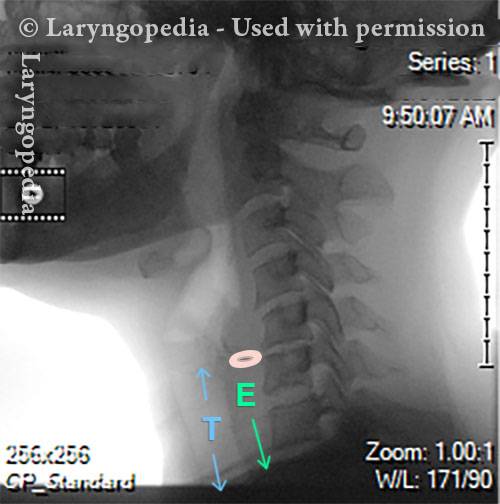
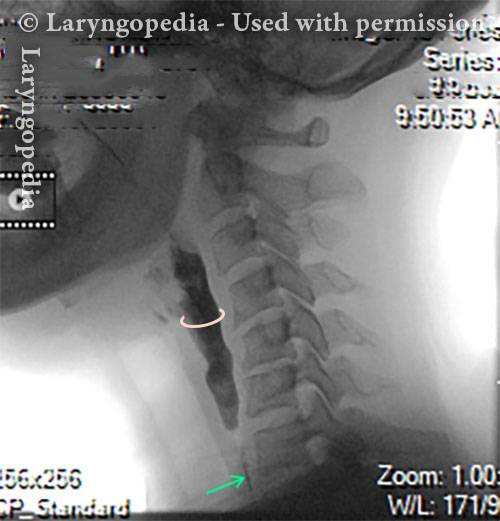
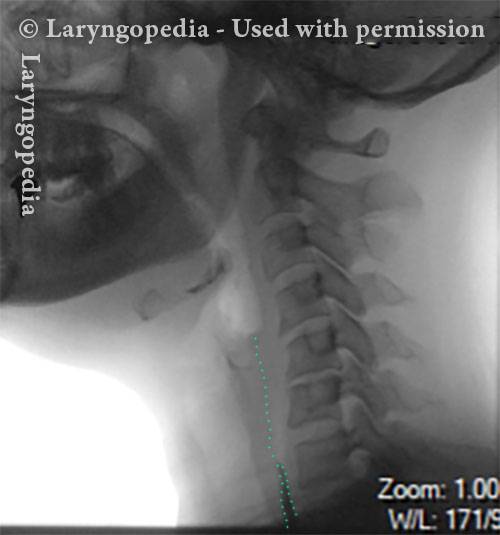
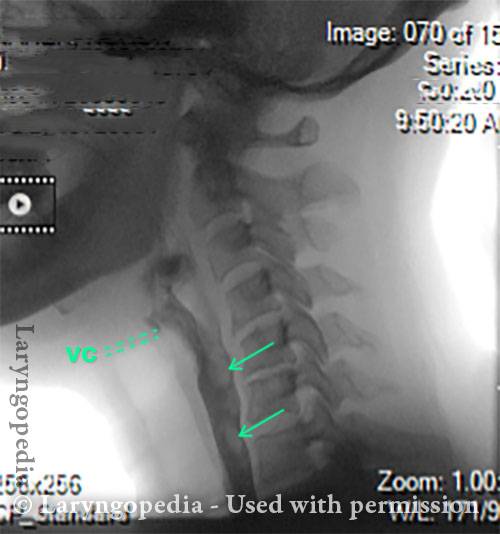
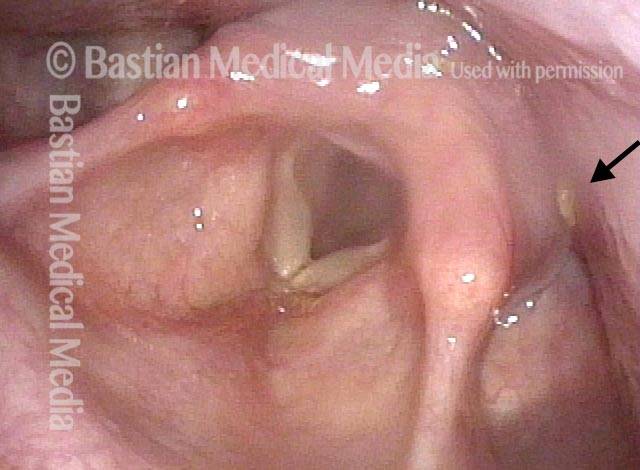
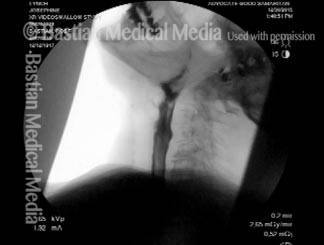
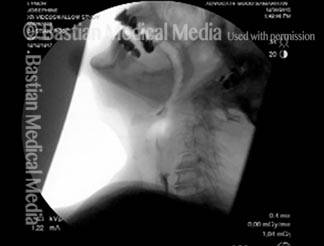
Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study (VFSS), (Modified Barium Swallow)
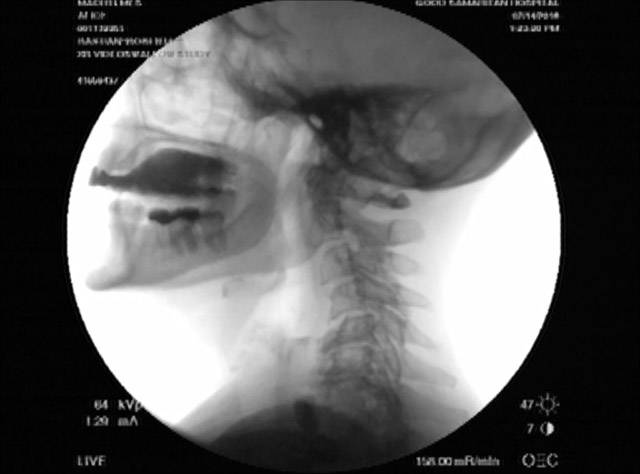
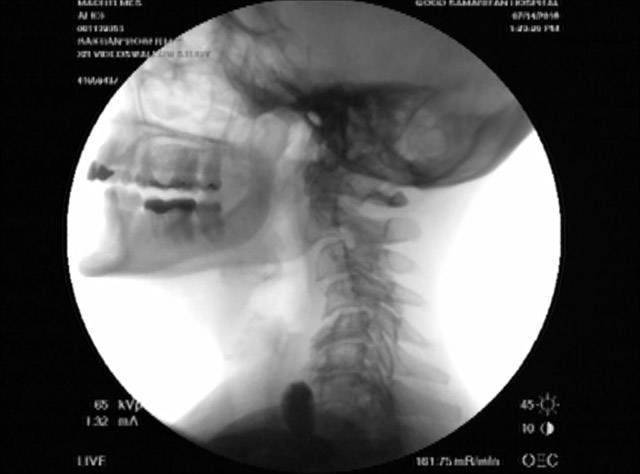
Videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) is an x-ray-based method of evaluating a person’s swallowing ability. VFSS is also sometimes called the modified barium swallow, or the “cookie swallow.”
In a radiology suite under fluoroscopy (which creates moving rather than still x-ray images), the patient is asked to swallow barium in thin liquid and paste consistencies, and then in paste on a cookie or cracker. The barium bolus is followed radiographically through the mouth, throat, and into the esophagus. Both lateral and anterior–posterior views are recorded and, depending on the facility, a simple screening sequence of the subsequent movement down the esophagus is also recorded.
