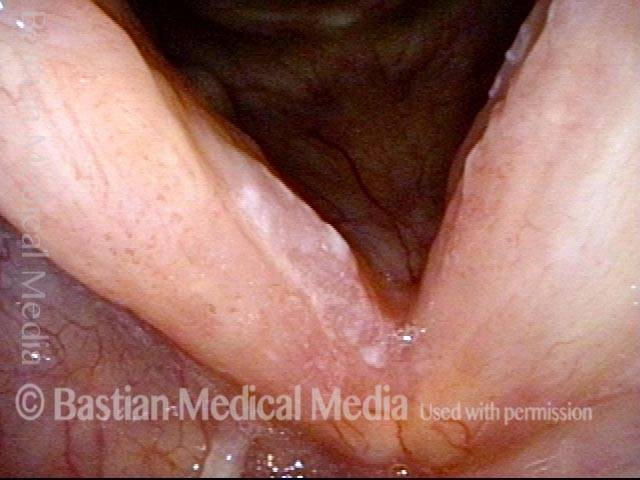
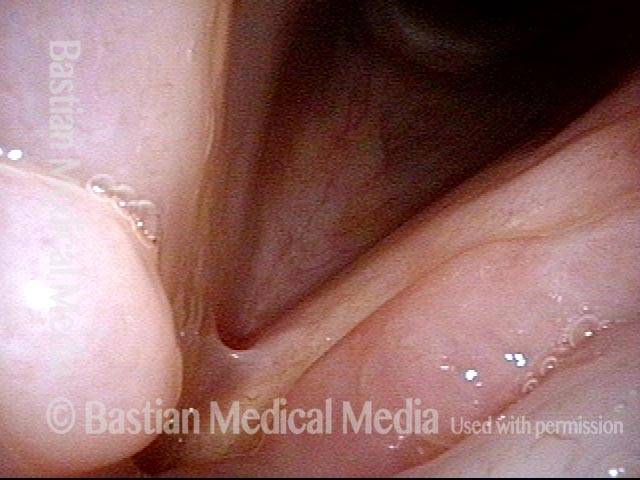
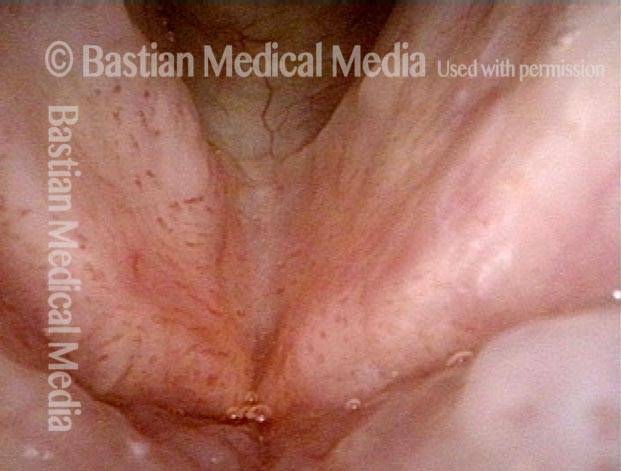
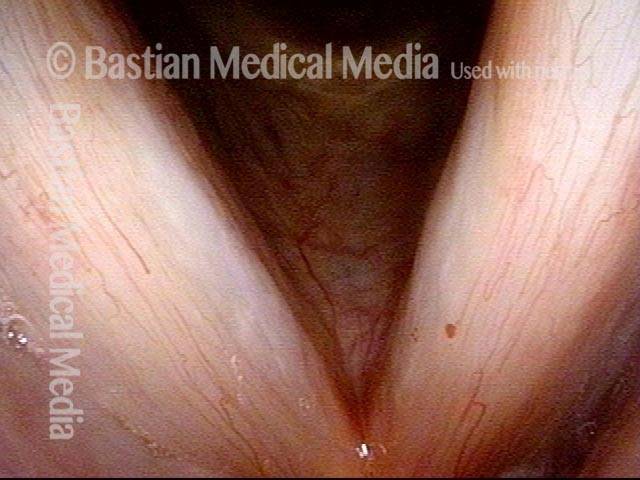
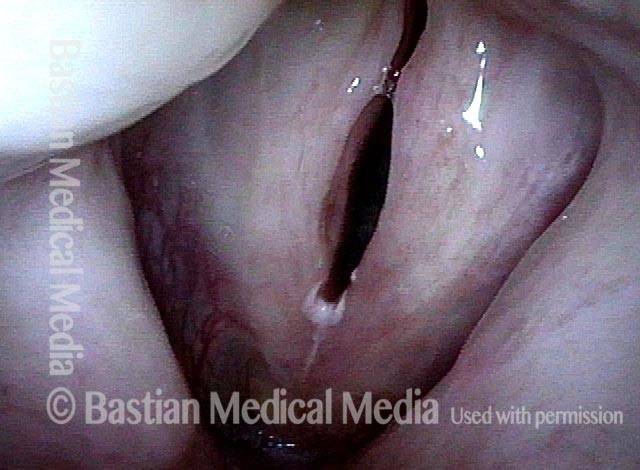
16 months later (5 of 8)
16 months later (5 of 8)
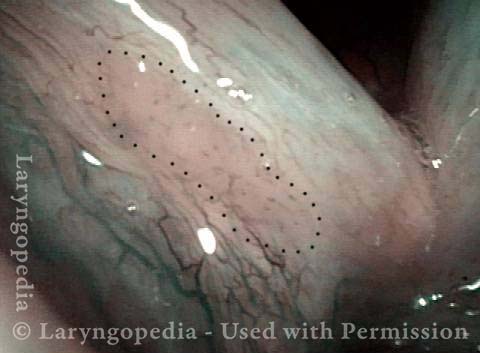
Is it long-term remission? (6 of 8)
Is it long-term remission? (6 of 8)
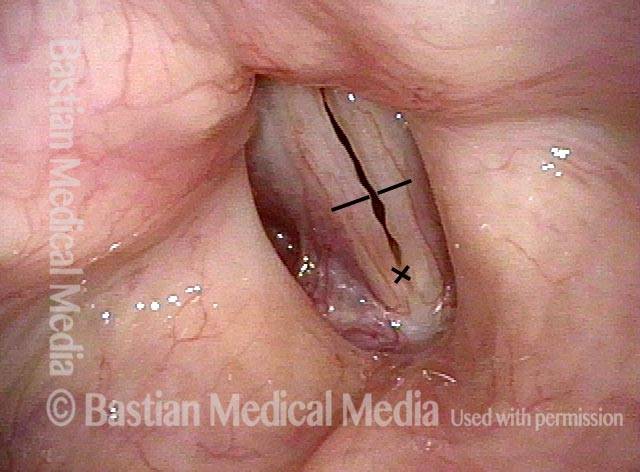
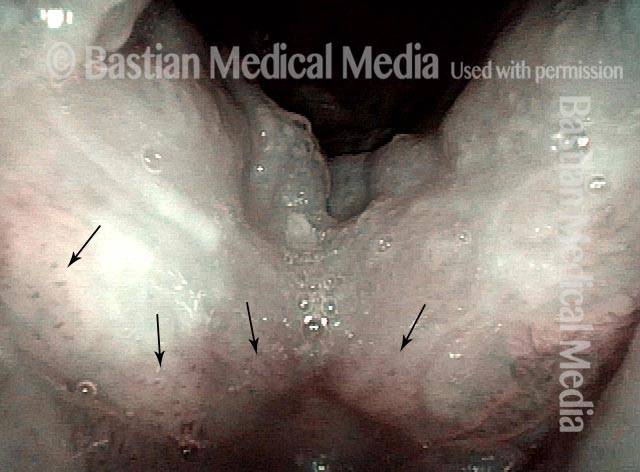
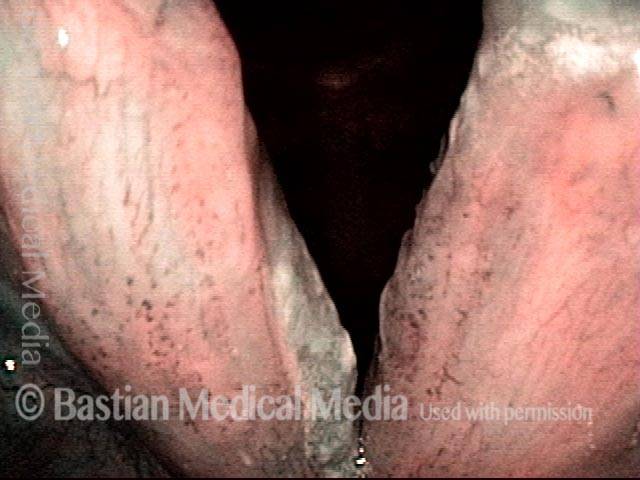
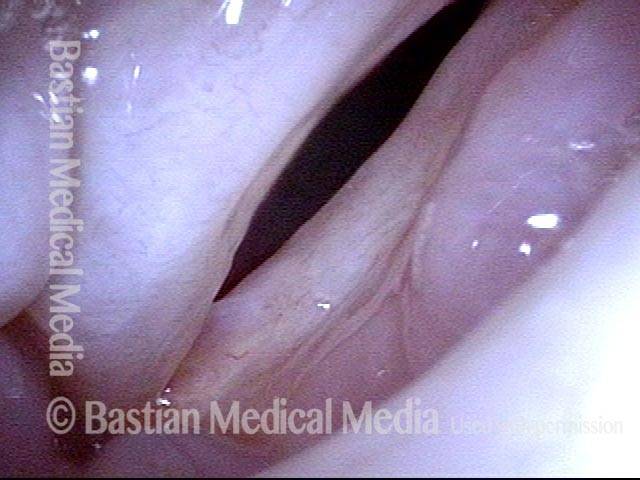
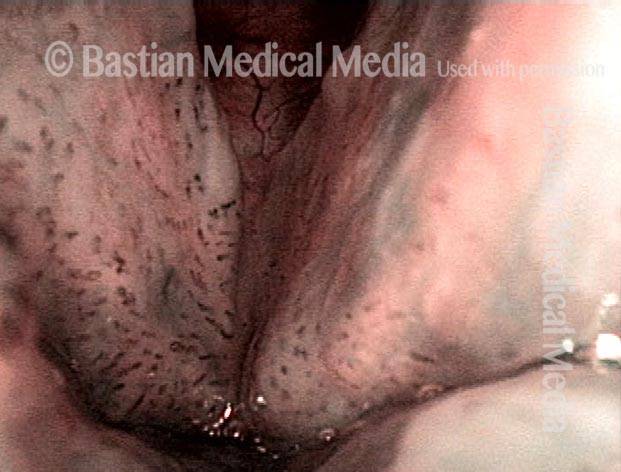
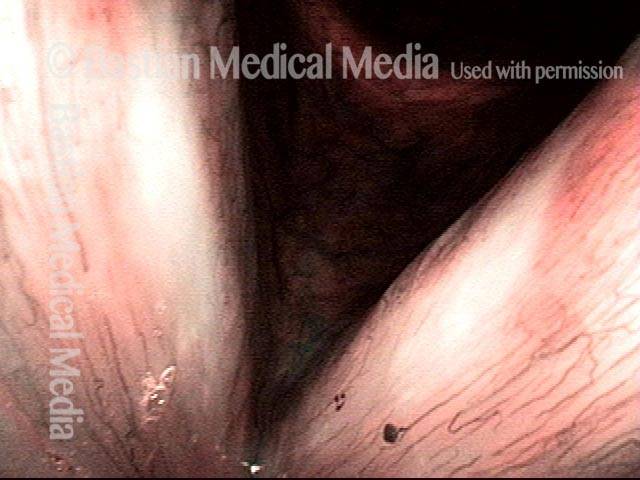
Recurrent Papilloma (7 of 8)
Recurrent Papilloma (7 of 8)
Stippled vascularity (8 of 8)
Stippled vascularity (8 of 8)
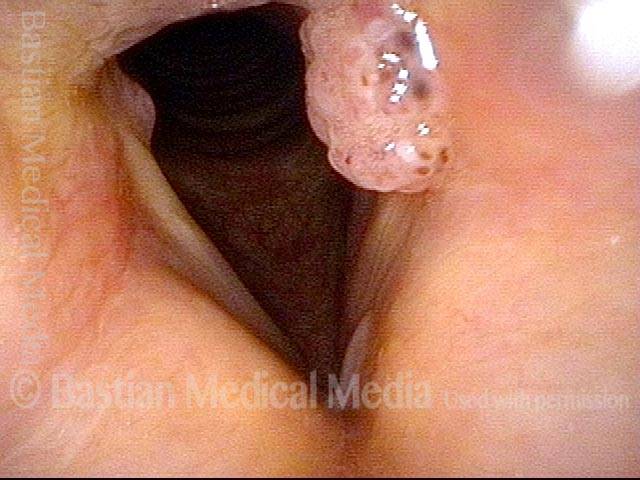
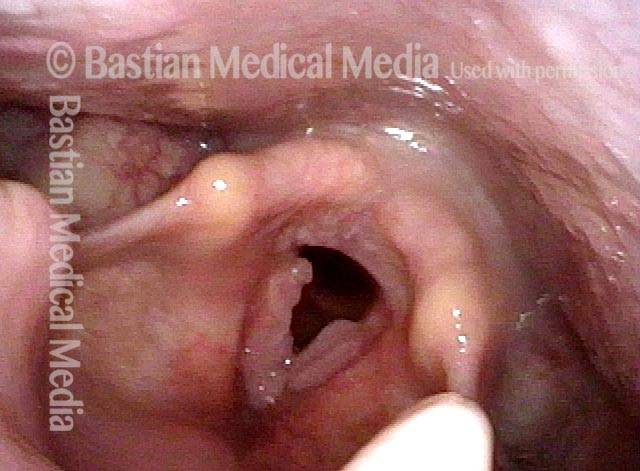
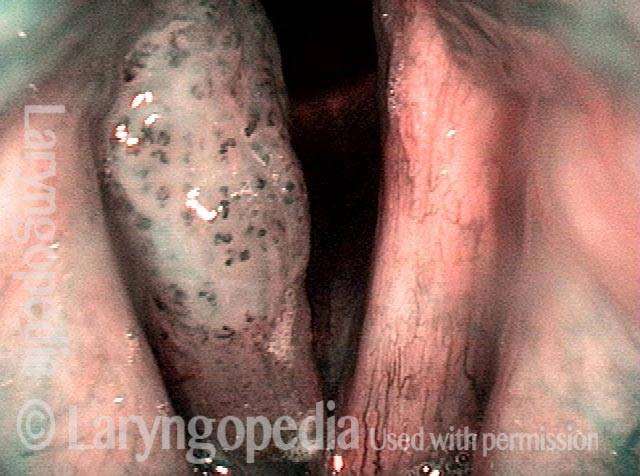
Papillomas, HPV subtype 6, before and after removal
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 6 (1 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 6 (1 of 4)
