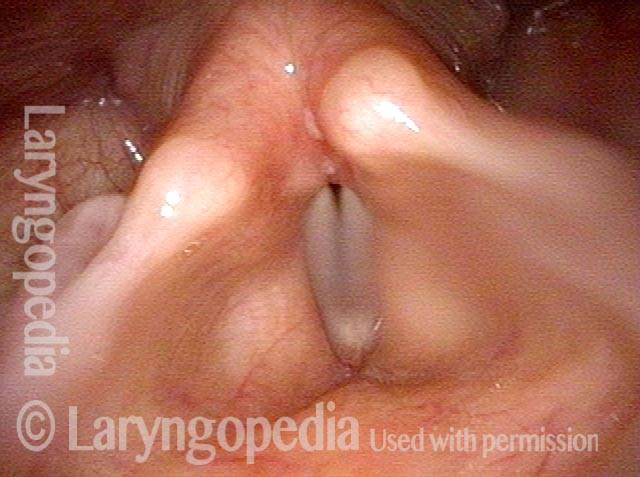
Posterior commissure is the flat, front-facing surface of the glottic aperture that lies between the vocal cord posterior ends. When the vocal cords are in abducted (breathing) position, the posterior commissure is at its widest, since the cords’ posterior ends are spread furthest apart from each other. When the vocal cords have come together into adducted (voicing) position, the posterior commissure is essentially just the point of contact between the posterior ends of the cords.
In individuals who have acid reflux or other inflammatory conditions, the mucosa at the posterior commissure may thicken (pachyderma).
See also: anterior commissure.
Phonatory Insufficiency
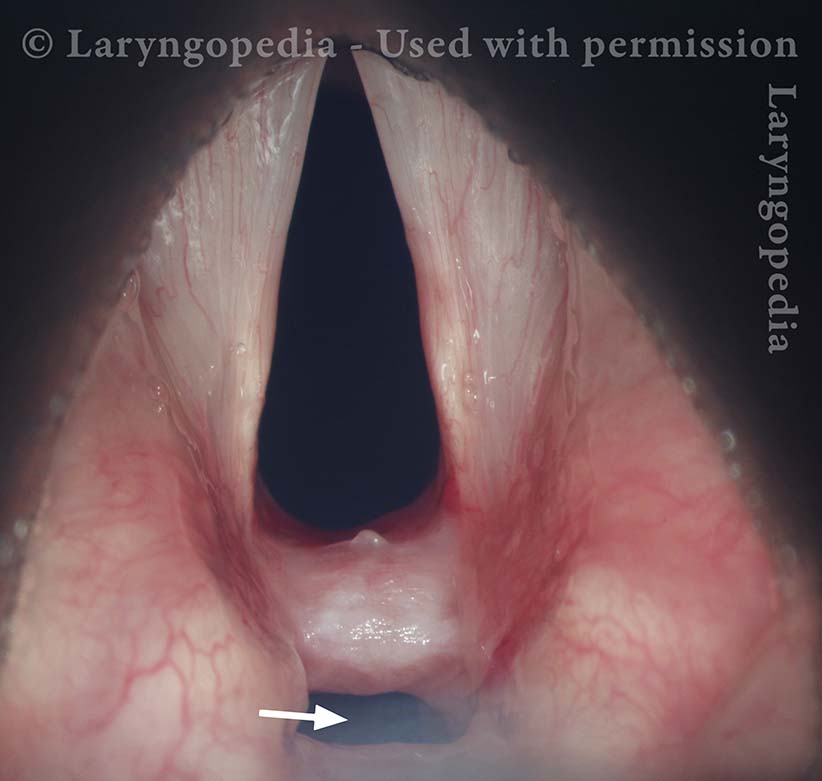
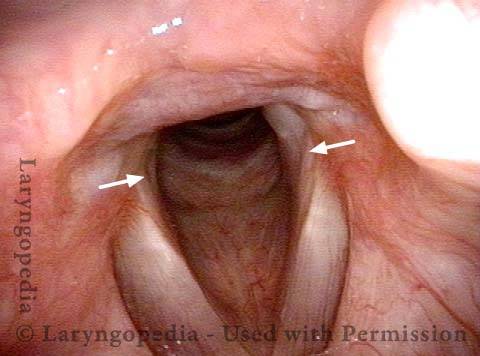
Phonatory insufficiency (1 of 3)
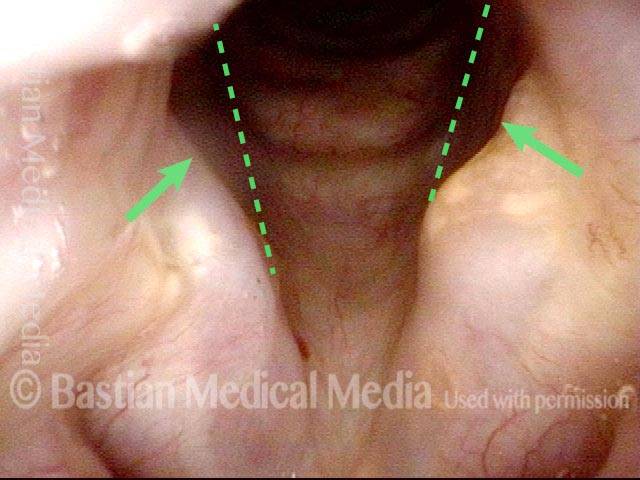
Abducted breathing position. Note the divots at the posterior commissure (arrows), likely due to pressure necrosis caused by intubation of long duration. Dotted lines indicate the lines of the normal cord, to show the divots more clearly.