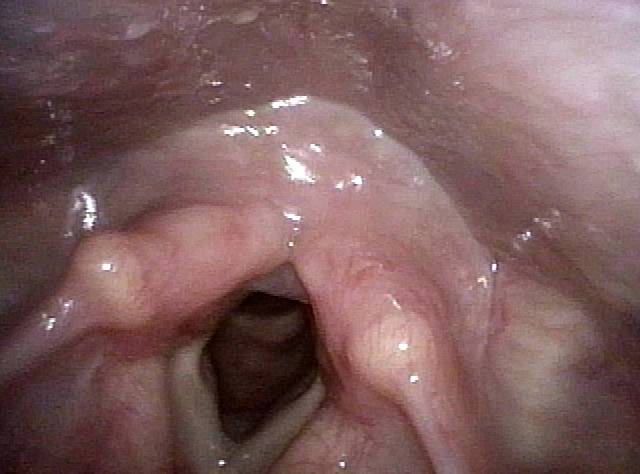
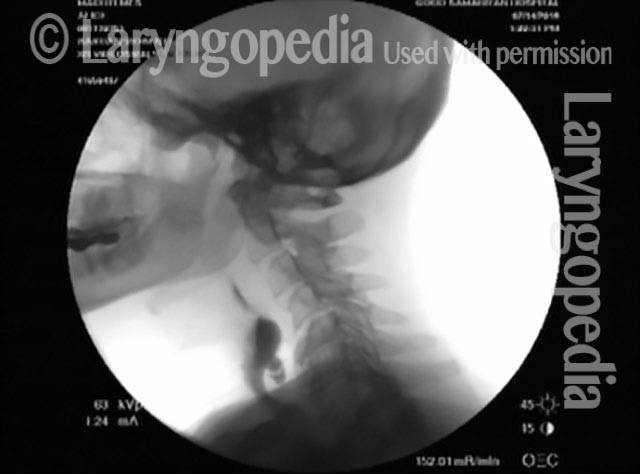
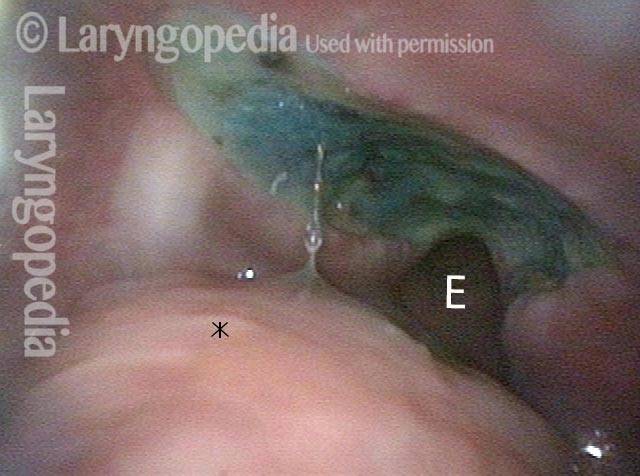
Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction, Before & After Myotomy
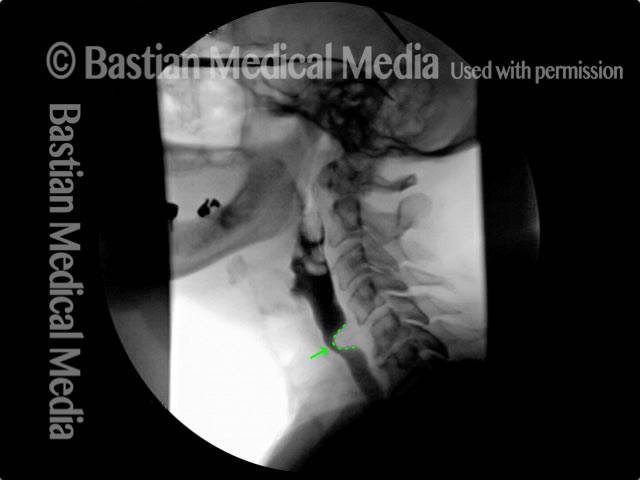
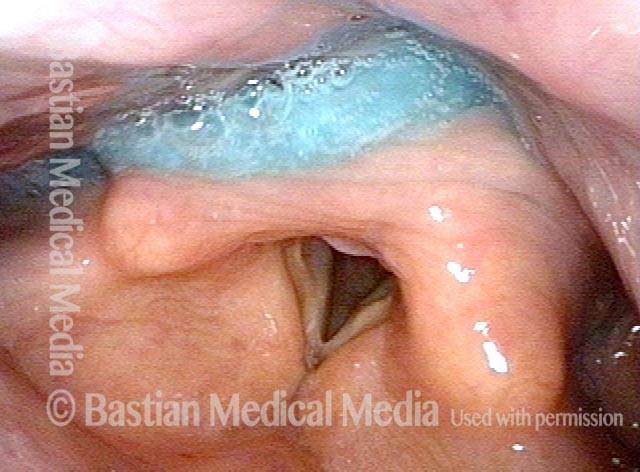
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: before myotomy (1 of 2)
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: before myotomy (1 of 2)
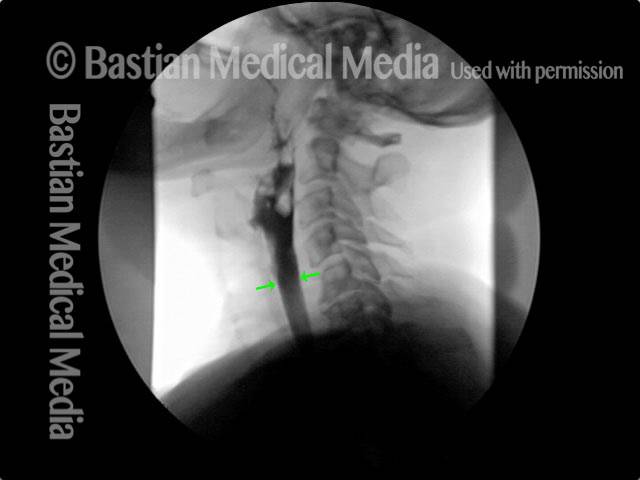