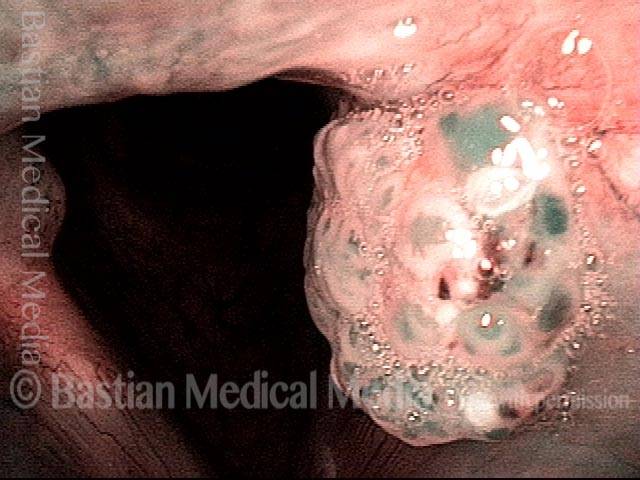
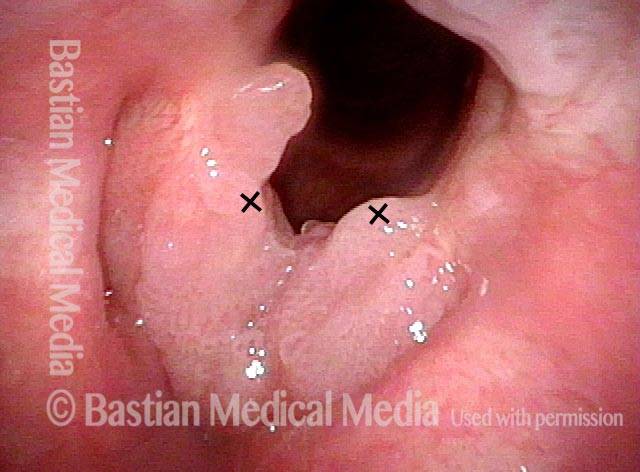
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 6 (2 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 6 (2 of 4)
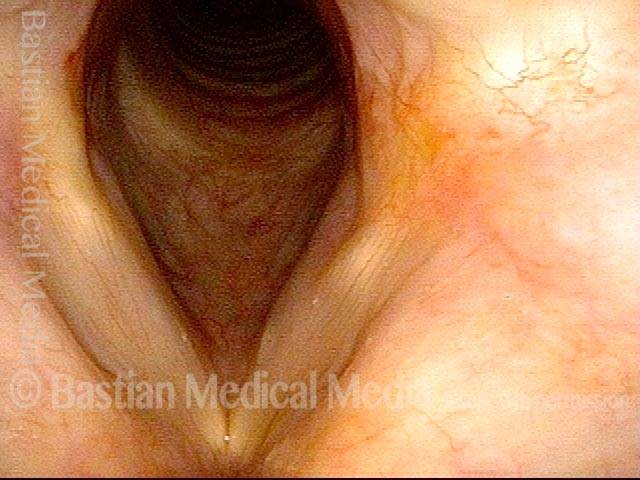
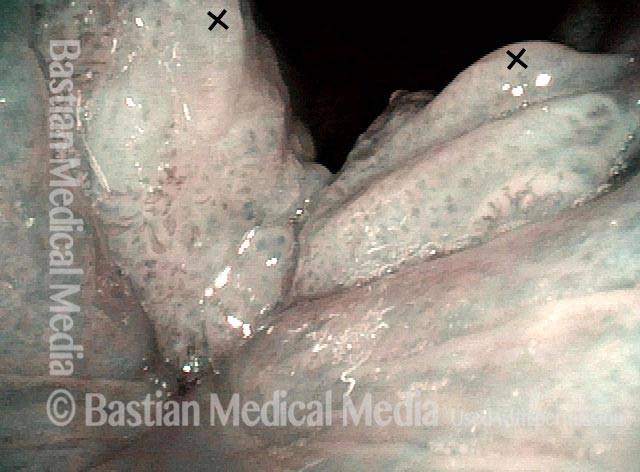
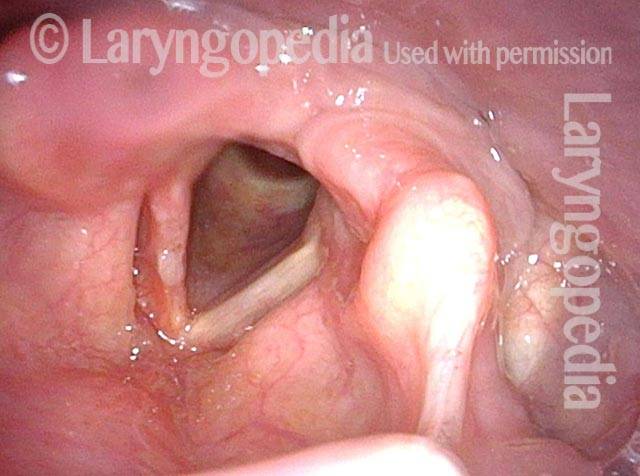
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 6 (3 of 4)
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 6 (3 of 4)
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 6 (4 of 4)
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 6 (4 of 4)
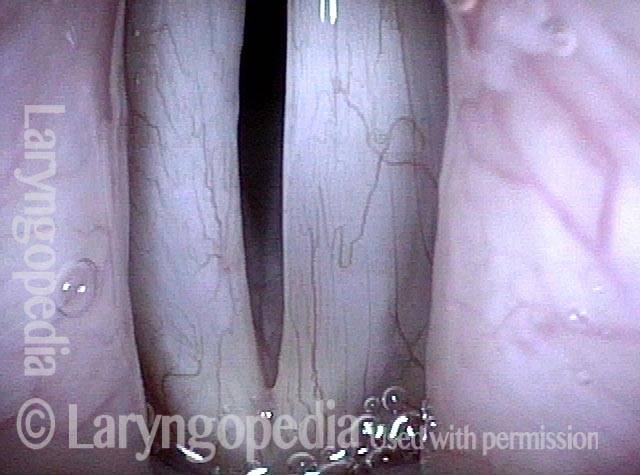
Subtle papillomas, HPV subtype 6
Subtle papillomas, HPV subtype 6 (1 of 3)
Subtle papillomas, HPV subtype 6 (1 of 3)
Subtle papillomas, HPV subtype 6 (2 of 3)
Subtle papillomas, HPV subtype 6 (2 of 3)
Subtle papillomas, HPV subtype 6 (3 of 3)
Subtle papillomas, HPV subtype 6 (3 of 3)