Phonatory insufficiency (1 of 3)
Abducted breathing position. Note the divots at the posterior commissure (arrows), likely due to pressure necrosis caused by intubation of long duration. Dotted lines indicate the lines of the normal cord, to show the divots more clearly.
Phonatory insufficiency (2 of 3)
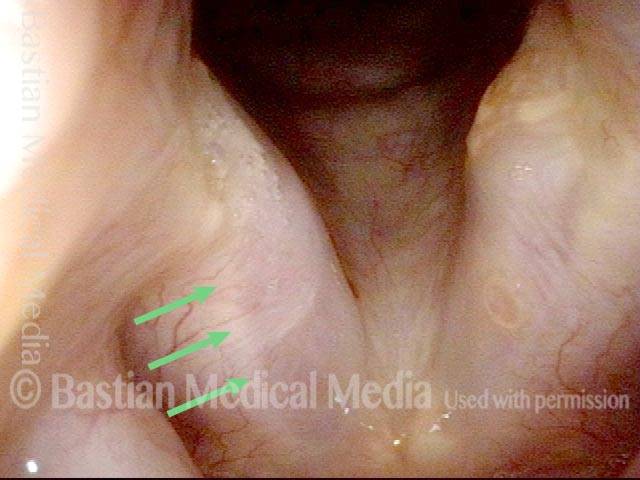
The irregular white line along the length of the vocal cords (arrows) suggests that there may have been pressure necrosis of the musculo-membranous portion of the vocal cord and that now the mucosa adheres directly to muscle, with no intervening vocal ligament layer.
Phonatory insufficiency (2 of 3)
The irregular white line along the length of the vocal cords (arrows) suggests that there may have been pressure necrosis of the musculo-membranous portion of the vocal cord and that now the mucosa adheres directly to muscle, with no intervening vocal ligament layer.