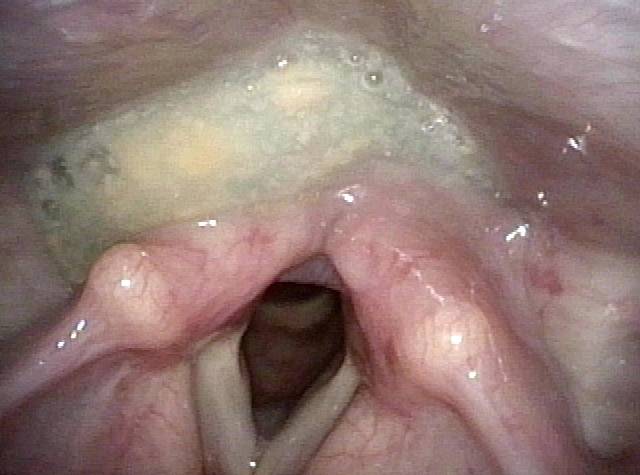
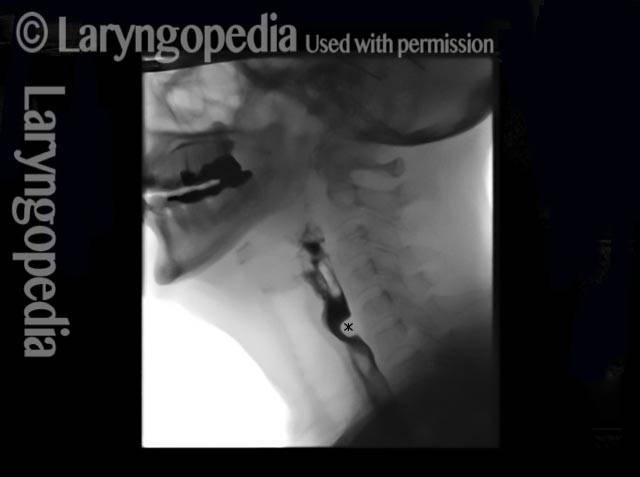
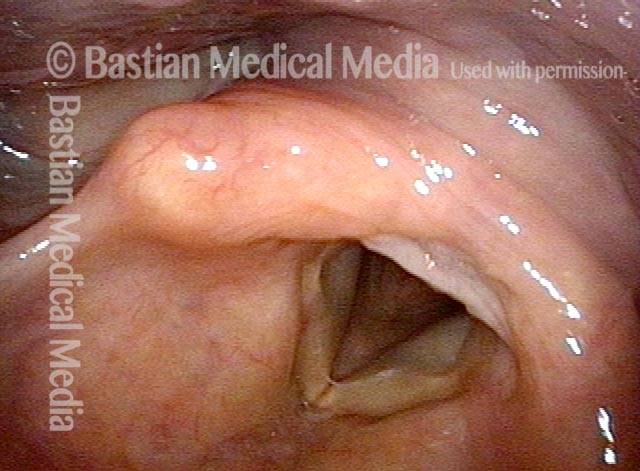
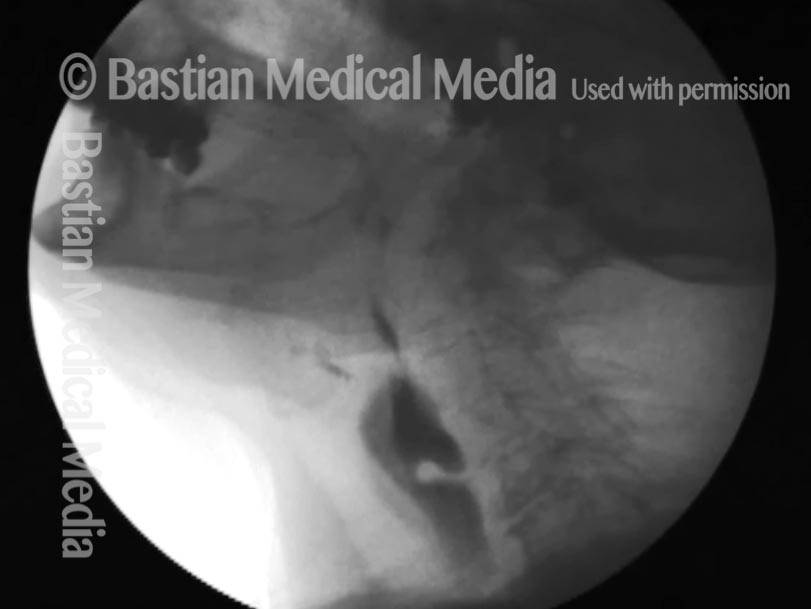
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: after myotomy, resolved (2 of 2)
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: after myotomy, resolved (2 of 2)
Example 2
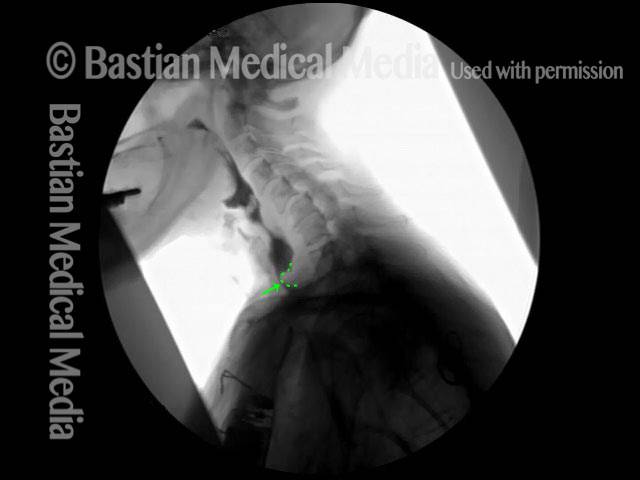
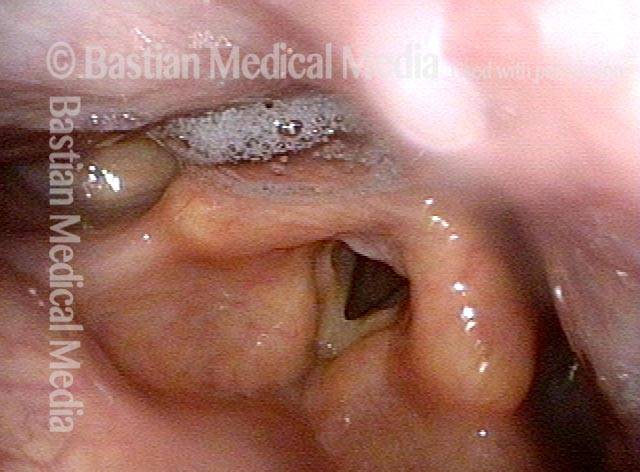
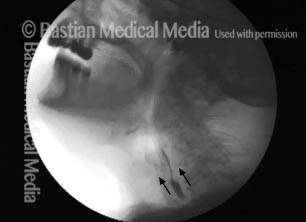