Subtle papillomas and the importance of a motivated examination
Standard light, HPV-6 infection (1 of 4)
Standard light, HPV-6 infection (1 of 4)
Stobe light, vocal cord margin irregularity (2 of 4)
Stobe light, vocal cord margin irregularity (2 of 4)
Narrow band light, vascular marks seen (3 of 4)
Narrow band light, vascular marks seen (3 of 4)
Narrow band light, papilloma formation (4 of 4)
Narrow band light, papilloma formation (4 of 4)
HPV Vascular Effect
Two papillomas (1 of 3)
Two papillomas (1 of 3)
Stippled vascularity (2 of 3)
Stippled vascularity (2 of 3)
HPV vascular effect (3 of 3)
HPV vascular effect (3 of 3)
Type 6 HPV Papillomas Firmer Than Most
Stippled vascularity not seen (1 of 4)
Stippled vascularity not seen (1 of 4)
HPV vascular effect (2 of 4)
HPV vascular effect (2 of 4)
Vascularity clearly seen (3 of 4)
Vascularity clearly seen (3 of 4)
Under narrow-band light (4 of 4)
Under narrow-band light (4 of 4)
HPV 6: Going, Going, Gone?
“Curative mode” plan (1 of 7)
“Curative mode” plan (1 of 7)