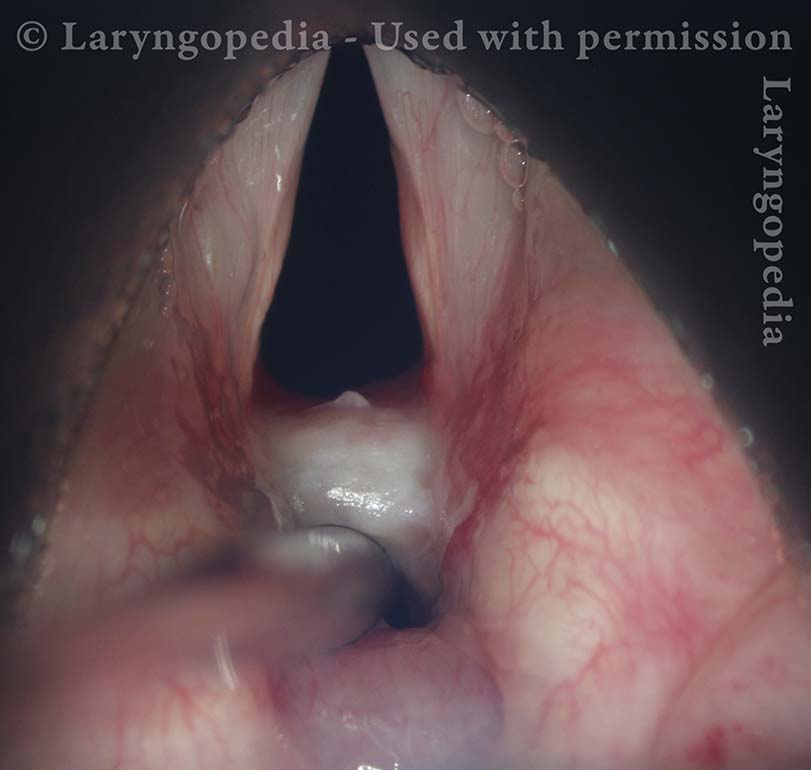
Phonatory insufficiency (3 of 3)
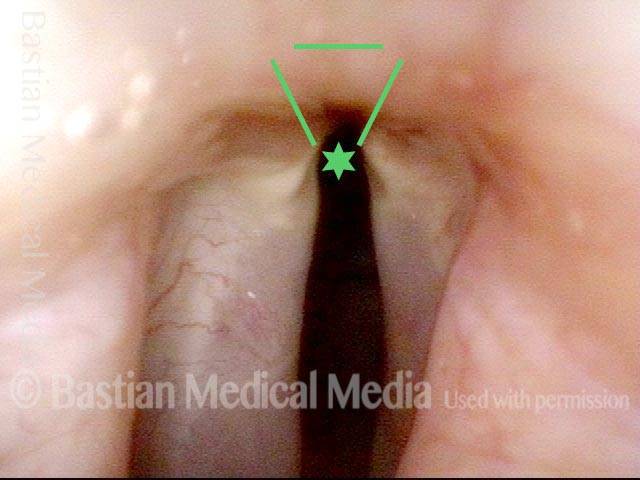
Maximum phonatory closure. Note that the posterior commissure defect is hidden by the partial closure of the arytenoid cartilages. Even so, the arytenoid cartilages are unable to come into contact. The musculomembranous cords are quite far apart due partly to tissue loss. Furthermore, the cords are stiff and inflexible. No glottic voice is possible.
Phonatory insufficiency (3 of 3)
Maximum phonatory closure. Note that the posterior commissure defect is hidden by the partial closure of the arytenoid cartilages. Even so, the arytenoid cartilages are unable to come into contact. The musculomembranous cords are quite far apart due partly to tissue loss. Furthermore, the cords are stiff and inflexible. No glottic voice is possible.
