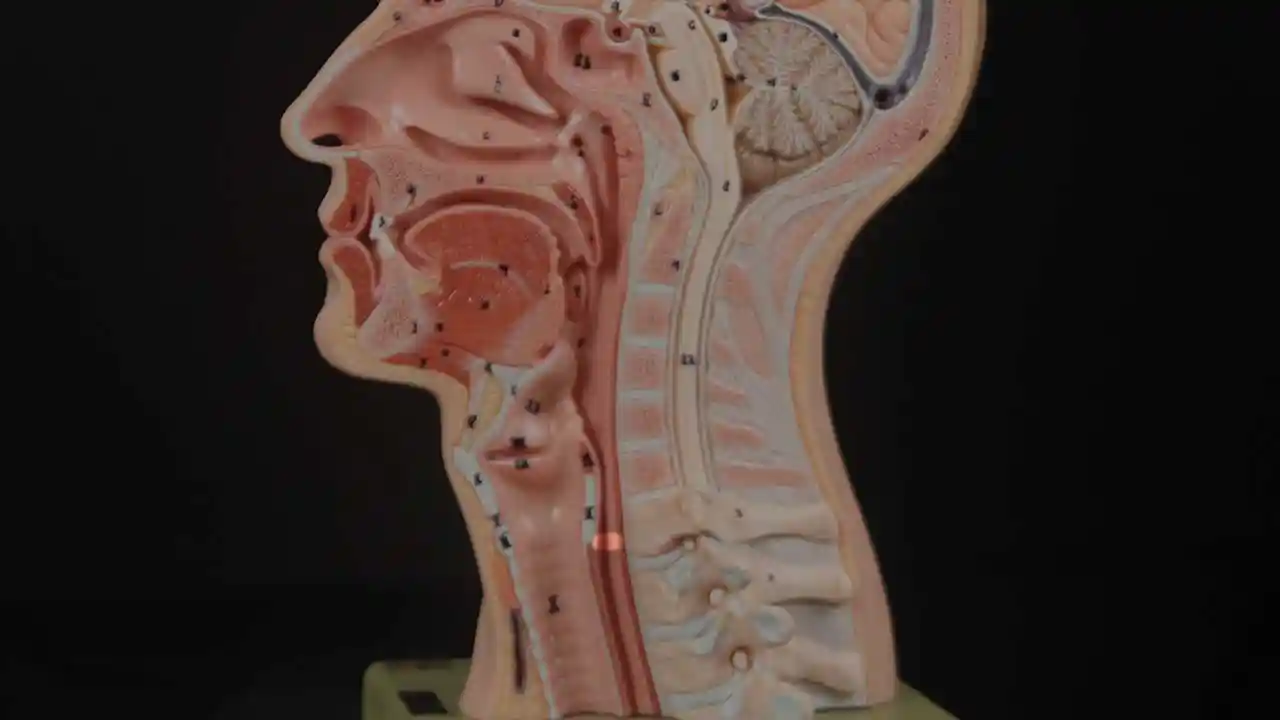
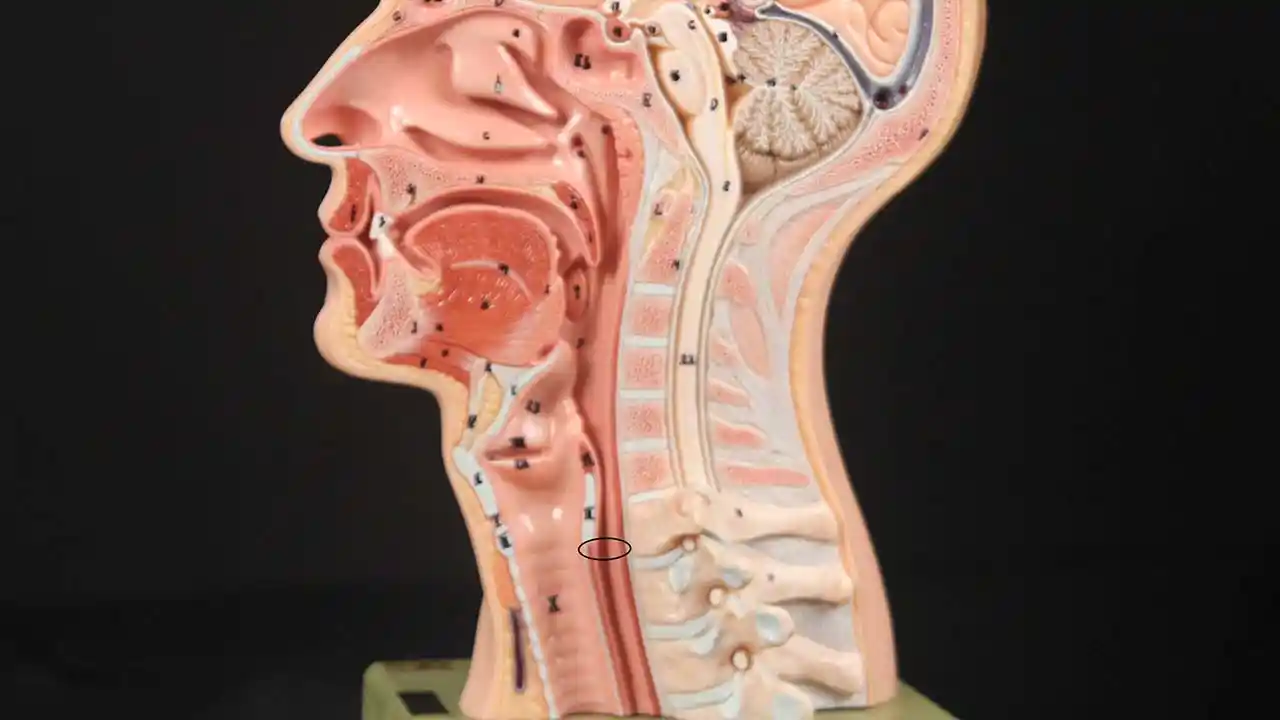
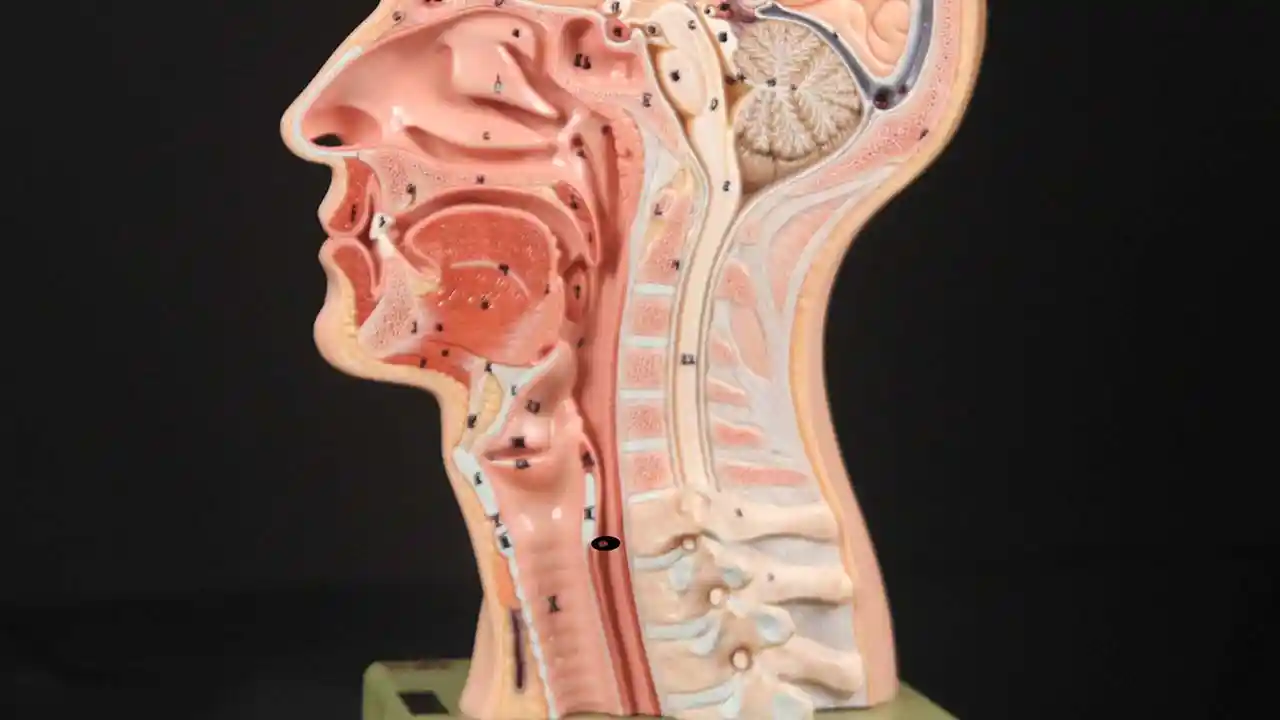
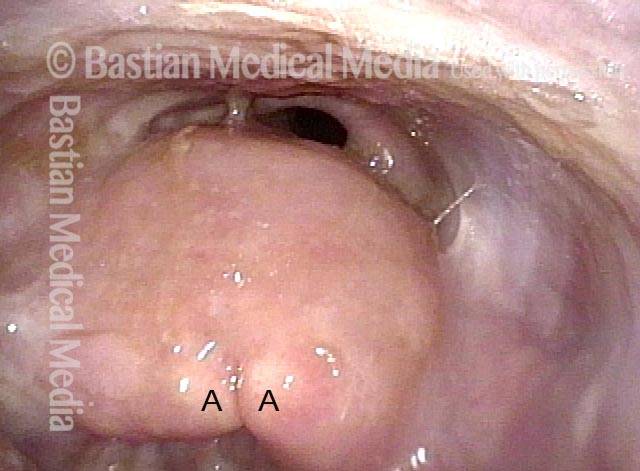
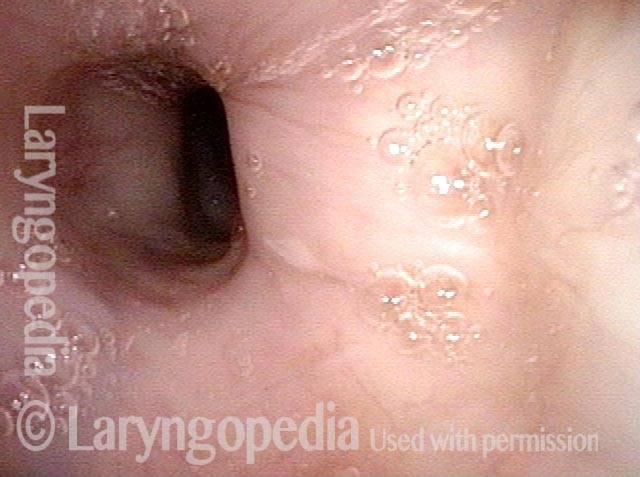
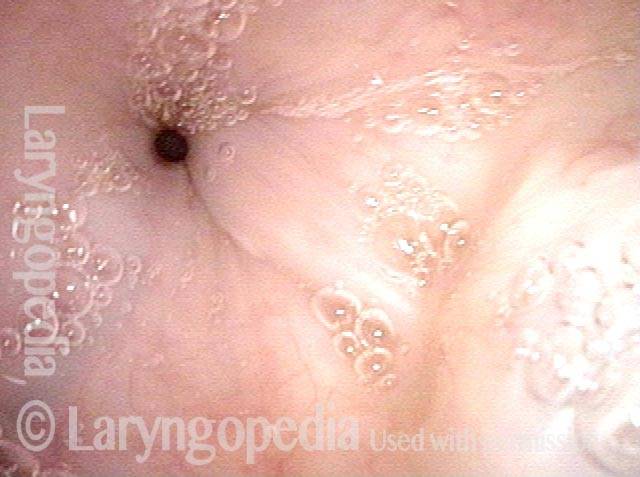