Closer view (2 of 7)
Closer view (2 of 7)
Narrow-band illumination (3 of 7)
Narrow-band illumination (3 of 7)
Post surgery (4 of 7)
Post surgery (4 of 7)
Towards “management mode” (5 of 6)
Towards “management mode” (5 of 6)
Same view under NBI (6 of 7)
Same view under NBI (6 of 7)
Stippled vascularity seen (7 of 7)
Stippled vascularity seen (7 of 7)
Subtype 11
One of the more common subtypes seen in the airway. HPV 11 is associated with a lesser risk of cancer formation, as well as HPV 6.
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (1 of 3)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (1 of 3)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (2 of 3)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (2 of 3)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (3 of 3)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (3 of 3)
Example 2
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (1 of 2)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (1 of 2)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (2 of 2)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (2 of 2)
Papillomas, HPV Subtype 11, Before and After Removal
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (1 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (1 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (2 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 11 (2 of 4)
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 11 (3 of 4)
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 11 (3 of 4)
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 11 (4 of 4)
Papillomas, removed: HPV Subtype 11 (4 of 4)
Subtype 16
Less common in the airway than the more common subtypes 6 and 11. HPV 16 is associated with a higher risk of cancer formation, along with HPV subtypes 18, 31, 45, 55, and others.
Lesions of HPV Subtype 16
Lesions of HPV Subtype 16 (1 of 3)
Lesions of HPV Subtype 16 (1 of 3)
Lesions of HPV Subtype 16 (2 of 3)
Lesions of HPV Subtype 16 (2 of 3)
Lesions of HPV Subtype 16 (3 of 3)
Lesions of HPV Subtype 16 (3 of 3)
Cancer, HPV Subtype 16, Before and After Radiation
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16 (1 of 5)
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16 (1 of 5)
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16, after radiation therapy (3 of 5)
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16, after radiation therapy (3 of 5)
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16, after radiation therapy (4 of 5)
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16, after radiation therapy (4 of 5)
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16, after radiation therapy (5 of 5)
Cancer: HPV Subtype 16, after radiation therapy (5 of 5)
Subtype 18
This is less common in the airway than the more common subtypes 6 and 11. HPV 18 is associated with a higher risk of cancer formation, along with HPV subtypes 16, 31, 45, 55, and others.
