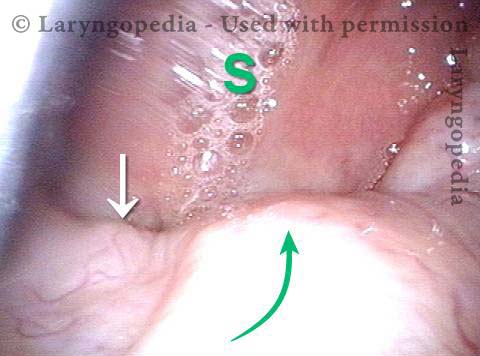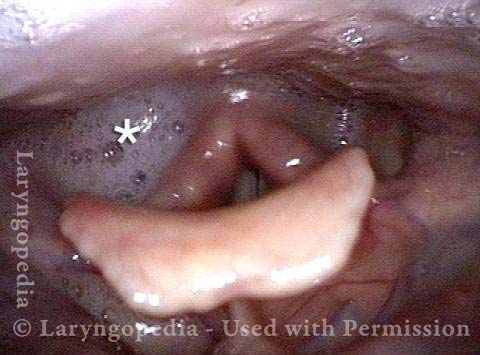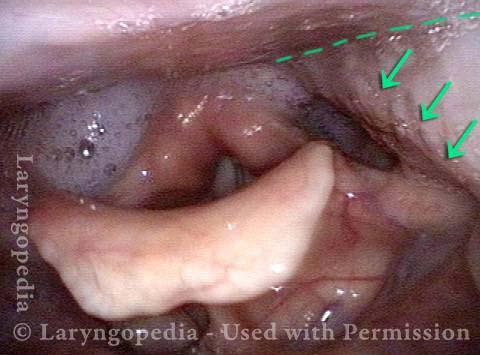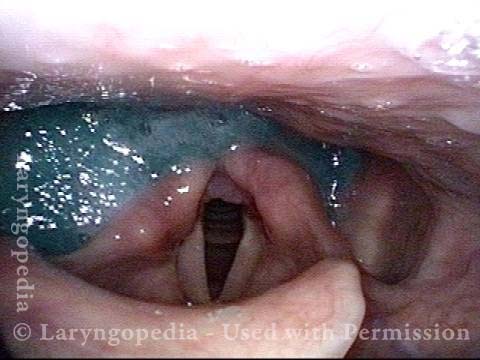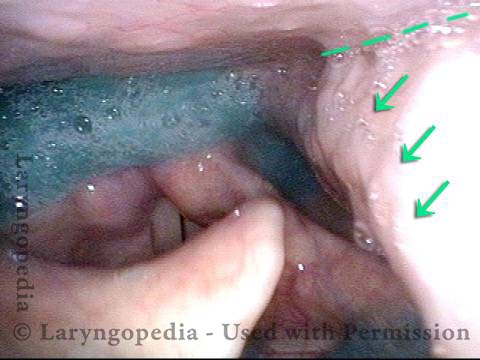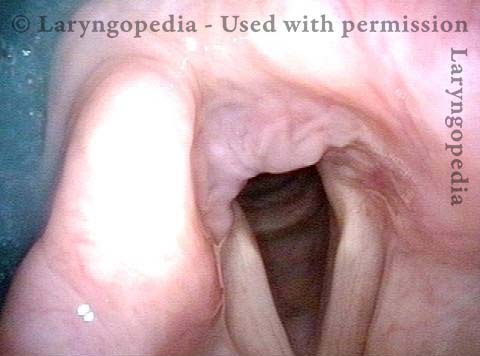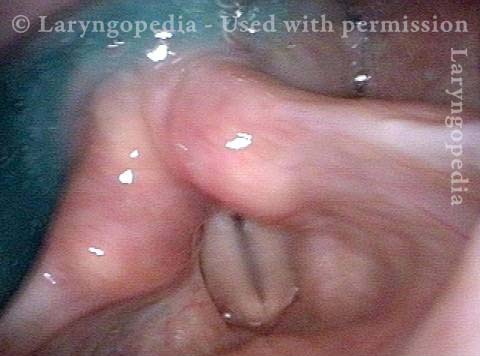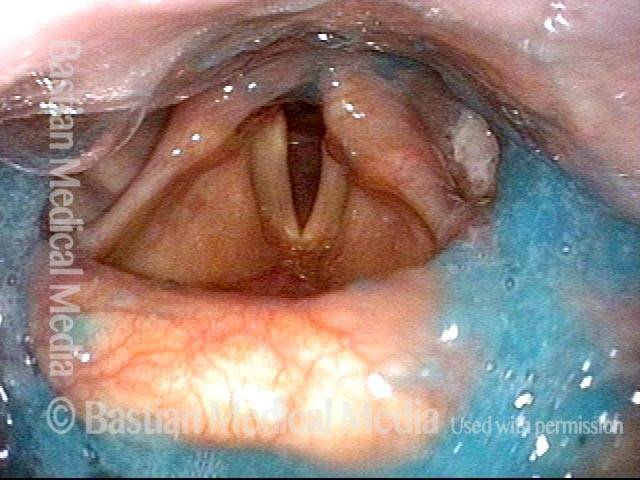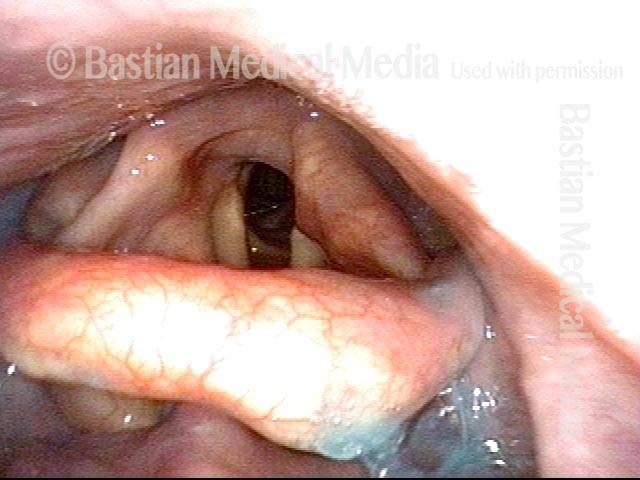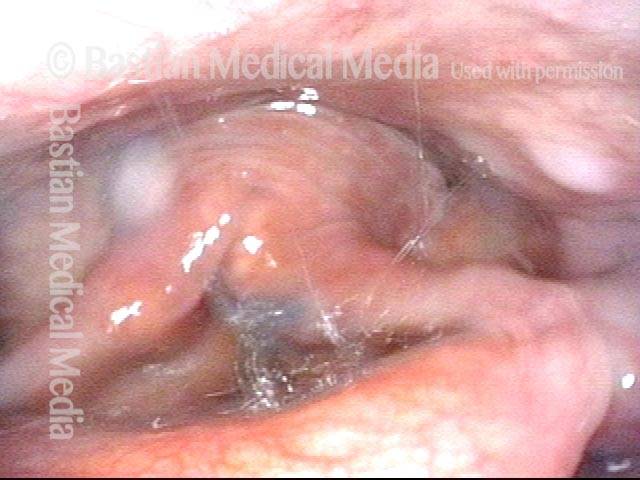
Pooling occurs when a person’s swallow does not successfully send the entire mass of food or liquid into the esophagus, so that some or all of the material remains in the hypopharynx. In such cases, the material commonly pools in the vallecula and pyriform sinuses. It can also cling to the base of the tongue or the pharyngeal walls. Pooling is often caused by presbyphagia, and its occurrence may put a patient at risk of aspiration.
High Vagus Nerve Injury
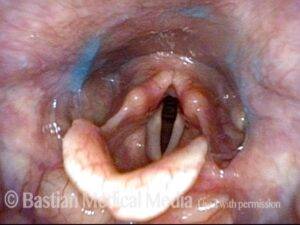
The vagus (10th cranial) nerve originates from the medulla (part of the brainstem), exits from the base of the skull through the jugular foramen, and among other things, supplies branches to the musculature of palate, pharynx, and larynx. Location of vagus nerve injury is sometimes evident by palate and pharynx findings. But these findings are sometimes overlooked as in this case, especially if palate and pharynx are weak but not completely paralyzed.
Case study: This 50-something woman developed a weak voice and moderate difficulty swallowing upon awakening 5 months prior to this visit. Fortunately, her symptoms of weak voice and difficulty swallowing were not devastating, and are improving. But up to this examination, there has been no diagnosis. This examination reveals a “lesion” of her right vagus nerve and it has to be at the base of the skull because palate, pharynx, and larynx muscles are all weak. Voice is functional but lacks the ability to project and has a “soft-edged” quality. A sophisticated listener can also hear mild hypernasality. The examination below prompts a scan with special attention to base of skull to be sure there is no mass lesion there.