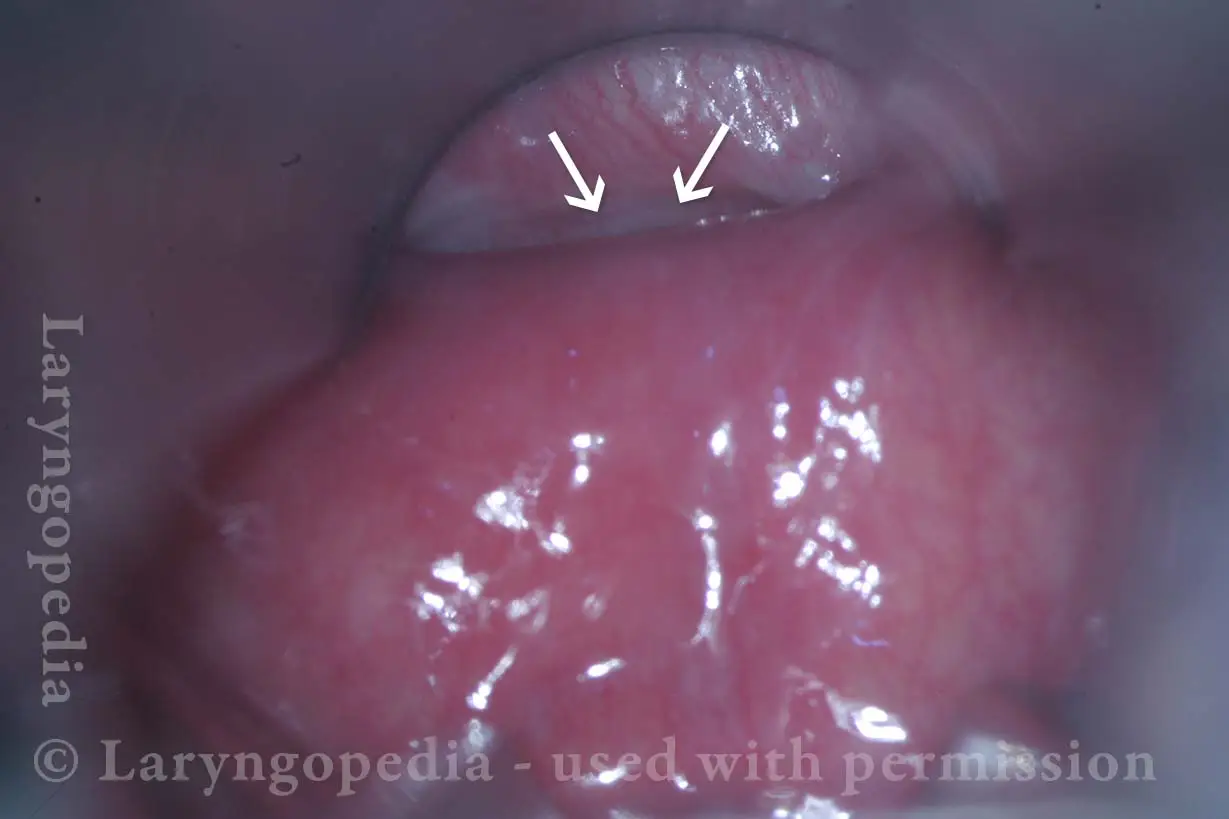
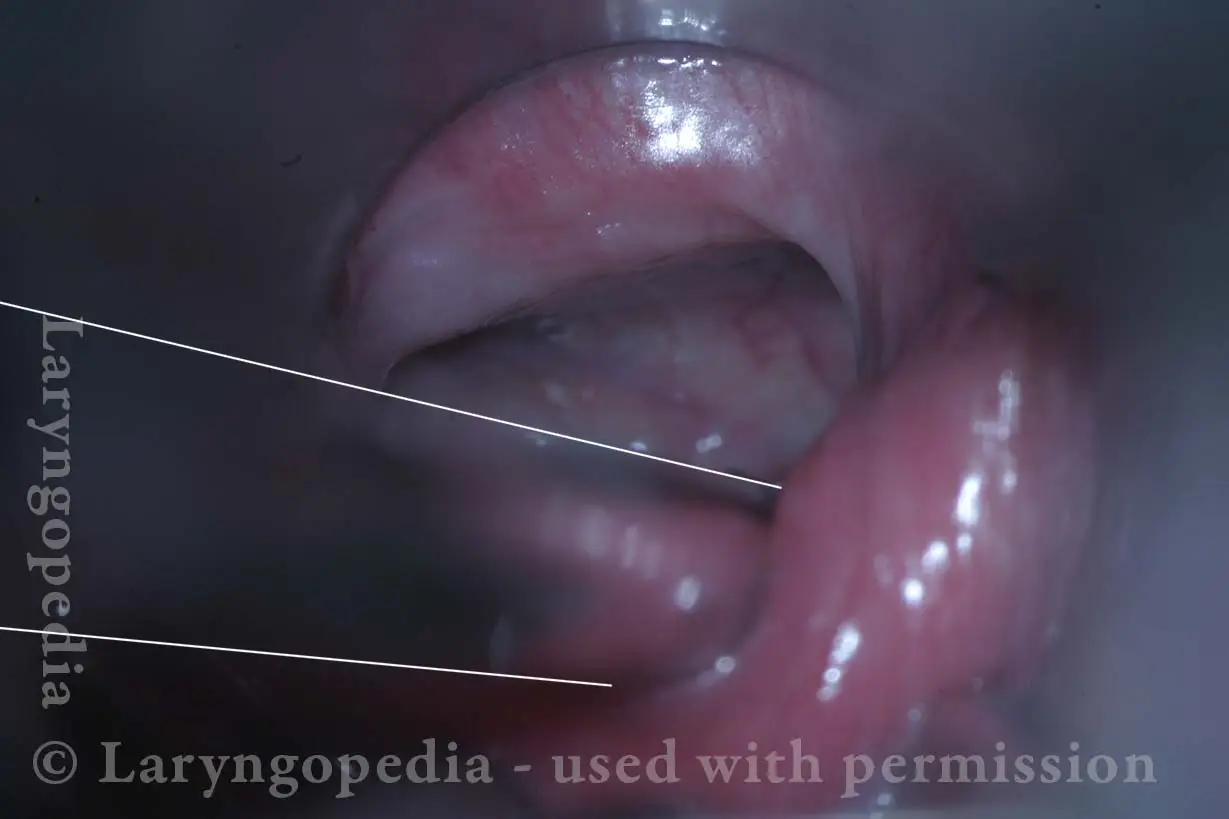
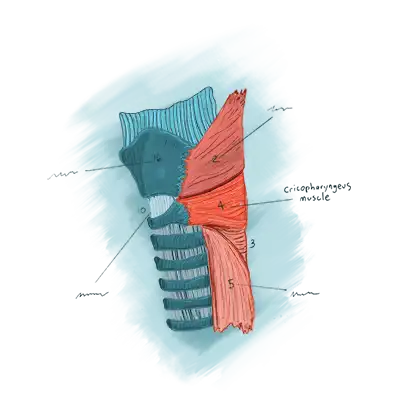
 The cricopharyngeus is a sphincter muscle encircling the upper end of the esophagus, also called the upper esophageal sphincter or UES. It is almost always in a contracted state, even during sleep. Its action is like a continually clenched fist. This contraction closes off the entrance to the esophagus.
The cricopharyngeus is a sphincter muscle encircling the upper end of the esophagus, also called the upper esophageal sphincter or UES. It is almost always in a contracted state, even during sleep. Its action is like a continually clenched fist. This contraction closes off the entrance to the esophagus.