Papillomas seen (1 of 4)
Papillomas seen (1 of 4)
Stippled vascularity (2 of 4)
Stippled vascularity (2 of 4)
Surgical removal (3 of 4)
Surgical removal (3 of 4)
Cidofovir injection (4 of 4)
Cidofovir injection (4 of 4)
Subtype 31
This is less common in the airway than the more common subtypes 6 and 11. HPV 31 is associated with a higher risk of cancer formation, along with HPV subtypes 16, 18, 45, 55, and others.
Papillomas, HPV Subtype 31, Going Into Remission
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 31 (1 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 31 (1 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 31 (2 of 4)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 31 (2 of 4)
Papillomas, in remission: HPV Subtype 31 (3 of 4)
Papillomas, in remission: HPV Subtype 31 (3 of 4)
Papillomas, in remission: HPV Subtype 31 (4 of 4)
Papillomas, in remission: HPV Subtype 31 (4 of 4)
HPV 31 As A Cause of “Chronic Laryngitis”
Hazy leukoplakia, HPV suspected (1 of 4)
Hazy leukoplakia, HPV suspected (1 of 4)
Leukoplakia remains (2 of 4)
Leukoplakia remains (2 of 4)
Leukoplakia demarcated (3 of 4)
Leukoplakia demarcated (3 of 4)
HPV effect confirmed (4 of 4)
HPV effect confirmed (4 of 4)
HPV 31 → Cancer → Cure
Carcinoma in situ (1 of 4)
Carcinoma in situ (1 of 4)
HPV subtype 31 (2 of 4)
HPV subtype 31 (2 of 4)
Excisions (3 of 4)
Excisions (3 of 4)
Seven years later (4 of 4)
Seven years later (4 of 4)
Subtype 44
Voiceless 50-year-old man (1 of 6)
Voiceless 50-year-old man (1 of 6)
Vascular stippling (2 of 6)
Vascular stippling (2 of 6)
Narrow band light, vascularity (3 of 6)
Narrow band light, vascularity (3 of 6)
4 months later, recurrent papillomas (4 of 6)
4 months later, recurrent papillomas (4 of 6)
Open position, narrow band light (5 of 6)
Open position, narrow band light (5 of 6)
Closing for voicing (6 of 6)
Closing for voicing (6 of 6)
Example 2
Stippled vascularity (1 of 4)
Stippled vascularity (1 of 4)
Narrow-band lighting (2 of 4)
Narrow-band lighting (2 of 4)
4 months later (3 of 4)
4 months later (3 of 4)
Closer view (4 of 4)
Closer view (4 of 4)
Subtype 45
This subtype is less common in the airway than the more common subtypes 6 and 11. HPV 45 is associated with a higher risk of cancer formation, along with HPV subtypes 16, 18, 31, 55, and others.
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 45 (1 of 2)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 45 (1 of 2)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 45 (2 of 2)
Papillomas: HPV Subtype 45 (2 of 2)
Example 2
HPV type 45 detected (1 of 7)
HPV type 45 detected (1 of 7)
Closer view of HPV effect (2 of 7)
Closer view of HPV effect (2 of 7)
Narrow band illunination (3 of 7)
Narrow band illunination (3 of 7)
Post radiotherapy, glottic web seen (4 of 7)
Post radiotherapy, glottic web seen (4 of 7)
Post-radiation web (5 of 7)
Post-radiation web (5 of 7)
Post-microlaryngoscopy, release of glottic web (6 of 7)
Post-microlaryngoscopy, release of glottic web (6 of 7)
HPV effect no longer seen (7 of 7)
HPV effect no longer seen (7 of 7)
Subtypes 33 & 45
Hoarse voice (1 of 5)
Hoarse voice (1 of 5)
Narrow band light (2 of 5)
Narrow band light (2 of 5)
Post excision (3 of 5)
Post excision (3 of 5)
Healed (4 of 5)
Healed (4 of 5)
“Cured” (5 of 5)
“Cured” (5 of 5)
Subtype 55
This subtype is less common in the airway than the more common subtypes 6 and 11. HPV 55 is associated with an intermediate degree of risk of cancer formation, as compared to other subtypes of HPV.