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: before myotomy (1 of 2)
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: before myotomy (1 of 2)
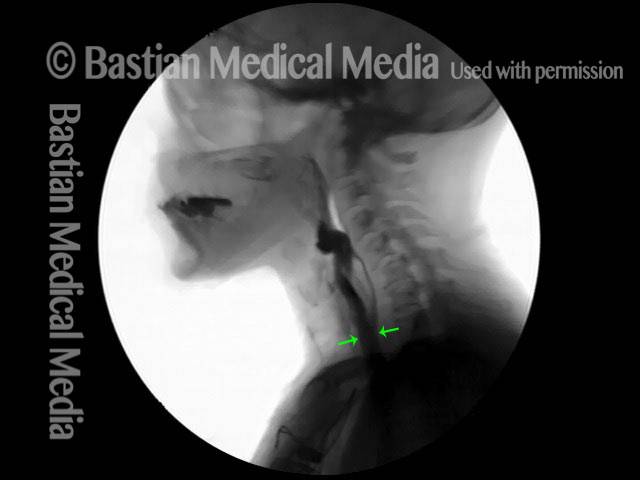
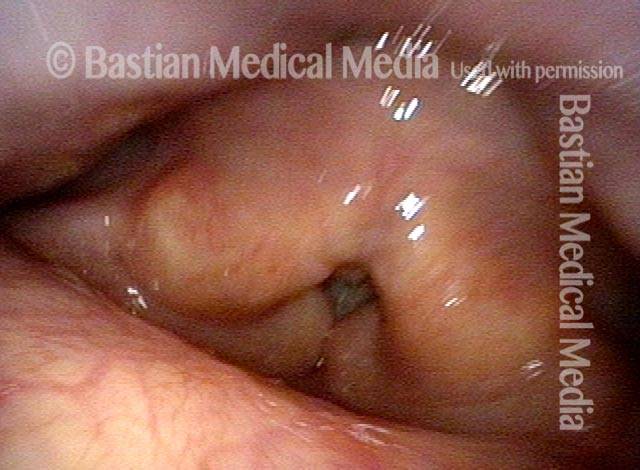
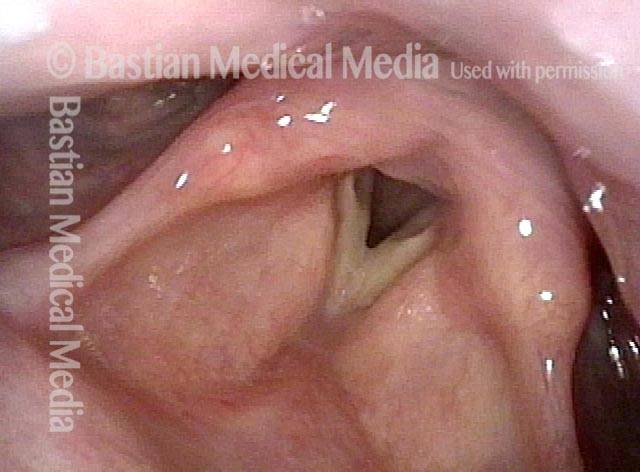
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: after myotomy, resolved (1 of 2)
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: after myotomy, resolved (1 of 2)
R-CPD, Aerophagia and Burping