Difficulty Breathing after a 3-day Intubation
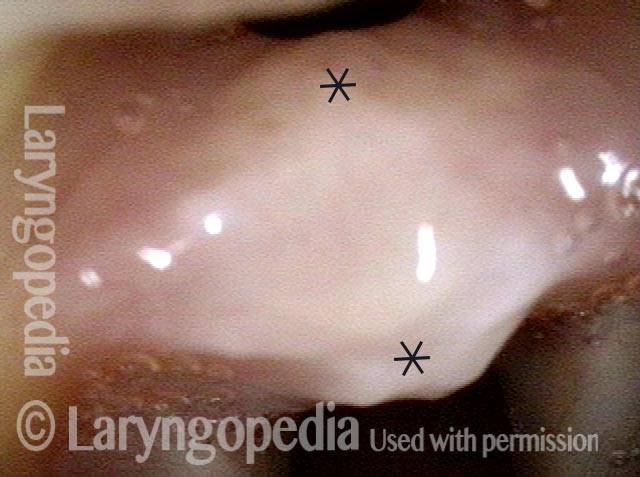
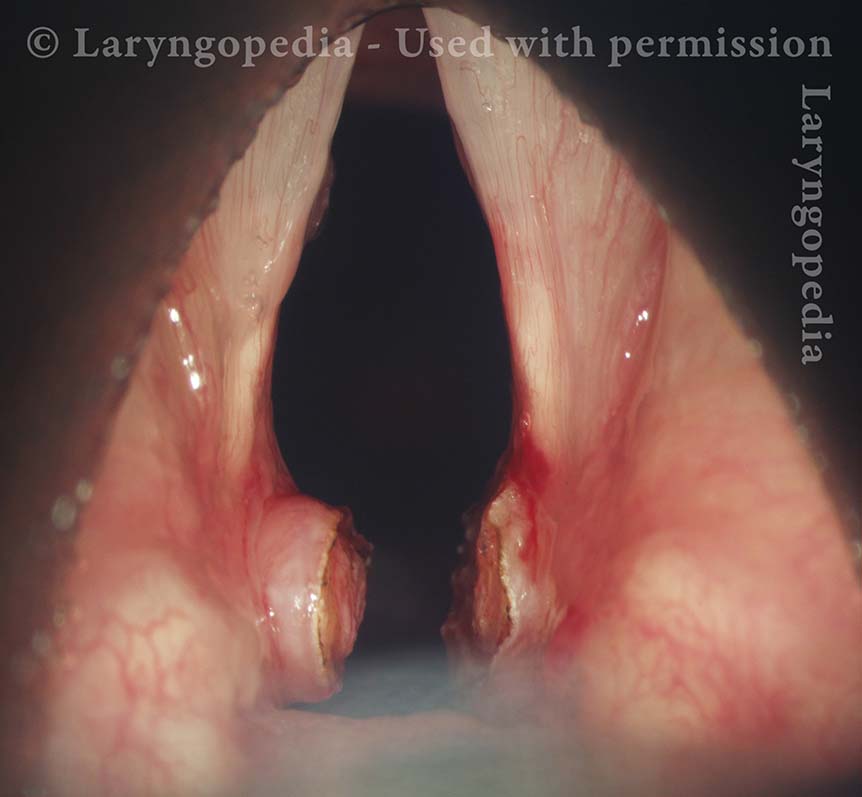
Noisy, restricted breathing following intubation (1 of 10)
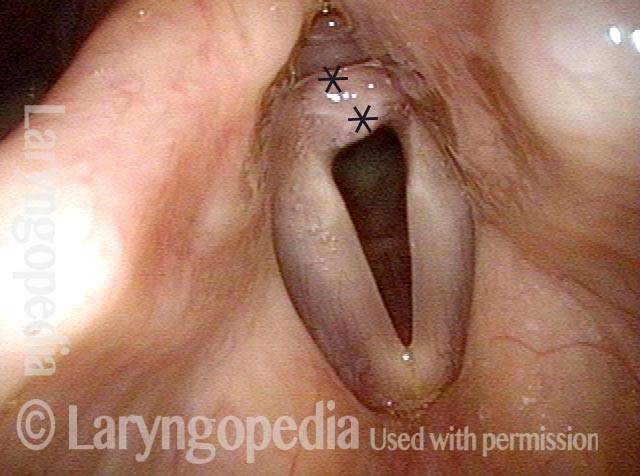
This teenager was intubated for 3 days due to tongue swelling. Breathing became noisy and restricted approximately 6 weeks later. Note that the vocal cords do not abduct fully and there is what appears to be granulation tissue at the posterior commissure (anterior asterisk).