Whenever a person swallows, the cricopharyngeus muscle momentarily relaxes, opening its grip and allowing food or liquid to pass through and enter the esophagus.
The muscle is subject to one of two disorders. Cricopharyngeal dysfunction is the failure of the muscle to relax, which causes swallowing difficulty. Cricopharyngeal spasm is hyper-contraction of the muscle, which causes a sensation of a lump in the throat but without interfering with swallowing.
Cricopharyngeus Muscle
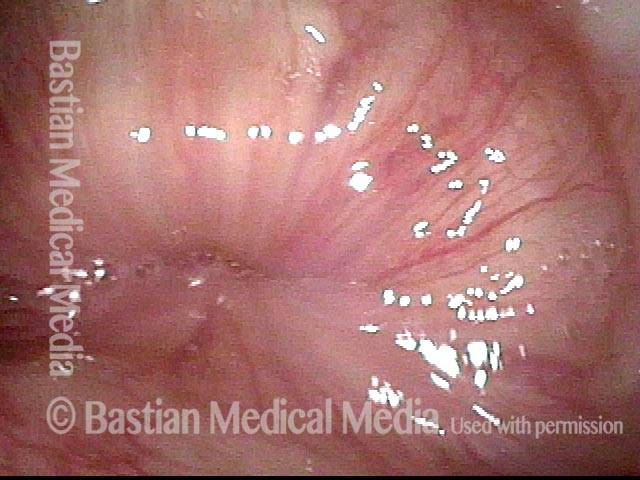