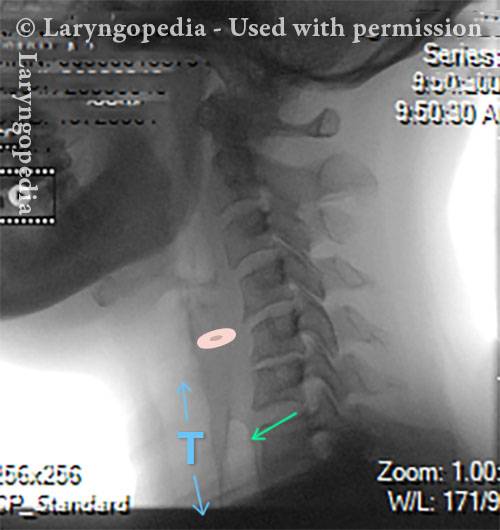
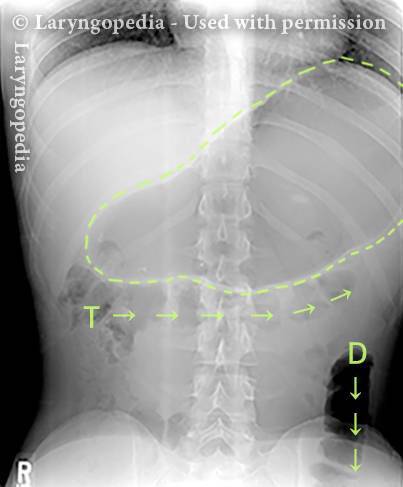
This lateral x-ray of the neck is part of a swallow study, and illustrates how air can accumulate and need to be burped up. The focus of this photo essay is the esophagus, or “foodway,” that connects the lower part of the throat to the stomach. The esophagus is a muscular tube that remains mostly collapsed—closed—except when food, liquid, or saliva traverses it. Read more about esophageal findings of R-CPD.