Noisy, restricted breathing following intubation (1 of 10)
This teenager was intubated for 3 days due to tongue swelling. Breathing became noisy and restricted approximately 6 weeks later. Note that the vocal cords do not abduct fully and there is what appears to be granulation tissue at the posterior commissure (anterior asterisk).
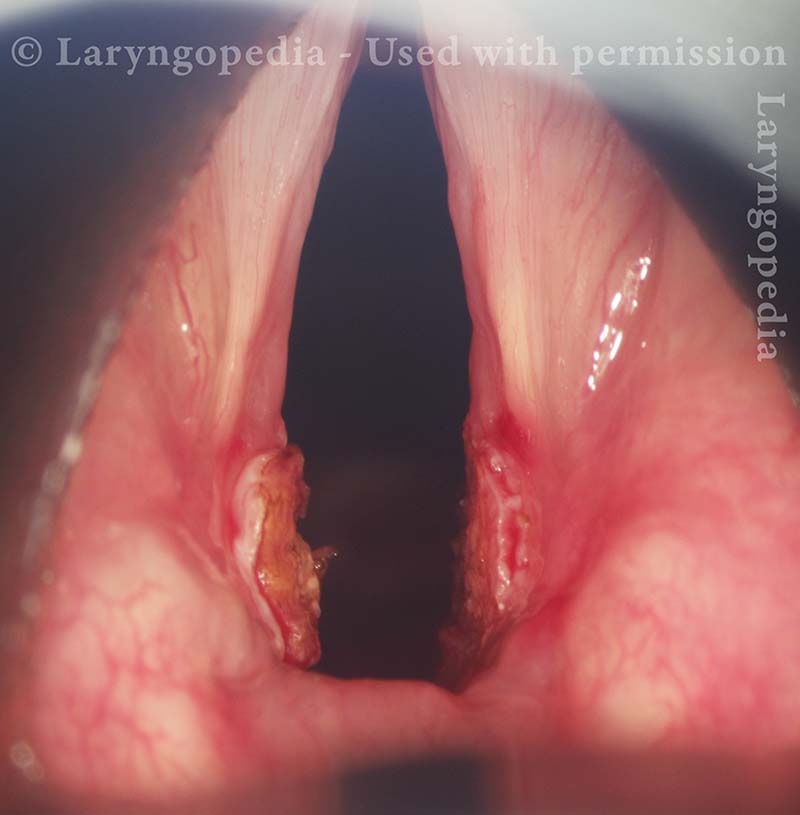
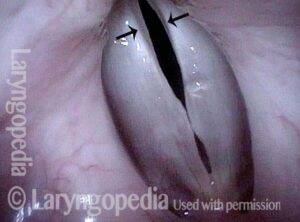
Normal voice (2 of 10)
The vocal cords can come into contact as shown here, consistent with her normal-sounding voice.
Normal voice (2 of 10)
The vocal cords can come into contact as shown here, consistent with her normal-sounding voice.
At close range (3 of 10)
At very close range within the posterior commissure, a small tract is seen posterior to the "granulation" which is now seen more clearly to be a broad-based synechiae with asterisks marking anterior and posterior limits.
At close range (3 of 10)
At very close range within the posterior commissure, a small tract is seen posterior to the "granulation" which is now seen more clearly to be a broad-based synechiae with asterisks marking anterior and posterior limits.
Mucosalized tract (4 of 10)
Intraoperatively, the synchia appears mature. There is a mucosalized tract posteriorly (arrow). This makes joint injury less likely.
Mucosalized tract (4 of 10)
Intraoperatively, the synchia appears mature. There is a mucosalized tract posteriorly (arrow). This makes joint injury less likely.