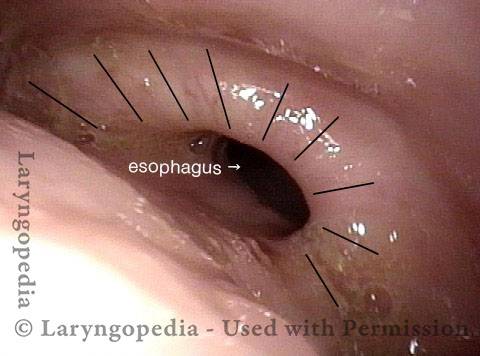
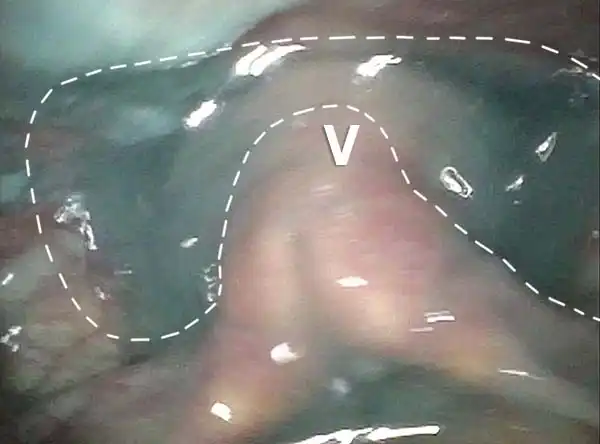
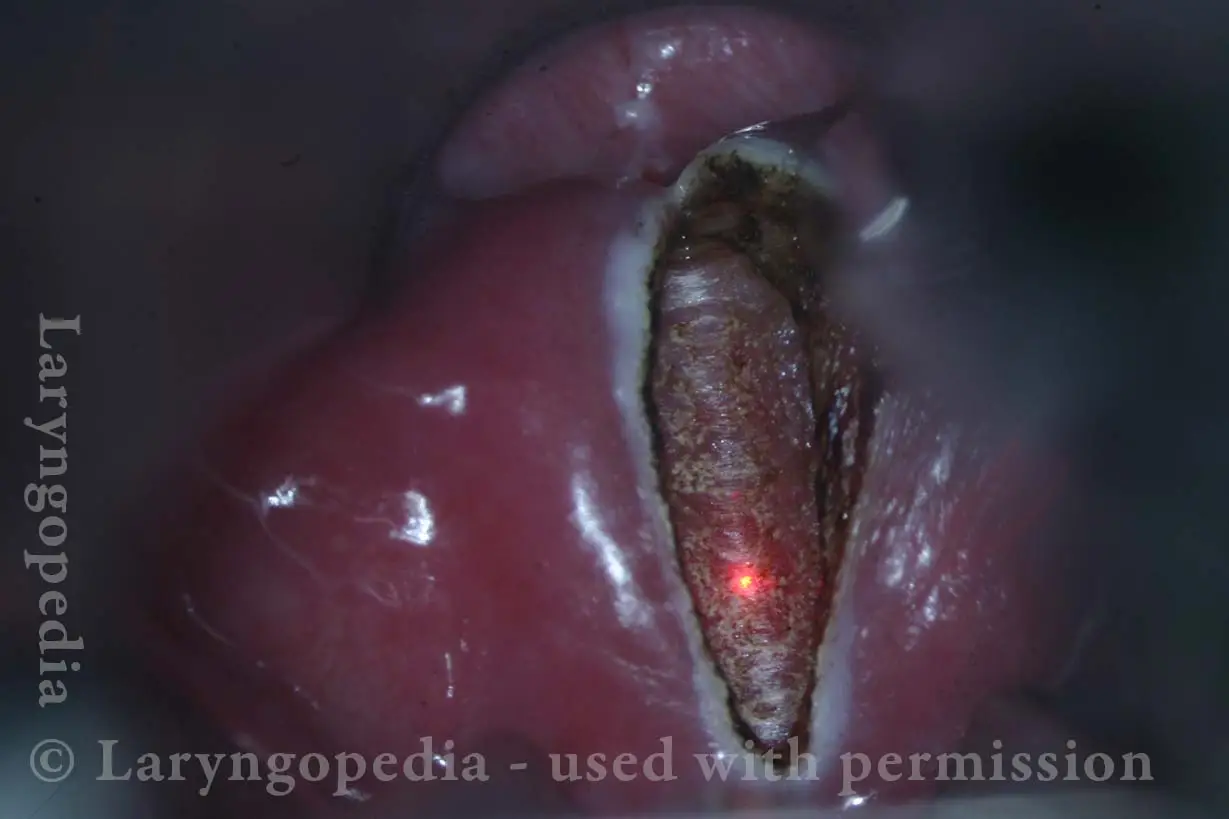
Cricopharyngeus muscle (1 of 4)
Cricopharyngeus muscle (1 of 4)
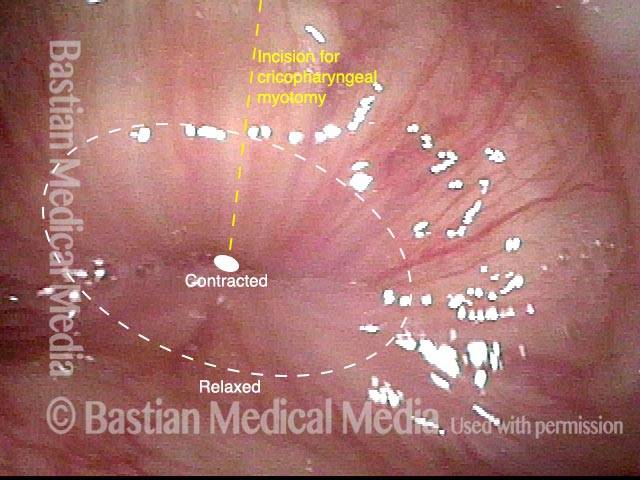
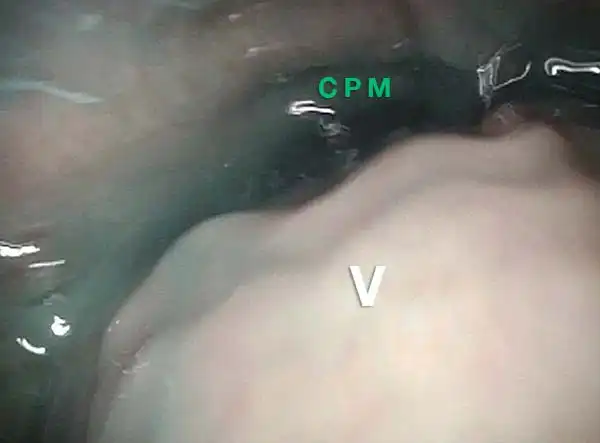
Opening when Contracted (2 of 4)
Opening when Contracted (2 of 4)
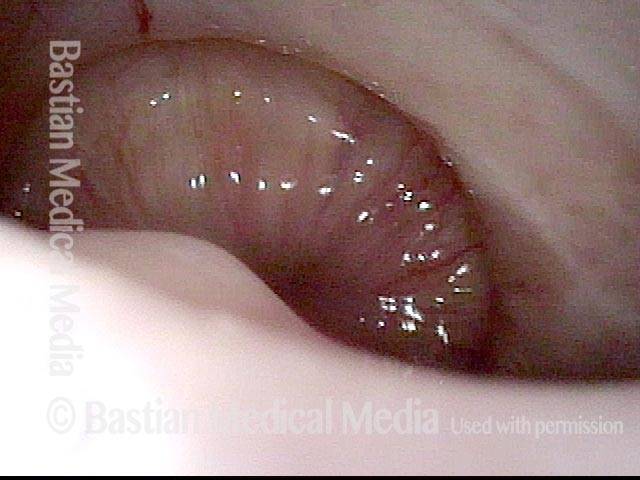
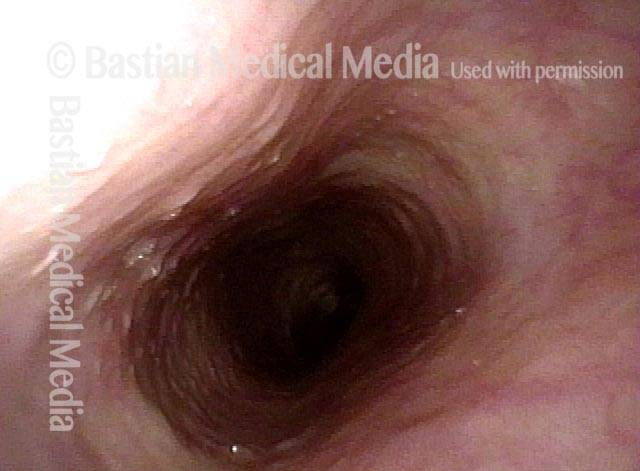
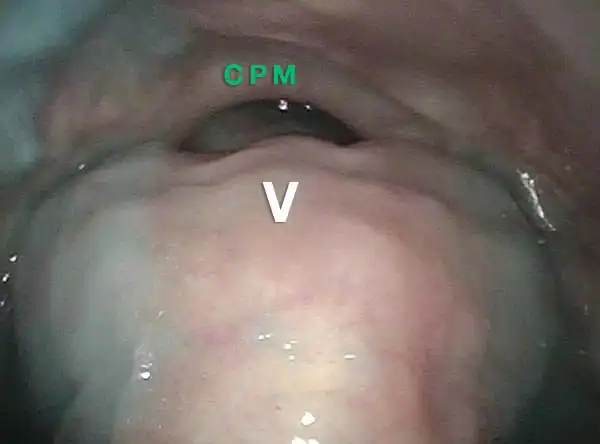
A distant view (3 of 4)
A distant view (3 of 4)