X-Ray of Larynx (1 of 6)
X-Ray of Larynx (1 of 6)
Barium swallow (2 of 6)
Barium swallow (2 of 6)
Collapsed esophagus (3 of 6)
Collapsed esophagus (3 of 6)
Air is swallowed (4 of 6)
Air is swallowed (4 of 6)
UES refuses to open for a burp (5 of 6)
UES refuses to open for a burp (5 of 6)
Abdominal Distention from R-CPD (6 of 6)
Abdominal Distention from R-CPD (6 of 6)
Post-swallow Hypopharyngeal Reflux (Zenker’s Diverticulum): VESS vs. VFSS
VESS (1 of 7)
VESS (1 of 7)
Reflux (2 of 7)
Reflux (2 of 7)
Post-swallow (3 of 7)
Post-swallow (3 of 7)
Reflux of cracker (4 of 7)
Reflux of cracker (4 of 7)
VFSS (5 of 7)
VFSS (5 of 7)
X-Ray (6 of 7)
X-Ray (6 of 7)
Continued reflux (7 of 7)
Continued reflux (7 of 7)
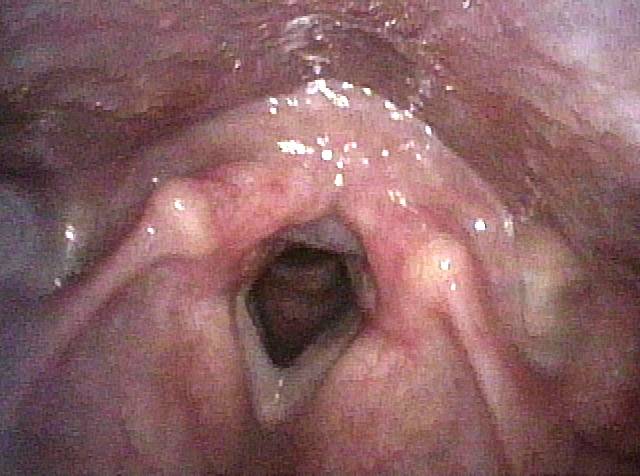
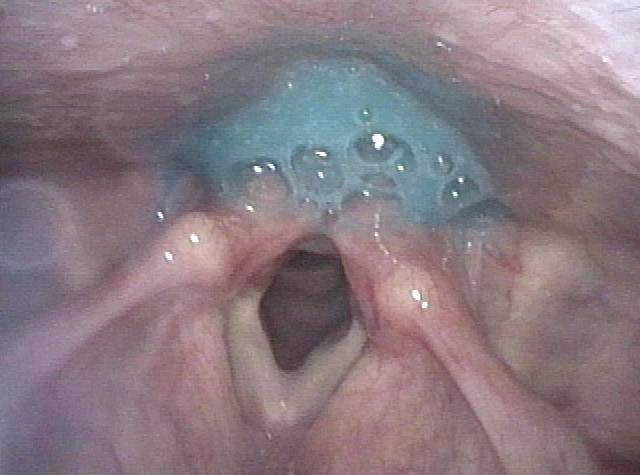
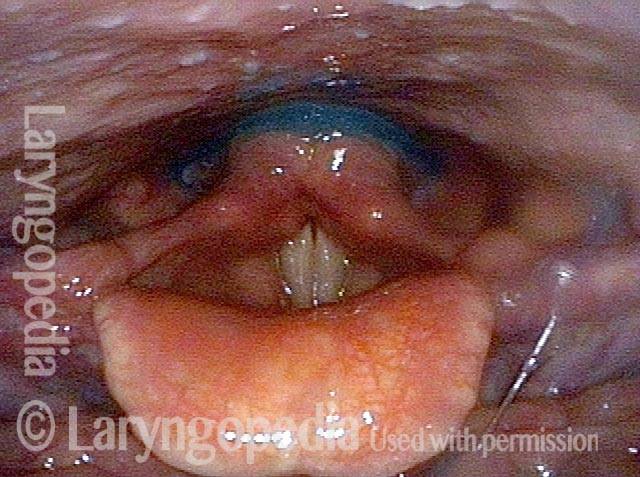
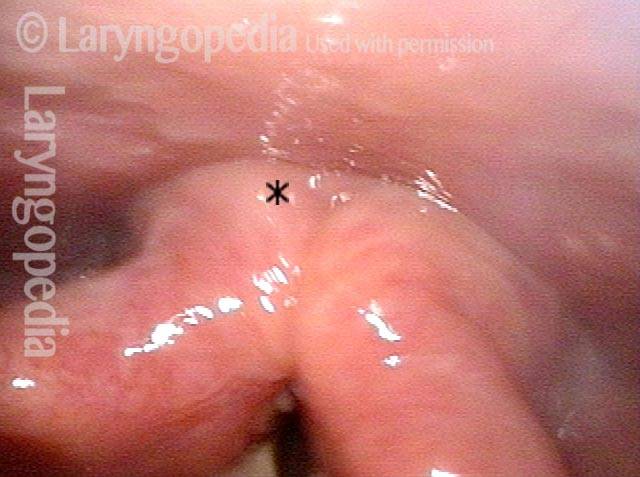
Great View of Fresh Cricopharyngeus Myotomy Surgical Wound
CPM dysfunction (1 of 4)
CPM dysfunction (1 of 4)
VFSS six years later (2 of 4)
VFSS six years later (2 of 4)
Five days post-op (3 of 4)
Five days post-op (3 of 4)
Cervical esopagus (4 of 4)
Cervical esopagus (4 of 4)
98 Year-old before and after Myotomy
Immediately after swallowing (1 of 10)
Immediately after swallowing (1 of 10)
Zenker’s (2 of 10)