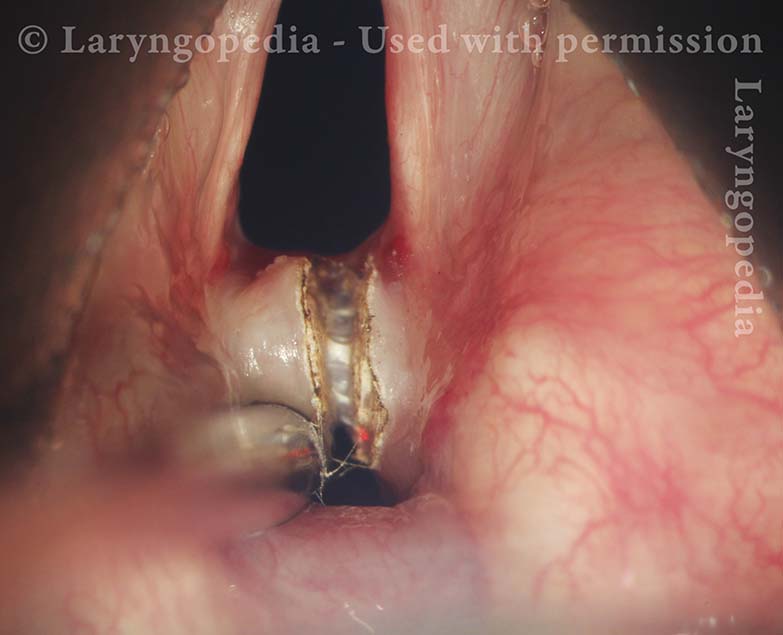
Suction Cannula (5 of 10)
A 4mm suction cannula is passed through the mucosalized tract posteriorly and lifted anteriorly, demonstrating its firmness.
Suction Cannula (5 of 10)
A 4mm suction cannula is passed through the mucosalized tract posteriorly and lifted anteriorly, demonstrating its firmness.
CO2 Laser during Microlaryngoscopy (6 of 10)
The carbon dioxide laser has begin transecting the synechia.
CO2 Laser during Microlaryngoscopy (6 of 10)
The carbon dioxide laser has begin transecting the synechia.
Separation complete (7 of 10)
One can already see better abduction of the cords, suggesting that the cricoarytenoid joints are indeed undamaged.
Separation complete (7 of 10)
One can already see better abduction of the cords, suggesting that the cricoarytenoid joints are indeed undamaged.
Core removal complete (8 of 10)
The “core” of the synechia has been excavated, leaving the overlying mucosa intact (and retracted).
Core removal complete (8 of 10)
The “core” of the synechia has been excavated, leaving the overlying mucosa intact (and retracted).
Complete abduction post-surgery (9 of 10)
Several months later, abduction of the cords is complete, proving that there is no injury to the cricoarytenoid joints. Arrows point to the subtle remnant of the base of the synechia.
Complete abduction post-surgery (9 of 10)
Several months later, abduction of the cords is complete, proving that there is no injury to the cricoarytenoid joints. Arrows point to the subtle remnant of the base of the synechia.
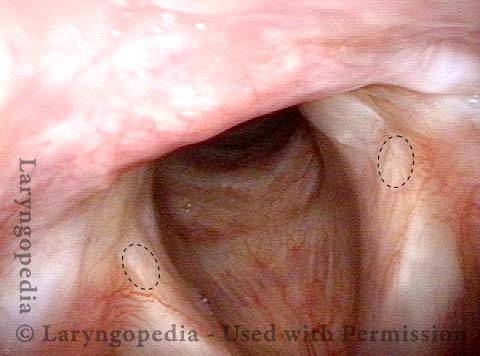
Complete healing (10 of 10)
Faint dotted lines encircle the only remaining evidence of the synechia.
Complete healing (10 of 10)
Faint dotted lines encircle the only remaining evidence of the synechia.
Tagged Anatomy & Physiology, Education