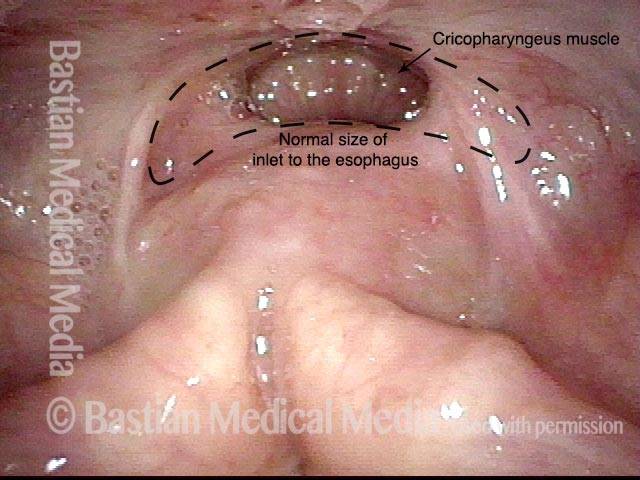
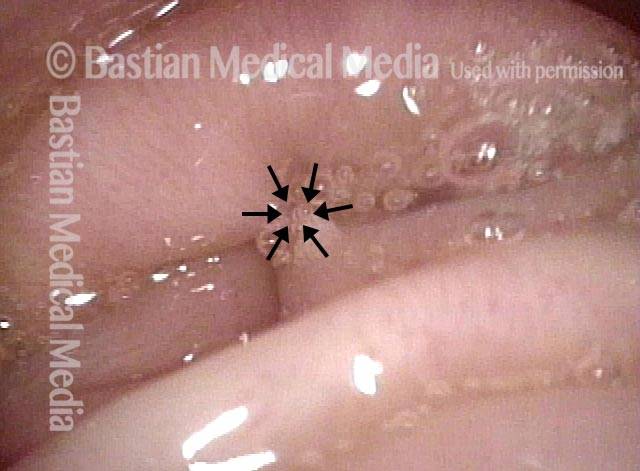
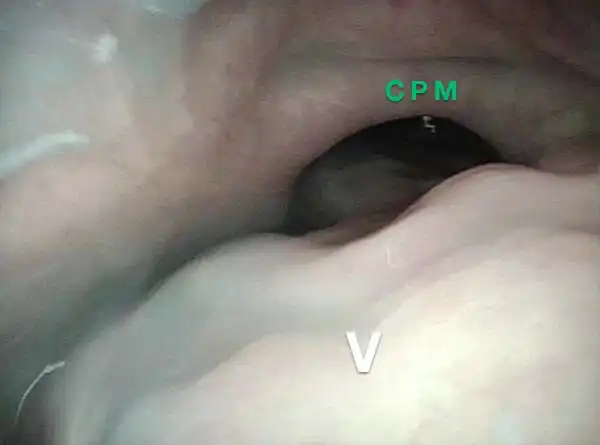
hypopharyngeal inlet (4 of 4)
hypopharyngeal inlet (4 of 4)
Location of the Cricopharyngeus Muscle
Cricopharyngeus Muscle (1 of 3)
Cricopharyngeus Muscle (1 of 3)
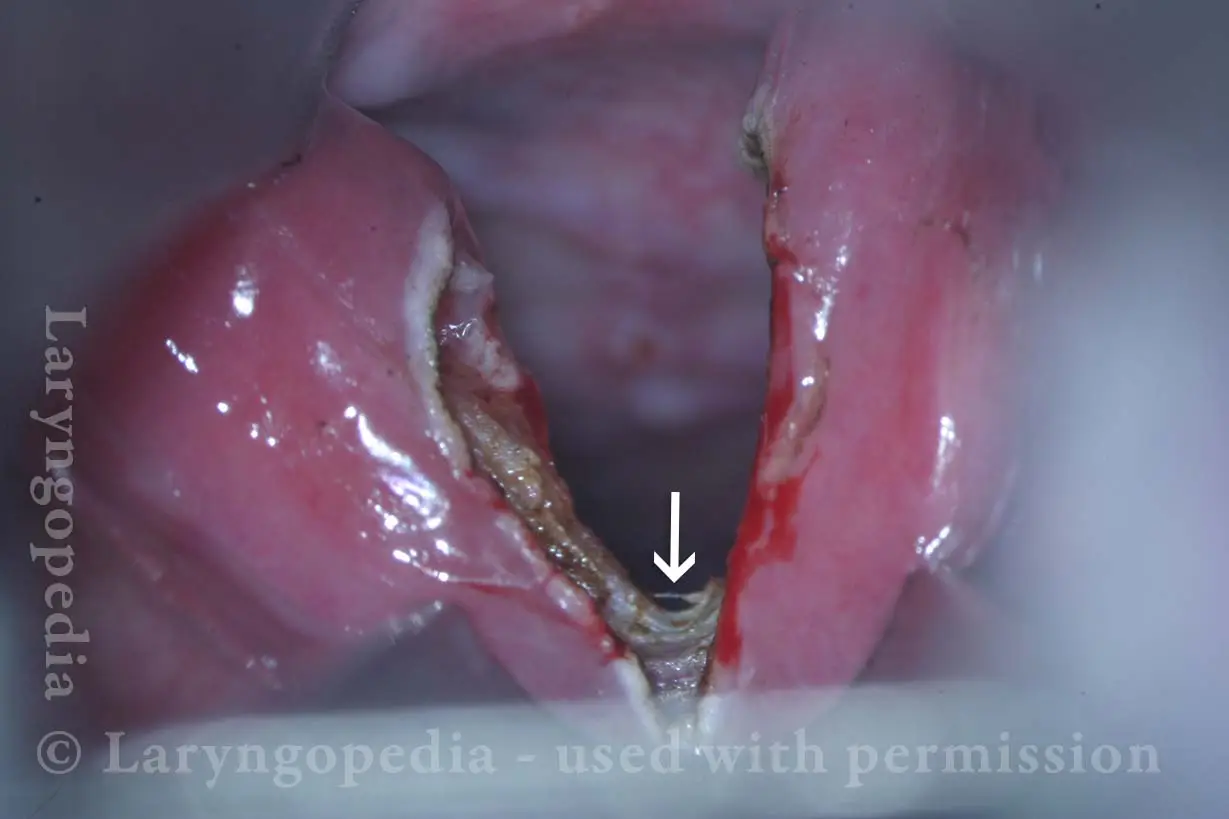
Open Cricopharyngeus Muscle (2 of 3)
Open Cricopharyngeus Muscle (2 of 3)
Closed (3 of 3)
Closed (3 of 3)
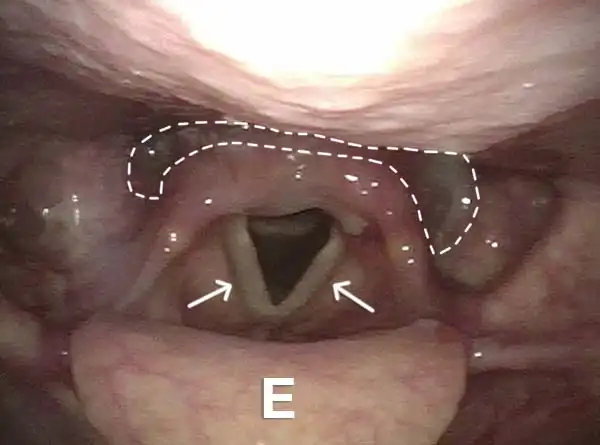
Trumpet Maneuver Reveals Cricopharyngeus Muscle
Trumpet maneuver (1 of 4)
Trumpet maneuver (1 of 4)
The “shelf” (2 of 4)
The “shelf” (2 of 4)
Cervical esophagus (3 of 4)
Cervical esophagus (3 of 4)
Closed position (4 of 4)
Closed position (4 of 4)
The Cricopharyngeus Muscle Seen During Swallowing
This person struggles to swallow due to a combination of prior tongue cancer surgery decades ago, and longterm radiation effects. Solid foods are the most problematic, and so this sequence shows an attempt to swallow water stained with blue food coloring.