Zenker’s (2 of 10)
Dysphagia (3 of 10)
Dysphagia (3 of 10)
Residue from Zenker’s (4 of 10)
Residue from Zenker’s (4 of 10)
X-ray showing Zenker’s (5 of 10)
X-ray showing Zenker’s (5 of 10)
Moments later (6 of 10)
Moments later (6 of 10)
After myotomy (7 of 10)
After myotomy (7 of 10)
No residue (8 of 10)
No residue (8 of 10)
Zenker’s gone (9 of 10)
Zenker’s gone (9 of 10)
No barium in hypopharynx (10 of 10)
No barium in hypopharynx (10 of 10)
Share this article
Barium Swallow (Barium Esophagram)
This video presents a clear visual example of a barium swallow, a test that involves having the patient swallow a barium solution while using x-rays to observe the flow of the barium, which can reveal swallowing deficiencies.

Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction
Before and After Cricopharyngeal Myotomy
This video shows x-rays of barium passing through the throat, first with a narrowed area caused by a non-relaxing upper esophageal sphincter (cricopharyngeus muscle), and then after laser division of this muscle.
Preoperatively, food and pills were getting stuck at the level of the mid-neck, and the person was eating mostly soft foods. After the myotomy (division of the muscle), the patient could again swallow meat, pizza, pills, etc. without difficulty.