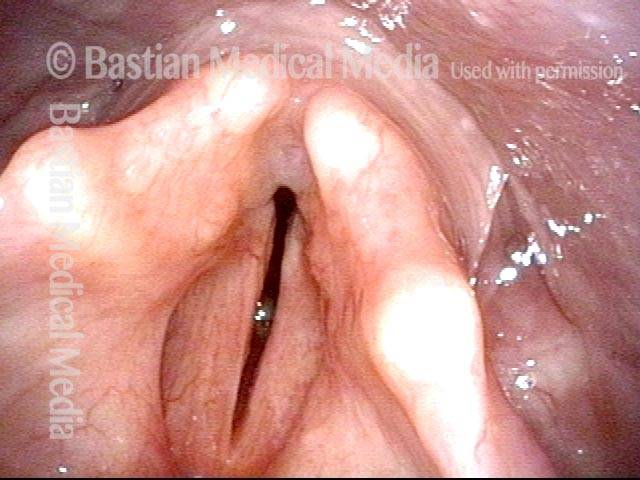
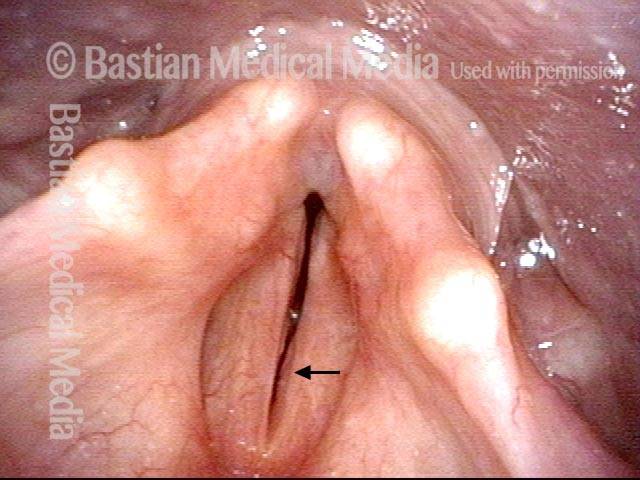
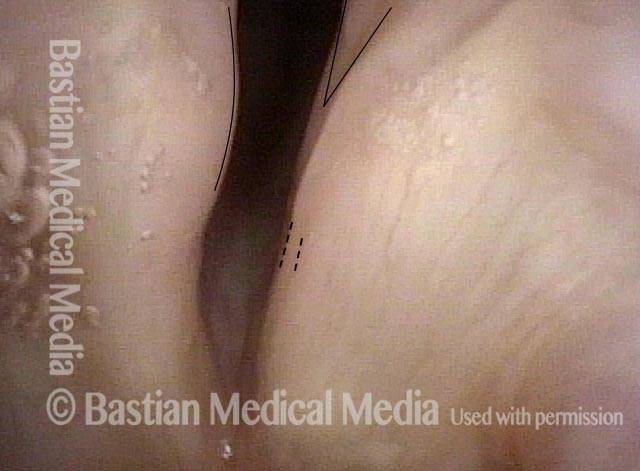
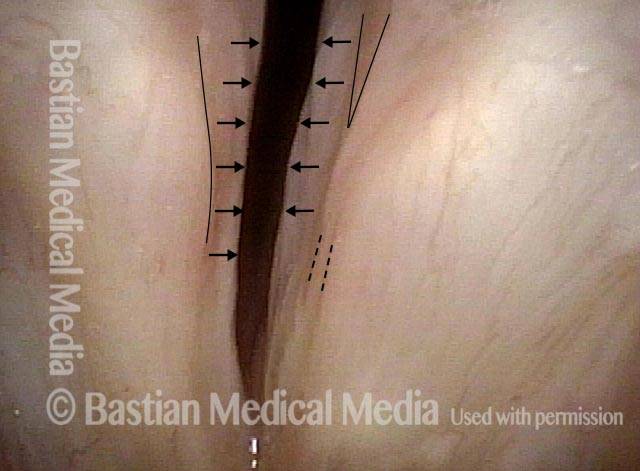
Un disturbo neurologico in cui il rifornimento nervoso ad entrambe le corde vocali è assente. Ciò può essere il risultato di lesioni dovute a traumi esterni, interventi chirurgici alla tiroide o traumi contundenti o penetranti al collo.
A volte l’immobilità delle corde vocali dovuta a cicatrici, ad esempio da un tubo endotracheale, viene scambiata per paralisi delle corde vocali, sebbene la distinzione sia solitamente facile da determinare, a condizione che venga eseguito un esame adeguatamente intenso e diretto. In particolare, questo workup deve includere l’anestesia topica della laringe in modo da consentire una visualizzazione estremamente ravvicinata della commissura posteriore e della sottoglottide, che può scoprire prove di cicatrici.
Guarda anche: lesione da intubazione, stenosi, sinechia delle corde vocali e paralisi unilaterale delle corde vocali